|
Central Cell
Double fertilization or double fertilisation (see spelling differences) is a complex fertilization mechanism of angiosperms. This process involves the fusion of a female gametophyte or megagametophyte, also called the embryonic sac, with two male gametes (sperm). It begins when a pollen grain adheres to the stigmatic surface of the carpel, the female reproductive structure of angiosperm flowers. The pollen grain begins to germinate (unless a type of self-incompatibility that acts in the stigma occurs in that particular species and is activated), forming a pollen tube that penetrates and extends down through the style toward the ovary as it follows chemical signals released by the egg. The tip of the pollen tube then enters the ovary by penetrating through the micropyle opening in the ovule, and releases two sperm into the embryonic sac (megagametophyte). The mature embryonic sac of an unfertilized ovule is 7-cellular and 8-nucleate. It is arranged in the form of 3+1+3 (from to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mature Flower Diagram
Mature is the adjectival form of Maturity (other), maturity, as immature is the adjectival form of immaturity, which have several meanings. Mature or immature may also refer to: *List of The King of Fighters characters#Vice & Mature, Mature, a character from ''The King of Fighters'' series *"Mature 17+", a rating in the Entertainment Software Rating Board video game rating system *Victor Mature (1913-1999), American actor *Immature (band), an American boy band See also * Adult (other) * Maturation (other) * Maturity (other) * Ripeness {{disambig, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, Tissue (biology), tissues, and Individual#Biology, individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploidy, polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexual reproduction, sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Navashin
Sergei Gavrilovich Navashin (; 14 December 1857 – 10 December 1930) was a Russian Empire The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ... and Soviet biologist. He discovered double fertilization in plants in 1898. Biography 1874 — enters the Medical Surgical Academy in St. Petersburg, works on chemistry in the laboratory of A. Borodin 1878 — moves to the Moscow University, obtains Candidate degree in 1881 in Biology. Under the influence of K. Timiryazev and V. Zinger starts to study Botany. Receives a position of a laboratory assistant at the chair of Plant Physiology and later (1885) in the Petrovskaya Agricultural Academy. 1894 — is invited to work at the chair of Systematics and Morphology of the Kiev University. During 1894-1914 works as a director of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Phytologist
''New Phytologist'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published on behalf of the New Phytologist Foundation by Wiley-Blackwell. It covers all aspects of botany and was established in 1902 by Arthur Tansley, who served as editor until 1931. Maarja Öpik took up the position of Editor-in-Chief of ''New Phytologist'' in January 2025. The previous Editor-in-Chief was Alistair M. Hetherington. Article categories The journal publishes articles in the following categories: * Original research articles * Priority reports * Research reviews * Commentaries * Letters * Meeting reports * Modelling/Theory and Methods papers * Tansley reviews * Tansley insights * Viewpoints * Community resources Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded, Current Contents/Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnetales
Gnetophyta () is a division of plants (alternatively considered the subclass Gnetidae or order Gnetales), grouped within the gymnosperms (which also includes conifers, cycads, and ginkgos), that consists of some 70 species across the three Relict (biology), relict genus, genera: ''Gnetum'' (Family (biology), family Gnetaceae), ''Welwitschia'' (family Welwitschiaceae), and ''Ephedra (genus), Ephedra'' (family Ephedraceae). The earliest unambiguous records of the group date to the Jurassic, and they achieved their highest diversity during the Early Cretaceous. The primary difference between gnetophytes and other gymnosperms is the presence of vessel elements, a system of small tubes (xylem) that transport water within the plant, similar to those found in flowering plants. Because of this, gnetophytes were once thought to be the closest gymnosperm relatives to flowering plants, but more recent molecular studies have brought this hypothesis into question, with many recent phylogenies f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trends In Plant Science
''Trends in Plant Science'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus *Chemical Abstracts * Embase *MEDLINE According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 18.313. References External links * English-language journals Elsevier academic journals Botany journals {{botany-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In drug discovery, for example, verification of efficacy ''in vivo'' is crucial, because ''in vitro'' assays can sometimes yield misleading results with drug c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally considered a weed. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome of around 135 Base pair#Length measurements, megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is an important tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and phototropism, light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual plant, annual (rarely biennial plant, biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaf, leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering Plant ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiotic
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary (botany)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels (e.g. dicarpel or tricarpel), and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the Style (botany), style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries. Fruits A fruit is the mature, ripened ovary of a flower following double fertilization in an angiosperm. Because gymnosperms do not have an ovary but reproduce through fertilization of unprotected ovules, they produce naked seeds th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
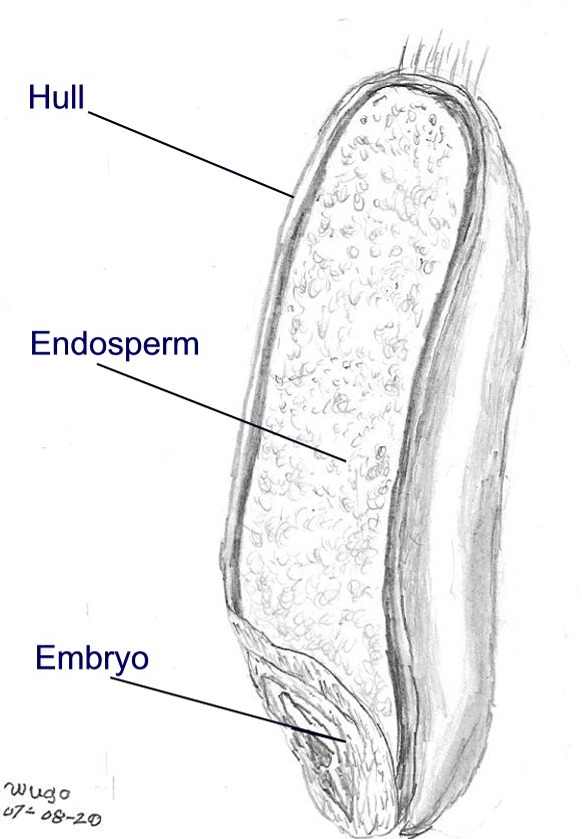
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each of two parents; each set contains the same number of chromosomes, and the chromosomes are joined in pairs of homologous chromosomes. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A Ploidy, monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have Biological life cycle, life cycles with two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular generations. The gamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |