|
Central Electronic System Of Payments
The Central Electronic System of Payments (CESOP) regime is an automatic exchange of information regime being introduced in the European Union from 1 January 2024. The rules were introduced by Council Directive 2020/284, amending the EU's Value-added tax Directive. The rules were introduced to tackle VAT fraud by requiring all payment service providers (PSPs) as defined under the EU Payment Services Directive (PSD2) to report on cross-border payments which originate in the EU. To separate business payments from personal transfers, PSPs are only required to report on payments where they know that the recipient has received more than 25 payments in a quarter. The reporting is expected to result in data sharing on 8 billion payment transactions per year, covering credit transfers, direct debit, credit and debit cards, as well as e-money and transactions by digital platforms actings as PSPs. The information shared includes transaction level detail, as well as information relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchange Of Information
Exchange of Information is an umbrella term which refers to international co-operation in the field of taxation through the exchange of information on taxpayers between tax authorities. International exchange of information rules shares many similarities with domestic tax information reporting, such as the United States' Form 1099 regime. However, rules are set on an international level; in recent years exchange of information efforts have been led by the OECD Global Forum on Transparency and Exchange of Information for Tax Purposes. There are 3 types of exchange of tax information which are currently in use: # Exchange Of Information on Request (EOIR) - Tax treaties and tax information exchange agreements generally provide for tax authorities to request information in relation to the assessment, collection or prosecution of tax related issues. The OECD Global Forum conduct peer reviews on compliance with EOIR standards. # Spontaneous Exchange of Information (SEI) - Certain int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
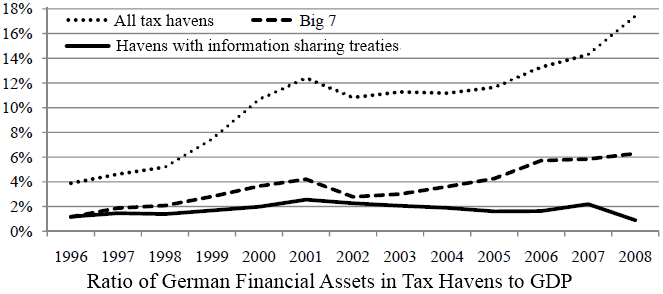
Tax Evasion
Tax evasion or tax fraud is an illegal attempt to defeat the imposition of taxes by individuals, corporations, trusts, and others. Tax evasion often entails the deliberate misrepresentation of the taxpayer's affairs to the tax authorities to reduce the taxpayer's tax liability, and it includes dishonest tax reporting, declaring less income, profits or gains than the amounts actually earned, overstating deductions, bribing authorities and hiding money in secret locations. Tax evasion is an activity commonly associated with the informal economy. One measure of the extent of tax evasion (the "tax gap") is the amount of unreported income, which is the difference between the amount of income that the tax authority requests be reported and the actual amount reported. In contrast, tax avoidance is the legal use of tax laws to reduce one's tax burden. Both tax evasion and tax avoidance can be viewed as forms of tax noncompliance, as they describe a range of activities that intend to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSD2
The Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2, Directive (EU) 2015/2366, which replaced the Payment Services Directive (PSD), Directive 2007/64/EC) is an EU Directive, administered by the European Commission (Directorate General Internal Market) to regulate payment services and payment service providers throughout the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA). The PSD's purpose was to increase pan-European competition and participation in the payments industry also from non-banks, and to provide for a level playing field by harmonizing consumer protection and the rights and obligations of payment providers and users. The key objectives of the PSD2 directive are creating a more integrated European payments market, making payments more secure and protecting consumers. Overview The SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) is a self-regulatory initiative by the European banking sector represented in the European Payments Council, which defines the harmonization of payment products, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payment Service Provider
A payment service provider (PSP) is a third-party company that allows businesses to accept electronic payments, such as credit card and debit card payments. PSPs act as intermediaries between those who make payments, i.e. consumers, and those who accept them, i.e. retailers. They will often provide merchant services and act as a payment gateway or payment processor for e-commerce and brick and mortar businesses. They may also offer risk management services for card and bank based payments, transaction payment matching, digital wallets, reporting, fund remittance, currency exchange and fraud protection. The PSP will typically provide software to integrate with e-commerce websites or point of sale systems. Operation PSPs establish technical connections with acquiring banks and card networks, enabling merchants to accept different payment methods without the need to partner with a particular bank. They fully manage payment processing and external network relationships, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BZSt
The Federal Central Tax Office (, abbreviated BZSt) is a German federal agency responsible for administering various sections of the country's tax code. It was created out of its current parent agency, the Federal Ministry of Finance, on 1 January 2006 and has approximately 2,200 employees. Beginning in July 2007, the BZSt began issuing a unique National identification number to every resident, replacing the formerly decentralized system. The BZSt also operates informational databases relating to the local tax offices. Departments * Department "Q" ("Querschnittsaufgaben": Cross-sectional responsibilities) ** General counsel ** Compliance ** Human Resources, Organisation, Budgetary, Internal services, IT ** Tax Information Center, Reporting, Informationszentrum Steuern, Berichtswesen, Regulatory impact analysis, Risk Management ** Automation, Legal documentation department * Tax Department "I" ("VAT") ** Administrative assistance for domestic and foreign government agenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |