|
Cedar River (Washington)
The Cedar River is a river in the U.S. state of Washington. About long, it originates in the Cascade Range and flows generally west and northwest, emptying into the southern end of Lake Washington. Its upper watershed is a protected area called the Cedar River Watershed, which provides drinking water for the greater Seattle area. The Cedar River drains into Puget Sound via Lake Washington and the Lake Washington Ship Canal. Course The Cedar River originates in the Cascade Range near Abiel Peak, Meadow Mountain, and Yakima Pass, along the King and Kittitas countyline. Several headwater streams join in the high mountains fed from glacial run-off, then the Cedar River flows generally west. It is impounded in Chester Morse Lake, a natural lake that was dammed in 1900 for use as a water storage reservoir. The Rex River joins the Cedar in Chester Morse Lake, as do the two forks of the Cedar River, the north and south forks. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington (state)
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, by the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. It was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C. Washington is the 18th-largest state, with an area of , and the 13th-most populous state, with more than 7.7 million people. The majority of Washington's residents live in the Seattle metropolitan area, the center o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abiel Peak
Abiel Peak is a mountain summit located in eastern King County of Washington state. It is set 1,000 feet west of the crest of the Cascade Range, on land managed by Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest. Abiel Peak is situated six miles south-southwest of Snoqualmie Pass, and neighbors include Silver Peak, three-quarters mile to the north-northeast, Tinkham Peak three-quarters mile to the east, and Humpback Mountain two miles to the northwest. Precipitation runoff from the south side of the mountain drains into headwaters of Tinkham Creek which is a tributary of the North Fork Cedar River, whereas the north side of the mountain drains into Annette Lake, thence the South Fork Snoqualmie River via Humpback Creek. Topographic relief is significant as the north aspect rises above Annette Lake in one-half mile. Etymology This geographic landform was named by The Mountaineers and has been officially adopted by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names to honor Lieutenant Abiel W. Tinkh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
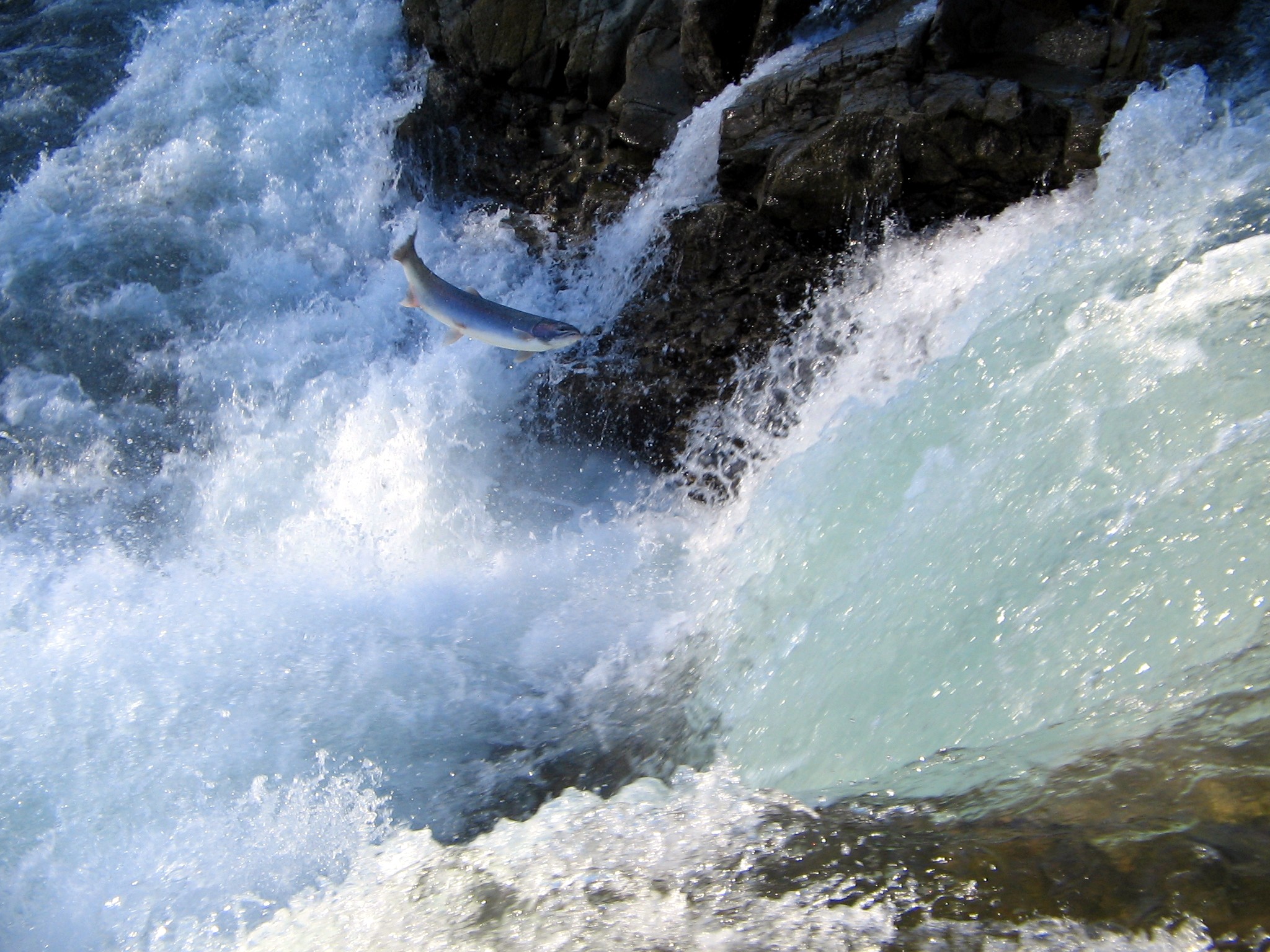
Fish Migration
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousands of kilometres. Such migrations are usually done for better feeding or to reproduce, but in other cases the reasons are unclear. Fish migrations involve movements of schools of fish on a scale and duration larger than those arising during normal daily activities. Some particular types of migration are ''anadromous'', in which adult fish live in the sea and migrate into fresh water to spawn; and ''catadromous'', in which adult fish live in fresh water and migrate into salt water to spawn. Marine forage fish often make large migrations between their spawning, feeding and nursery grounds. Movements are associated with ocean currents and with the availability of food in different areas at different times of year. The migratory movements ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Union
Lake Union is a freshwater lake located entirely within the city limits of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is a major part of the Lake Washington Ship Canal, which carries fresh water from the much larger Lake Washington on the east to Puget Sound on the west. The easternmost point of the lake is the Ship Canal Bridge, which carries Interstate 5 over the eastern arm of the lake and separates Lake Union from Portage Bay. Lake Union is the namesake of the neighborhoods located on its east and west shores: Eastlake and Westlake respectively. The northern shore of the lake is home to Gas Works Park. Notable features of the southern area of the lake—collectively known as the South Lake Union district—include Lake Union Park, Museum of History & Industry (MOHAI), and the Center for Wooden Boats. The Aurora Bridge (officially the George Washington Memorial Bridge) carries State Route 99 over the western arm of Lake Union. The Aurora Bridge is so named because it carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
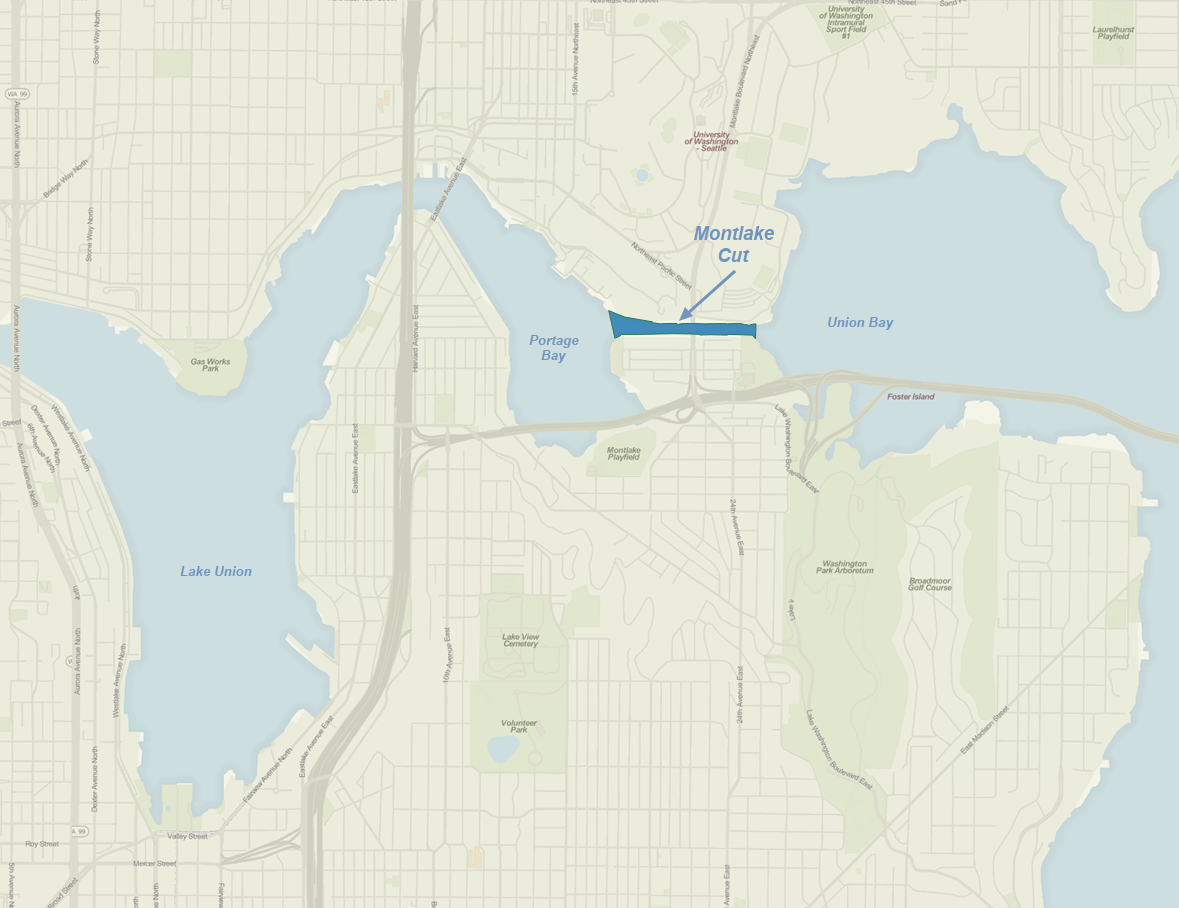
Montlake Cut
The Montlake Cut is the easternmost section of the Lake Washington Ship Canal, which passes through the city of Seattle, linking Lake Washington to Puget Sound. It was completed in 1916 and is approximately long and wide. The center channel is wide and deep. The path along the cut was designated a National Recreation Trail as Montlake Cut National Waterside in 1971. The Cut provides a connection between Union Bay, part of Lake Washington, to the east and Portage Bay, an arm of Lake Union, to the west. It is spanned by the Montlake Bridge, a bascule drawbridge carrying Montlake Boulevard ( State Route 513). Most of the land on the north shore of the Cut is occupied by the University of Washington, its medical school to the west and its stadium parking lot to the east; residences and a recreational trail occupy the south bank, which is part of the Montlake neighborhood. It is the site of the annual Windermere Cup crew regatta and the Seattle Yacht Club's Opening Day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Bay
Elliott Bay is a part of the Central Basin region of Puget Sound. It is in the U.S. state of Washington, extending southeastward between West Point in the north and Alki Point in the south. Seattle was founded on this body of water in the 1850s and has since grown to encompass it completely. The waterway it provides to the Pacific Ocean has served as a key element of the city's economy, enabling the Port of Seattle to become one of the busiest ports in the United States. History The Duwamish people lived in the vicinity of Elliott Bay and the Duwamish River for thousands of years and had established at least 17 settlements by the time white settlers came in the 1850s. Among the earliest white settlements was by the Denny Party at New York Alki, which is in the present-day neighborhood of Alki in West Seattle, however after a hard winter they shifted across Elliott Bay near the present-day Pioneer Square, which became Seattle. Over the years the city expanded to cover all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duwamish River
The Duwamish River is the name of the lower of Washington (state), Washington state's Green River. Its industrialized estuary is known as the Duwamish Waterway. In 2009, the Duwamish Longhouse and Cultural Center was opened on the west bank of the river as part of the tribe's reassertion of its histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green River (Duwamish River)
The Green River is a long river in the state of Washington in the United States, arising on the western slopes of the Cascade Range south of Interstate 90. The upper Green River valley forms the western approach to Stampede Pass, and was once home to many small railroad and logging towns such as Weston, Lester, Green River Hot Springs, Nagrom, Maywood, Humphreys, Eagle Gorge, Lemolo, and Kanaskat. Shortly before World War I, the City of Tacoma, Washington, filed for water rights on the Green River. Today, much of the upper valley has become a gated water supply watershed for Tacoma and access is heavily restricted, creating controversy among recreation enthusiasts. Between 1880 and 1888, the Northern Pacific Railway explored and surveyed the Green River. The railway constructed the first direct rail link across Washington's Cascade Range with the opening of their Stampede Tunnel in 1888. History Until 1906, the Green River flowed into the White in downtown Auburn. In 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black River (Duwamish River)
The Black River is a tributary of the Duwamish River in King County, Washington, King County in the U.S. state of Washington. It drained Lake Washington until 1916, when the opening of the Lake Washington Ship Canal lowered the lake, causing part of the Black River to dry up. It still exists as a dammed stream about long. Before the 20th century, Lake Washington emptied from its south end into the Black River, which was joined by the Cedar River before meeting the White River (now the lower Green River; the White River has been diverted south). The confluence of the Black and White rivers created the Duwamish River, which emptied into Elliott Bay in Puget Sound. Thus, the water of rivers emptying into Lake Washington, such as the Sammamish River, once flowed through the Black and Duwamish rivers. Today, Lake Washington's water empties into Puget Sound via the Lake Washington Ship Canal. In November 1911, the Cedar River flooded Renton. In 1912, the Cedar was diverted from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally referred to terrestrial environments, though growing attention is being placed on marine wilderness. Recent maps of wilderness suggest it covers roughly one quarter of Earth's terrestrial surface, but is being rapidly degraded by human activity. Even less wilderness remains in the ocean, with only 13.2% free from intense human activity. Some governments establish protection for wilderness areas by law to not only Protected area, preserve what already exists, but also to promote and advance a natural expression and development. These can be set up in preserves, conservation preserves, national forests, national parks and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches or otherwise undeveloped areas. Often these areas are considered important for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seattle Public Utilities
Seattle Public Utilities (SPU) is a public utility agency of the city of Seattle, Washington, which provides water, sewer, drainage and garbage services for 1.3 million people in King County, Washington. The agency was established in 1997, consolidating the city's Water Department with other city functions. Water supply SPU owns two water collection facilities: one in the Cedar River watershed, which supplies 70 percent of the drinking water used by 1.3 million people in Seattle and surrounding suburbs (primarily the city south of the Lake Washington Ship Canal) and the other in the Tolt River watershed which supplies the other 30 percent (primarily the city north of the canal). From the city's founding through the 1880s, Seattle's water was provided by several private companies. In a July 8, 1889 election,Alan J. SteinSeattle voters authorize Cedar River Water Supply system on July 8, 1889. HistoryLink, January 1, 2000. Accessed online 6 December 2007. barely a month ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benchmark Maps
Benchmark may refer to: Business and economics * Benchmarking, evaluating performance within organizations * Benchmark price * Benchmark (crude oil), oil-specific practices Science and technology * Benchmark (surveying), a point of known elevation marked for the purpose of surveying * Benchmarking (geolocating), an activity involving finding benchmarks * Benchmark (computing), the result of running a computer program to assess performance * Benchmark, a best-performing, or gold standard test in medicine and statistics Companies * Benchmark Electronics, an electronics manufacturer * Benchmark (venture capital firm), a venture capital firm * Benchmark Recordings, a music label with CDs by the Fabulous Thunderbirds and Mike Bloomfield Other uses * ''Benchmarking'' (journal), a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal relating to the field of quality management * McAfee's Benchmark McAfee's Benchmark is a brand of Kentucky Straight Bourbon Whiskey produced by the Sazerac Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |