|
Central Force
In classical mechanics, a central force on an object is a force that is directed towards or away from a point called center of force. \mathbf(\mathbf) = F( \mathbf ) where F is a force vector, ''F'' is a scalar valued force function (whose absolute value gives the magnitude of the force and is positive if the force is outward and negative if the force is inward), r is the position vector, , , r, , is its length, and \hat = \mathbf r / \, \mathbf r\, is the corresponding unit vector. Not all central force fields are conservative or spherically symmetric. However, a central force is conservative if and only if it is spherically symmetric or rotationally invariant. Examples of spherically symmetric central forces include the Coulomb force and the force of gravity. Properties Central forces that are conservative can always be expressed as the negative gradient of a potential energy: \mathbf(\mathbf) = - \mathbf V(\mathbf) \; \text V(\mathbf) = \int_^ F(r)\,\mathrmr (the upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular/rotational mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is defined relatively to a rotational axis. It is the ratio between the torque applied and the resulting angular acceleration about that axis. It plays the same role in rotational motion as mass does in linear motion. A body's moment of inertia about a particular axis depends both on the mass and its distribution relative to the axis, increasing with mass and distance from the axis. It is an intensive and extensive properties, extensive (additive) property: for a point particle, point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second Moment (physics), mome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
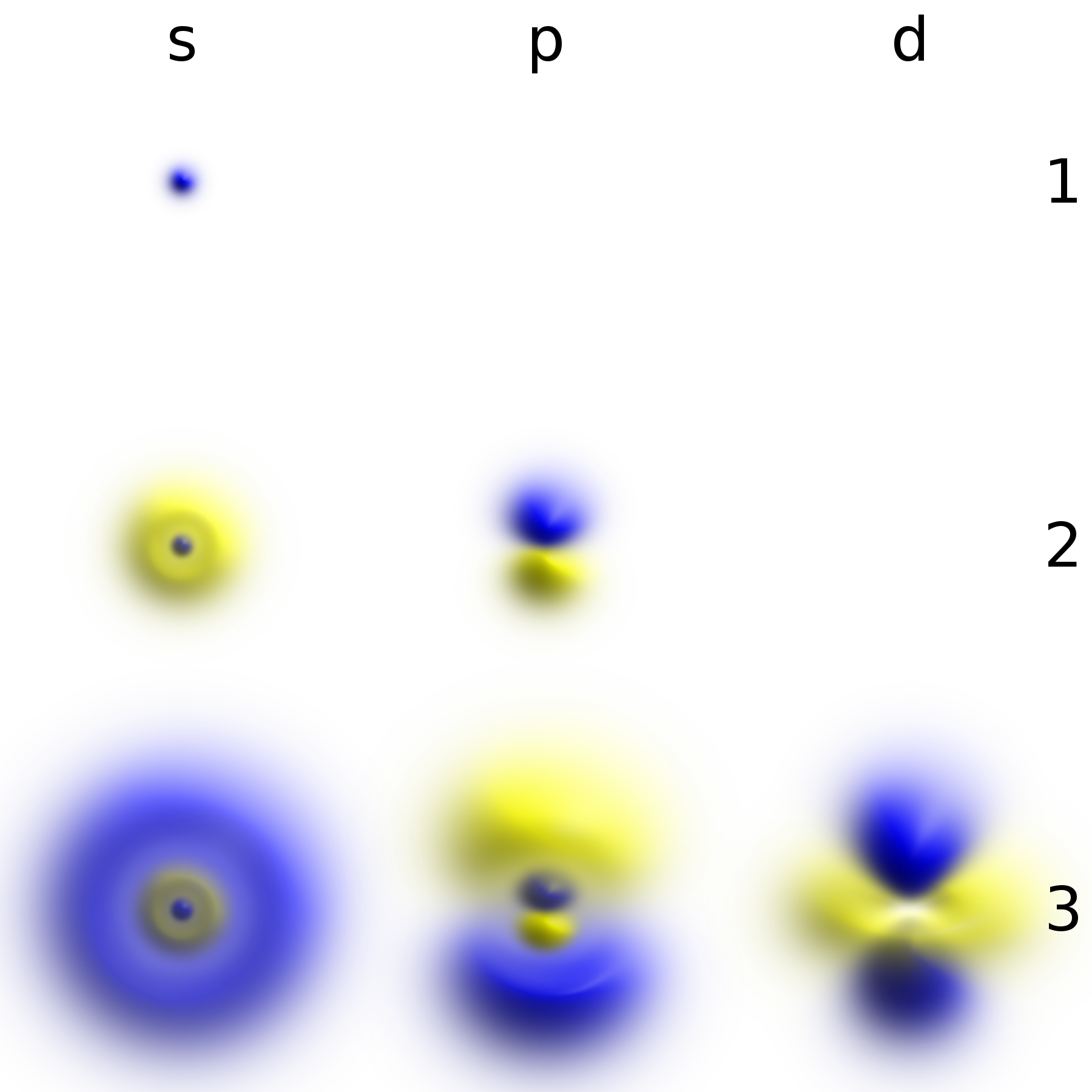
Particle In A Spherically Symmetric Potential
In quantum mechanics, a spherically symmetric potential is a system of which the potential only depends on the radial distance from the spherical center and a location in space. A particle in a spherically symmetric potential will behave accordingly to said potential and can therefore be used as an approximation, for example, of the electron in a hydrogen atom or of the formation of chemical bonds. In the general time-independent case, the dynamics of a particle in a spherically symmetric potential are governed by a Hamiltonian of the following form:\hat = \frac + V() Here, m_0 is the mass of the particle, \hat is the momentum operator, and the potential V(r) depends only on the vector magnitude of the position vector, that is, the radial distance from the origin (hence the spherical symmetry of the problem). To describe a particle in a spherically symmetric system, it is convenient to use spherical coordinates; denoted by r, \theta and \phi. The time-independent Schrödin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Central-force Problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle in a single central force, central potential field. A central force is a force (possibly negative) that points from the particle directly towards a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In a few important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions. The solution of this problem is important to classical mechanics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand's Theorem
In classical mechanics, Bertrand's theorem states that among central-force potentials with bound orbits, there are only two types of central-force (radial) scalar potentials with the property that all bound orbits are also closed orbits. The first such potential is an inverse-square central force such as the gravitational or electrostatic potential: V(r) = -\frac with force f(r) = -\frac = -\frac. The second is the radial harmonic oscillator potential: V(r) = \frac k r^2 with force f(r) = -\frac = -k r. The theorem is named after its discoverer, Joseph Bertrand. Derivation All attractive central forces can produce circular orbits, which are naturally closed orbits. The only requirement is that the central force exactly equals the centripetal force, which determines the required angular velocity for a given circular radius. Non-central forces (i.e., those that depend on the angular variables as well as the radius) are ignored here, since they do not produce circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive constant. The harmonic oscillator model is important in physics, because any mass subject to a force in stable equilibrium acts as a harmonic oscillator for small vibrations. Harmonic oscillators occur widely in nature and are exploited in many manmade devices, such as clocks and radio circuits. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force ( damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse-square Law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that the observed "intensity" of a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental cause for this can be understood as geometric dilution corresponding to point-source radiation into three-dimensional space. Radar energy expands during both the signal transmission and the reflected return, so the inverse square for both paths means that the radar will receive energy according to the inverse fourth power of the range. To prevent dilution of energy while propagating a signal, certain methods can be used such as a waveguide, which acts like a canal does for water, or how a gun barrel restricts hot gas expansion to one dimension in order to prevent loss of energy transfer to a bullet. Formula In mathematical notation the inverse square law can be expressed as an intensity (I) varying as a function of distance (d) from s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curl (mathematics)
In vector calculus, the curl, also known as rotor, is a vector operator that describes the Differential (infinitesimal), infinitesimal Circulation (physics), circulation of a vector field in three-dimensional Euclidean space. The curl at a point in the field is represented by a vector (geometry), vector whose length and direction denote the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and axis of the maximum circulation. The curl of a field is formally defined as the circulation density at each point of the field. A vector field whose curl is zero is called irrotational. The curl is a form of derivative, differentiation for vector fields. The corresponding form of the fundamental theorem of calculus is Kelvin–Stokes theorem, Stokes' theorem, which relates the surface integral of the curl of a vector field to the line integral of the vector field around the boundary curve. The notation is more common in North America. In the rest of the world, particularly in 20th century scientific li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Law Of Universal Gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation describes gravity as a force by stating that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct proportionality, proportional to the product of their masses and Proportionality (mathematics)#Inverse proportionality, inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers of mass. Separated objects attract and are attracted Shell theorem, as if all their mass were concentrated at their centers. The publication of the law has become known as the "Unification (physics)#Unification of gravity and astronomy, first great unification", as it marked the unification of the previously described phenomena of gravity on Earth with known astronomical behaviors. This is a general physical law derived from empirical observations by what Isaac Newton called ''inductive reasoning''. It is a part of classical mechanics and was formulated in Newton's work ''Philosophiæ Natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler's Laws Of Planetary Motion
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler in 1609 (except the third law, which was fully published in 1619), describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. These laws replaced circular orbits and epicycles in the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus with elliptical orbits and explained how planetary velocities vary. The three laws state that: # The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci. # A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time. # The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the length of the semi-major axis of its orbit. The elliptical orbits of planets were indicated by calculations of the orbit of Mars. From this, Kepler inferred that other bodies in the Solar System, including those farther away from the Sun, also have elliptical orbits. The second law establishes that when a planet is closer to the Sun, it travels fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |