|
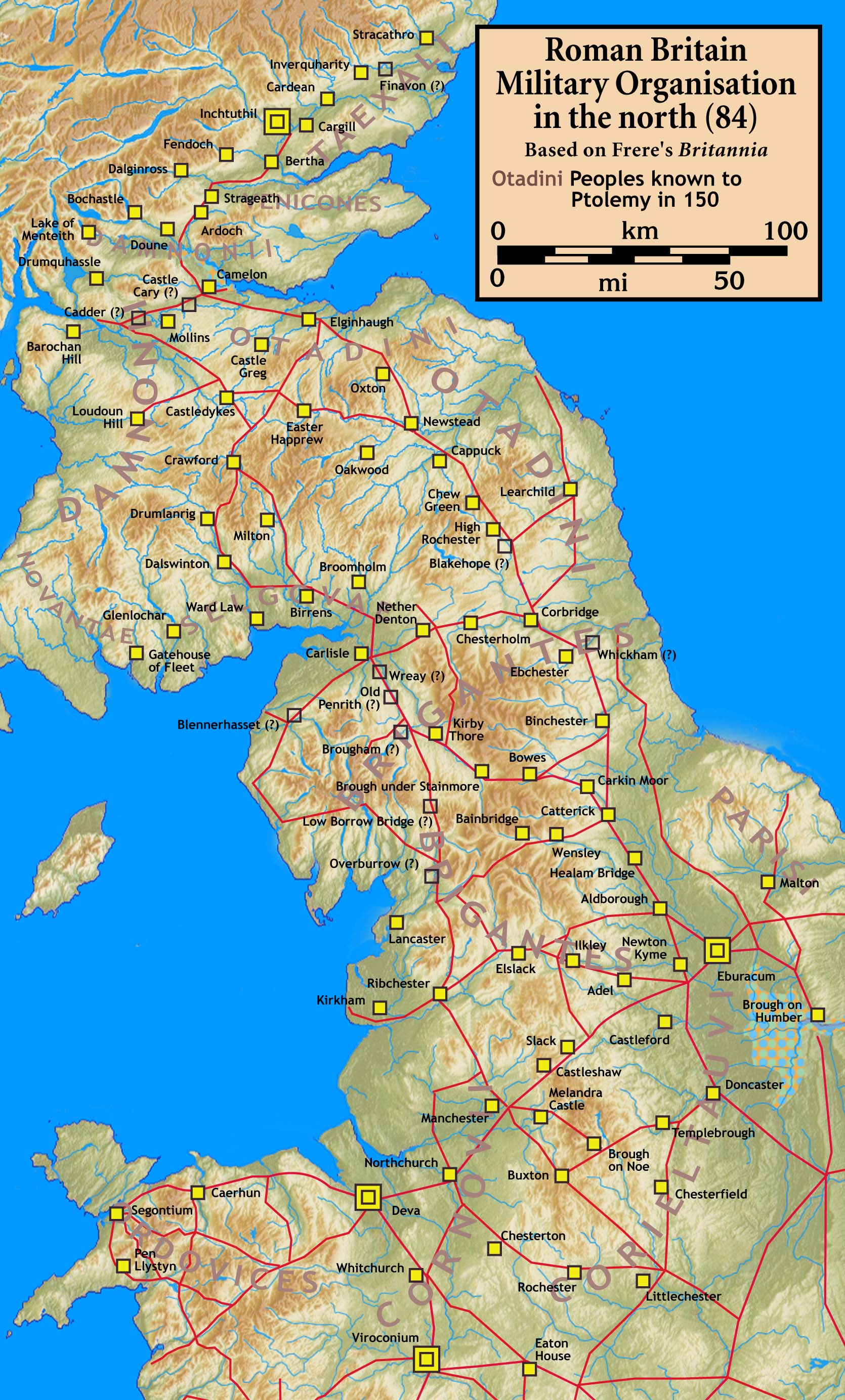
Castlehill Fort
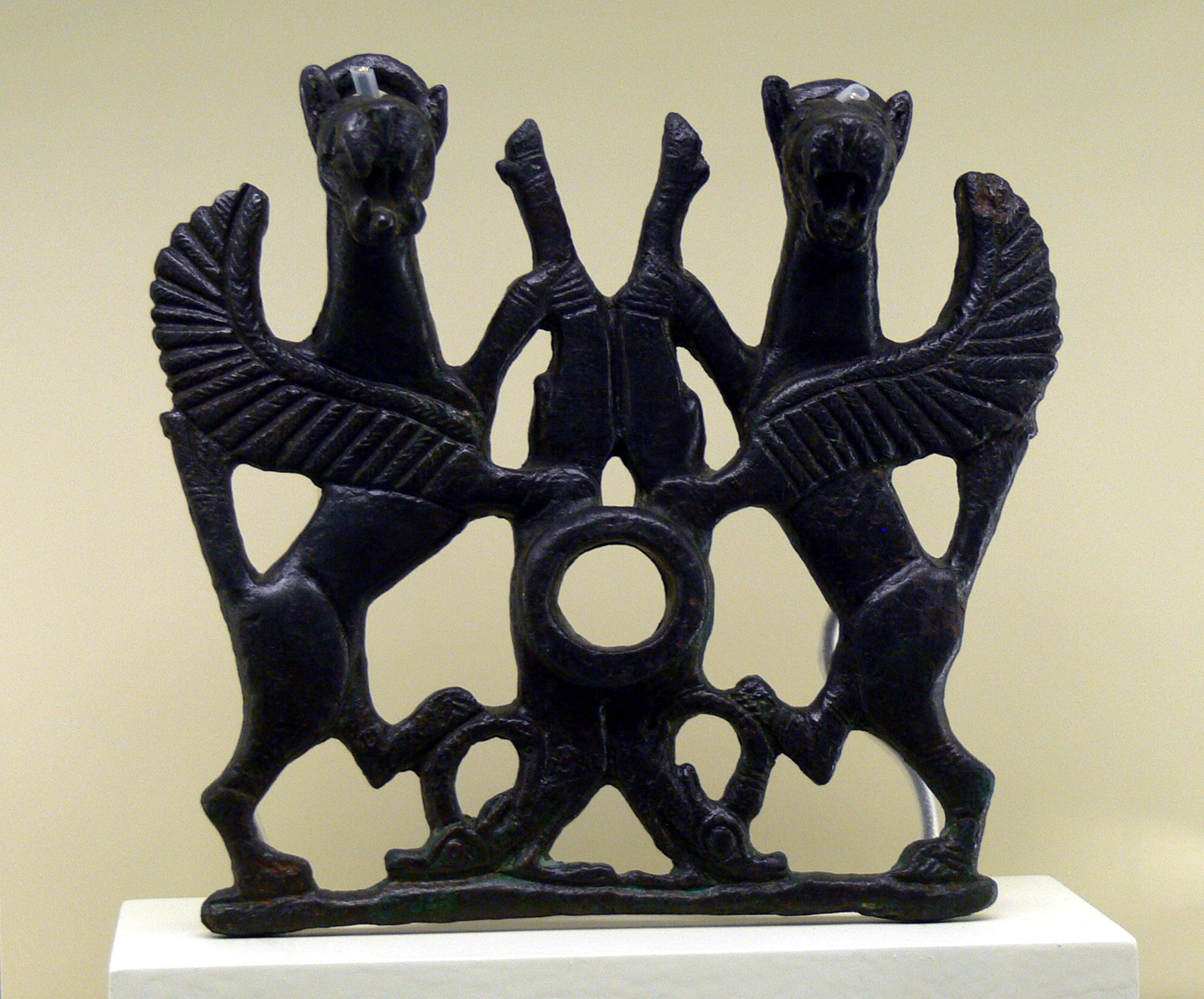
Castlehill was a Roman fort on the Antonine Wall in Scotland. Location The fort is located in East Dunbartonshire, west of Bearsden and east of Duntocher, south of the A810 Duntocher Road. Its neighbouring forts are Bearsden to the east and Duntocher to the west although there is a fortlet at Cleddans in between, with Hutcheson Hill nearer still. A circular enclosed plantation of beech trees is about all a visitor can see nowadays. The summit of Castlehill provides a wide panorama overlooking many historical finds. It's sometimes hard to see the exact line of the Antonine Wall at the location but there is some existing signage. In the 1900s several historians gave their own idiosyncratic descriptions of the site. Finds Two Roman distance slabs were found at the site. One can be compared with another found near Summerston. Both these similar slabs, like two others from Duntocher have two decorative pelta shields, one on either side of the slab. The horns of each shield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. Born into a senatorial family, Antoninus held various offices during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. He married Hadrian's niece Faustina, and Hadrian adopted him as his son and successor shortly before his death. Antoninus acquired the cognomen Pius after his accession to the throne, either because he compelled the Senate to deify his adoptive father, or because he had saved senators sentenced to death by Hadrian in his later years. His reign is notable for the peaceful state of the Empire, with no major revolts or military incursions during this time. A successful military campaign in southern Scotland early in his reign resulted in the construction of the Antonine Wall. Antoninus was an effective administrator, leaving his successors a large surplus in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearsden From The Air (geograph 5186835)
Bearsden () is a town in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the northwestern fringe of Greater Glasgow. Approximately from Glasgow City Centre, the town is effectively a suburb, and its housing development coincided with the 1863 introduction of a railway line. The town was named after Bearsden railway station, which was named after a nearby cottage. Bearsden was ranked the seventh-wealthiest area in Britain in a 2005 survey, and has the least social housing of any town in Scotland. The Roman Antonine Wall runs through the town, and the remains of a military bath house can be seen near the town centre. In 1649, the first New Kilpatrick parish church was built, which became the centre of administration for the area. The town's official Gaelic name ''Cille Phàdraig Ùr'' (meaning "new church of Patrick") reflects the name of the parish. By the early 20th century, a town had grown, with large townhouses, primarily occupied by wealthy commuter business workers. Further deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blatobulgium
Blatobulgium was a Roman fort, located at the modern-day site known as Birrens, in Dumfriesshire, Scotland. Name Blatobulgium is recorded in the Antonine Itinerary. The name derives from the Brittonic roots ''*blāto-'' 'bloom, blossom' or ''*blāto-'' (from earlier ''*mlāto-''), 'flour' and ''*bolgo-'', 'bag, bulge'. The name may mean 'flowery hillock' or 'flowery hollow'. However, as there are granaries at the fort, Blatobulgium may be a nickname meaning ' Flour Sacks'. History The fort formed the northern terminus of the Roman-era Watling Street (using an extended definition of this road), or more simply Route 2 of the Antonine Itinerary. It was located in the territory of the Selgovae. Birrens was first occupied in the Flavian Flavian may refer to: * A member of the Flavian dynasty of Roman emperors, during the late 1st century AD, or their works * Flavian Zeija, a Ugandan lawyer, academic and judge. Principal Judge of Uganda, since December 2019. * A person named Flav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlecary
Castlecary () is a small historic village in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, directly adjacent to the border with Falkirk. It has long been associated with infrastructure, being adjacent to a bridged river, a Roman fort and roads, a nationwide canal, a Victorian railway viaduct, and a modern motorway. Castlecary is close to the town of Cumbernauld but like Dullatur and Luggiebank is not officially part of the town. Around 1725, the barony of Castlecary, with a population of just seventeen families, was disjoined from the parish of Falkirk, and annexed to Cumbernauld quoad sacra. Castlecary is also near Allandale which, though in the Falkirk council area, was built for Castlecary fireclay workers. Roman Heritage Castlecary, like many other settlements in the area, is steeped in the Roman history of Scotland. The route of the Antonine Wall passes through the village. Around 80 AD, a Roman camp was built at Castlecary. It may have been during governor Agricola's fourth camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summerston
Summerston is a residential area of Glasgow, Scotland. With most of the housing constructed in the 1970s, it is situated in the far north of the city and is considered to be part of the larger Maryhill district, but has a different postcode; other nearby neighbourhoods are Gilshochill to the south and Cadder to the south-east. With open farmland to the north-east, Summerston is separated from the southern parts of the town of Bearsden to the north-west by the River Kelvin and a golf course. Amenities Summerston has a riding school run by UK charity Riding for the Disabled. The area is also home to St Blane's Primary and John Paul Academy. The 4th Glasgow Scout Beaver Colony and Cub Scout Pack are based in Caldercuilt Primary School at 101 Invershiel Road. It is also home to Summerston Childcare which is the most popular Family Learning and Out of School centre in Summerston having had a waiting list for their classes since their opening in 1995. Maryhill Harriers running cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (Ancient Greek: , ''gryps''; Classical Latin: ''grȳps'' or ''grȳpus''; Late Latin, Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a legendary creature with the body, tail, and Hindlimb, back legs of a lion; the head and wings of an eagle; and sometimes an eagle's talons as its front feet. Because the lion was traditionally considered the king of the beasts, and the eagle the king of the birds, by the Middle Ages, the griffin was thought to be an especially powerful and majestic creature. Since classical antiquity, griffins were known for guarding treasures and priceless possessions. In Greek and Roman texts, griffins and Arimaspians were associated with gold deposits of Central Asia. Indeed, as Pliny the Elder wrote, "griffins were said to lay eggs in burrows on the ground and these nests contained gold nuggets." In medieval heraldry, the griffin became a Christian symbol of Divinity, divine power and a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosette (design)
A rosette is a round, stylized flower design. Origin The rosette derives from the natural shape of the botanical rosette, formed by leaves radiating out from the stem of a plant and visible even after the flowers have withered. History The rosette design is used extensively in sculptural objects from antiquity, appearing in Mesopotamia, and in funeral steles' decoration in Ancient Greece. The rosette was another important symbol of Ishtar which had originally belonged to Inanna along with the Star of Ishtar. It was adopted later in Romaneseque and Renaissance architecture, and also common in the art of Central Asia, spreading as far as India where it is used as a decorative motif in Greco-Buddhist art. Ancient origins One of the earliest appearances of the rosette in ancient art is in early fourth millennium BC Egypt. Another early Mediterranean occurrence of the rosette design derives from Minoan Crete; Among other places, the design appears on the Phaistos Disc, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltarion (Shield)
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis distinguishes the Thracian and Greek peltast troops. The peltast often served as a skirmisher in Hellenic and Hellenistic armies. In the Medieval period, the same term was used for a type of Byzantine infantryman. Description ''Pelte'' shield ''Peltasts'' carried a crescent-shaped wicker shield called a "''pelte''" (Ancient Greek grc, πέλτη, peltē, label=none; Latin: ) as their main protection, hence their name. According to Aristotle, the ''pelte'' was rimless and covered in goat- or sheepskin. Some literary sources imply that the shield could be round, but in art it is usually shown as crescent-shaped. It also appears in Scythian art and may have been a common type in Central Europe. The shield could be carried with a central strap a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duntocher
Duntocher (Scottish Gaelic: ''Dùn Tòchair'' or ''Druim Tòchair'') is a village in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It has an estimated population of 6,850. The etymology of the name of the village indicates that its name means "the fort on the causeway". Duntocher has effectively become a northern suburb of the nearby town of Clydebank, as have neighbouring Hardgate and Faifley. Duntocher expanded due to housebuilding by Clydebank Burgh Council after the Second World War, although the area was never formally absorbed into the burgh. When burghs were abolished by local government reorganisation in 1975, however, Duntocher was included in the larger Clydebank District, which existed until the creation of West Dunbartonshire in 1997. Further housing was built by the Wimpey firm in the late 1960s and early 1970s, on what had been green belt land. Along with Faifley and Hardgate, Duntocher falls within West Dunbartonshire's ''Kilpatrick'' ward with a combined population of 12,719 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XX Valeria Victrix
Legio XX Valeria Victrix, in English Twentieth Victorious Valeria Legion was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The origin of the Legion's name is unclear and there are various theories, but the legion may have gained its title ''Valeria Victrix'' from a victory it achieved during the Great Illyrian revolt under the command of the general Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus. The legion had a boar as its emblem. History The legion was probably founded shortly after 31 BC by the emperor Augustus. XX ''Valeria victrix'' was probably part of the large Roman force that fought in the Cantabrian Wars in Hispania from 25 to 19 BC. The legion then moved to Burnum in Illyricum at the beginning of the Pannonian uprising (''Bellum Batonianum'') in AD 6. It is recorded operating against the Marcomanni in AD 6 in the army of Tiberius. In Illyria they were led by the governor of Illyricum, Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus, who may have given his clan (''gens'') name '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |