|
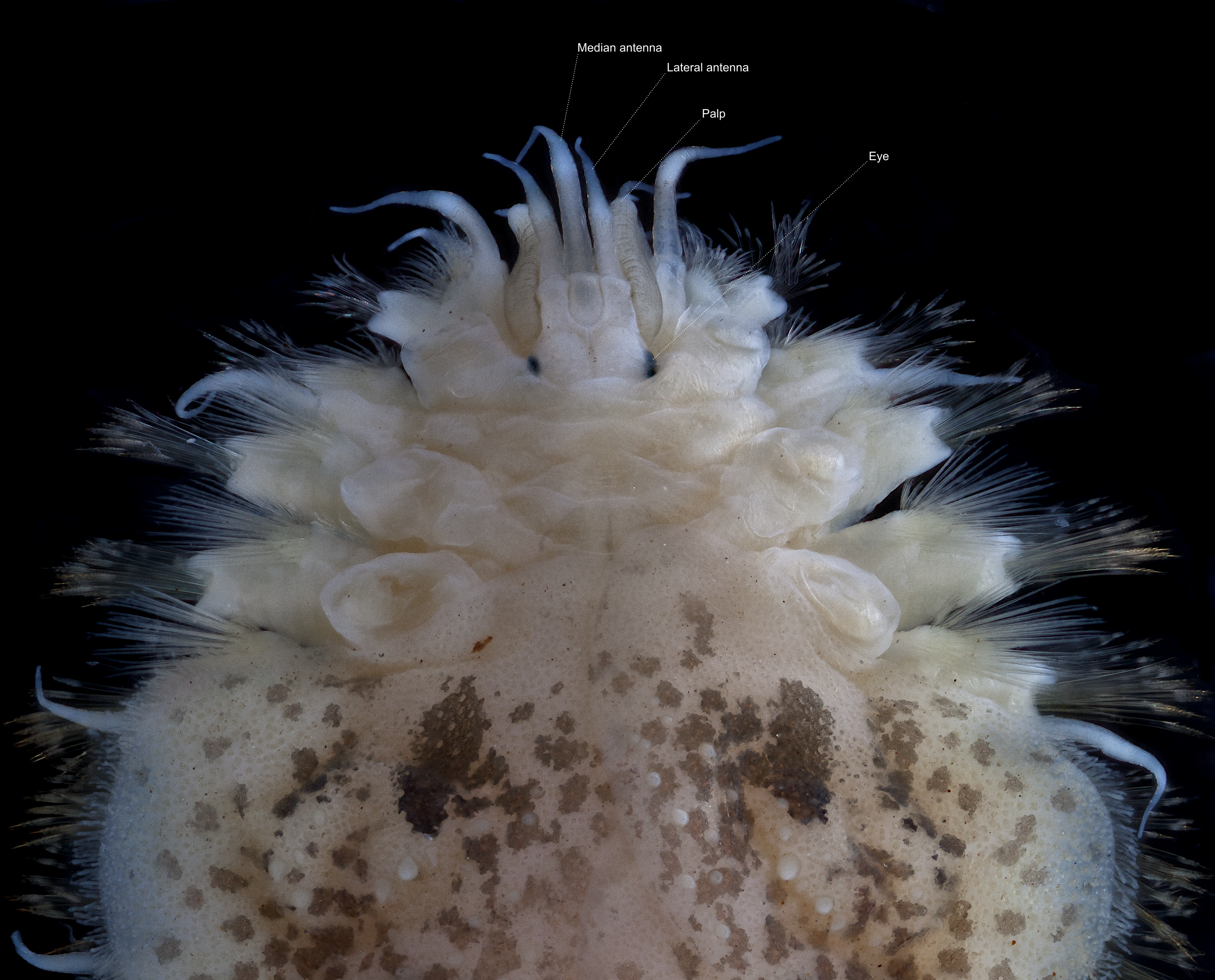
Catworm
Nephtyidae is a family of polychaete worms. They are commonly referred to as catworms. Characteristics Nephtyidae are pale, clearly segmented polychaetes with a small pentagonal prostomium with two pairs of small antennae. Their segments are little differentiated and have a rectangular cross-section. Nephtyids are active predators, with a strong muscular proboscis A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a pr ..., armed with two well developed jaws. They can dig relatively fast through sandy sediments. They can also swim with sinuous movements. References Annelid families Phyllodocida {{Annelid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aglaophamus
''Aglaophamus'' is a genus Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ... of free-burrowing nephtyid worms. Species The following species are accepted in the genus ''Aglaophamus'': *'' Aglaophamus agilis'' *'' Aglaophamus amakusaensis'' *'' Aglaophamus australiensis'' *'' Aglaophamus circinata'' *'' Aglaophamus dibranchis'' *'' Aglaophamus dicirroides'' *'' Aglaophamus digitatus'' *'' Aglaophamus elamellatus'' *'' Aglaophamus erectanoides'' *'' Aglaophamus erectans'' *'' Aglaophamus eugeniae'' *'' Aglaophamus fabrun'' *'' Aglaophamus foliocirrata'' *'' Aglaophamus foliosa'' *'' Aglaophamus foliosus'' *'' Aglaophamus fossae'' *'' Aglaophamus gippslandicus'' *'' Aglaophamus groenlandiae'' *'' Aglaophamus hedlandensis'' *'' Aglaophamus heteroserrata'' *'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentinephtys
''Nephtys'' is a genus of marine catworms. Some species are halotolerant to a degree in that they can survive in estuaries and estuarine lagoons down to a salinity of 20 psu ( Practical Salinity Units). Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Nephtys'': *'' Nephtys abranchiata'' *'' Nephtys acrochaeta'' *'' Nephtys assignis'' *'' Nephtys assimilis'' *'' Nephtys bangladeshi'' *'' Nephtys bilobatus'' *'' Nephtys brachycephala'' *''Nephtys brevibranchis'' *'' Nephtys bruuni'' *'' Nephtys bucera'' *'' Nephtys caeca'' (Fabricius, 1780) *''Nephtys caecoides'' *''Nephtys californiensis'' *''Nephtys capensis'' *''Nephtys chemulpoensis'' *''Nephtys ciliata'' (Müller, 1788) - typetaxon *''Nephtys cirrosa'' *''Nephtys cryptomma'' *''Nephtys cuvieri'' *''Nephtys discors'' *''Nephtys dussumieri'' *''Nephtys ectopa ''Nephtys'' is a genus of marine catworms. Some species are halotolerant to a degree in that they can survive in estuaries and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephtys
''Nephtys'' is a genus of Marine (ocean), marine catworms. Some species are halotolerance, halotolerant to a degree in that they can survive in estuaries and estuarine lagoons down to a salinity of 20 psu (Practical Salinity Unit, Practical Salinity Units). Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Nephtys'': *''Nephtys abranchiata'' *''Nephtys acrochaeta'' *''Nephtys assignis'' *''Nephtys assimilis'' *''Nephtys bangladeshi'' *''Nephtys bilobatus'' *''Nephtys brachycephala'' *''Nephtys brevibranchis'' *''Nephtys bruuni'' *''Nephtys bucera'' *''Nephtys caeca'' (Johan Christian Fabricius, Fabricius, 1780) *''Nephtys caecoides'' *''Nephtys californiensis'' *''Nephtys capensis'' *''Nephtys chemulpoensis'' *''Nephtys ciliata'' (Müller, 1788) - typetaxon *''Nephtys cirrosa'' *''Nephtys cryptomma'' *''Nephtys cuvieri'' *''Nephtys discors'' *''Nephtys dussumieri'' *''Nephtys ectopa'' *''Nephtys ferruginea'' *''Nephtys fluviatilis'' *''Nephtys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepest known spot in the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; : prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the Cephalization, cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx#Invertebrates, pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the simple eye in invertebrates, eyes, antenna (biology), antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., Insect mouthparts#Proboscis, moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, Nemertea, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala, the thorny-headed worms or spiny-headed worms, are characterized by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephtyidae Polychaetes
Nephtyidae is a family of polychaete worms. They are commonly referred to as catworms. Characteristics Nephtyidae are pale, clearly segmented polychaetes with a small pentagonal prostomium with two pairs of small antennae. Their segments are little differentiated and have a rectangular cross-section. Nephtyids are active predators, with a strong muscular proboscis A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a pr ..., armed with two well developed jaws. They can dig relatively fast through sandy sediments. They can also swim with sinuous movements. References Annelid families Phyllodocida {{Annelid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid Families
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The annelids are Symmetry in biology, bilaterally symmetrical, Triploblasty, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have Parapodium, parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistics, Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Siboglinidae, Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |