|
Cerro De La Estrella (archaeological Site)
Cerro de la Estrella is a Mesoamerican archaeological site located in southeastern Central Mexico's Valley of Mexico, in the Iztapalapa '' alcaldĂa'' () of Mexico City at an elevation of 2460 meters (8070 ft) above sea level, hence its Summit is 224 m over the Valley of Mexico level.INEGI (1995): ''Topographical Chart'' (Spanish). At the southeast edge of what was the Great Texcoco Lake. Historical sources establish that ancient inhabitants of the Mexican Plateau knew this place as Huizachtecatl. The site was very important since the âNew Fireâ ritual ceremony was performed here; it had a profound meaning for the population here and in surrounding regions. Occupation stages The oldest traces of human occupation in the Iztapalapa territory originated at Santa MarĂa Aztahuacan village. In 1953 remains of two individuals were found and, according to analysis performed by National University of Mexico (UNAM) and by Instituto Nacional de AntropologĂa e Historia, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro De La Estrella
Cerro de la Estrella (English: Star Hill) may refer to: * Cerro de la Estrella, Mexico City a 2,613 m high mountain in Mexico City ** Cerro de la Estrella (archaeological site) ** Cerro de la Estrella National Park Cerro de la Estrella National Park is centered on the Cerro de la Estrella mountain which is located entirely within eastern Mexico City, in the borough of Iztapalapa. The park was originally designated in 1938 with 1,100 hectares, but the growth ... ** Cerro de la Estrella metro station, a metro station in Mexico City * Cerro de la Estrella, Sierra Morena, a 1,298 m high mountain in Sierra Morena, Spain {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuicuilco
Cuicuilco is an important archaeological site located on the southern shore of Lake Texcoco in the southeastern Valley of Mexico, in what is today the borough of Tlalpan in Mexico City. Construction of the Cuicuilco pyramid began a few centuries BCE, during the Late Preclassic period of Mesoamerican history.PASTRANA, Alejandro and Patricia Fournier''Cuicuilco. In The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican Cultures''.The Civilizations of Mexico and Central America. Vol. 1. David Carrasco (ed.), pp. 290â292. New York: Oxford University Press. 2001 The site was occupied until its destruction by the eruption of Xitle, sometime between 245 and 315 CE. Based on its date of occupation, Cuicuilco may be the oldest city in the Valley of Mexico and was roughly contemporary with, and possibly interacting with, the Olmecs of Mexico's Gulf Coast region (also known as the Olmec heartland). Importance Based on known facts, it was the first important civic-religious center of the Mexican Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Sites
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and northwestern part of Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. In the pre-Columbian era, many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas began on Hispaniola in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Mexico City
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America â the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Sites
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521â1821). The definitions of Aztec and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvania, United States. Founded in 1855 as Farmers' High School of Pennsylvania, Penn State was named the state's first land-grant university eight years later, in 1863. Its primary campus, known as Penn State University Park, is located in State College, Pennsylvania, State College and College Township, Pennsylvania, College Township. Penn State enrolls more than 89,000 students, of which more than 74,000 are undergraduates and more than 14,000 are postgraduates. In addition to its land-grant designation, the university is a National Sea Grant College Program, sea-grant, National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program, space-grant, and one of only six Sun Grant Association, sun-grant universities. It is Carnegie Classification of Instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copilco
Copilco was an important Mesoamerican ceremonial center, southwest of Mexico City, Mexico. Copilco is located approximately four kilometers north of Cuicuilco. Both were covered by lava from several eruptions of the Xitle volcano three thousand years ago. It is very likely that founding, development and destiny of both cities had common causes, from their geographical location, and chronology. The area is located on the west side of CoyoacĂĄn or CoyohuacĂĄn (Nahuatl: coyĆ-hua-cÄn, 'place of coyotes') in the area covered by the lava from the Xitle volcano (according to Chronicles, one eruption of the volcano occurred on April 24, 76). Founding There are several theories regarding its founding; some historical records may establish Copilco's founding in the year 100 BCE. Another version places it at 500 BCE. Background Copilco was one of the first and most important ceremonial centers in the Valley of Mexico. In the mid-Preclassical (800 BC), several villages developed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitzimimeh
A TzitzimÄ«tl (plural TzitzimÄ«meh) is a type of celestial deity associated with stars in Aztec mythology. They were depicted as skeletal female figures wearing skirts often with skull and crossbones designs. In post-conquest descriptions they are often described as "demons" or "devils", but this does not necessarily reflect their function in the prehispanic belief system of the Aztecs. The Tzitzimimeh were female deities and related to fertility. They were associated with the Cihuateteo and other female deities such as Tlaltecuhtli, CĆÄtlÄ«cue, CitlÄlicue and CihuacĆÄtl, and they were worshipped by midwives and parturient women. The leader of the tzitzimimeh was the goddess Itzpapalotl, who was the ruler of Tamoanchan, the paradise where the Tzitzimimeh resided. The Tzitzimimeh were also associated with the stars and especially the stars that can be seen around the Sun during a solar eclipse. This was interpreted as the Tzitzimimeh attacking the Sun, thus causing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
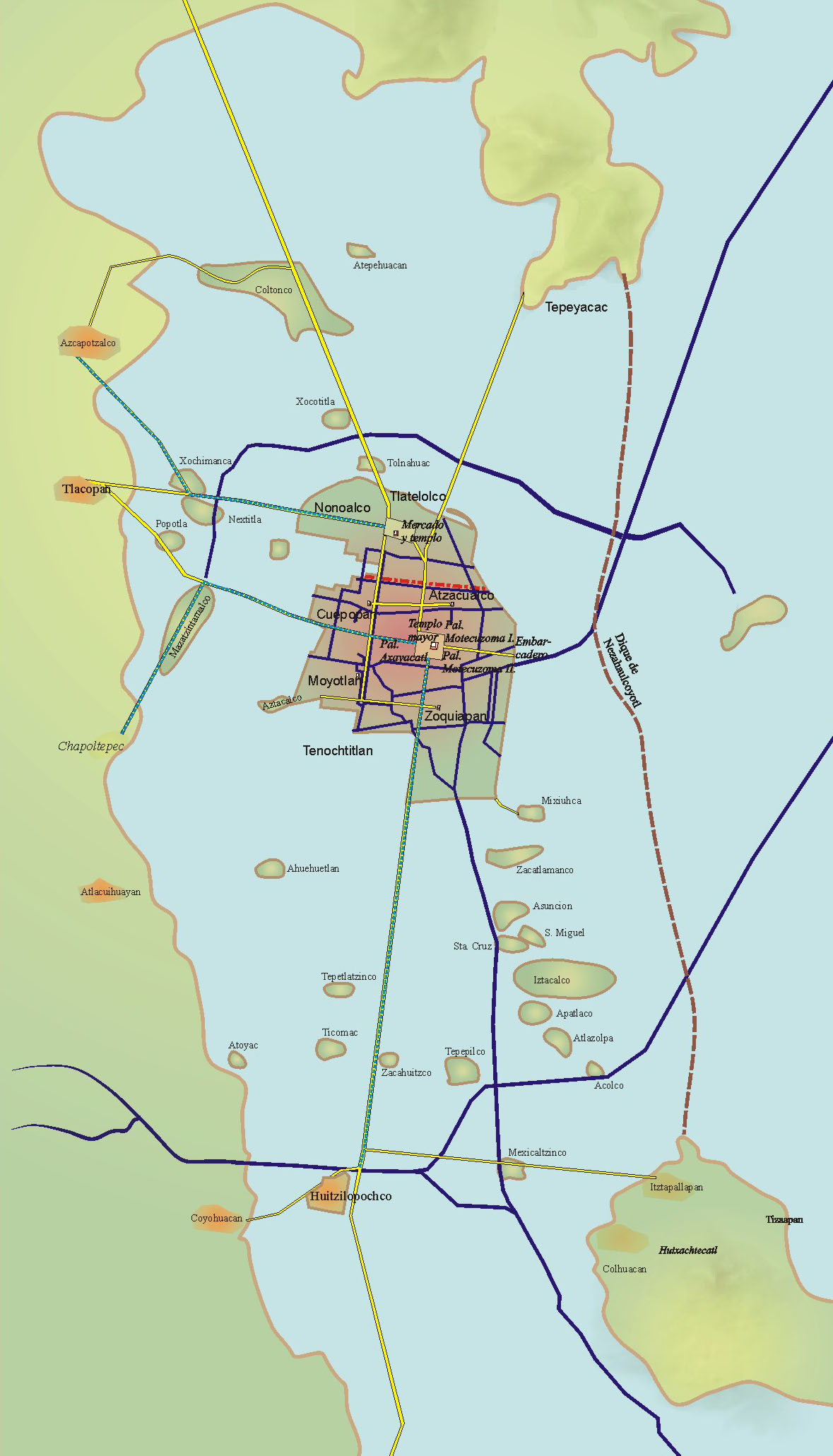
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altepetl
The ( , plural ''altepeme'' or ''altepemeh'') was the local, ethnically-based political entity, usually translated into English as "city-state", of pre-Columbian Nahuatl-speaking societiesSmith 1997 p. 37 in the Americas. The ''altepetl'' was constituted of smaller units known as ''calpolli'' and was typically led by a single dynastic ruler known as a ''tlatoani'', although examples of shared rule between up to five rulers are known. Each ''altepetl'' had its own jurisdiction, origin story, and served as the center of Indigenous identity. Residents referred to themselves by the name of their ''altepetl'' rather than, for instance, as "Mexicas". ''"Altepetl"'' was a polyvalent term rooting the social and political order in the creative powers of a ''sacred mountain'' that contained the ancestors, seeds and life-giving forces of the community. The word is a combination of the Nahuatl words (meaning "water") and (meaning "mountain"). A characteristic Nahua mode was to imagine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixtapalapa
Iztapalapa () is a borough (''demarcaciĂłn territorial'') in Mexico City, located on the eastern side of the city. The borough is named after and centered on the formerly independent municipality of Iztapalapa (officially Iztapalapa de CuitlĂĄhuac). The rest is made up of a number of other communities which are governed by the city of Iztapalapa. With a population of 1,835,486 as of 2020, Iztapalapa is the most populous borough of Mexico City as well as the most populous municipality in the country. Over 90% of its territory is urbanized. The formerly rural borough, which was home to some farms and canals as late as the 1970s, to an area with its only greenery in parks; nearly all of its population employed in commerce, services and industry. This is the result of a large influx of people into the borough starting beginning in the 1970s, with the borough still attracting migrants. Iztapalapa remains afflicted by high levels of economic deprivation, and a significant number of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states ('' altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521â1821). The definitions of Azt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |