|
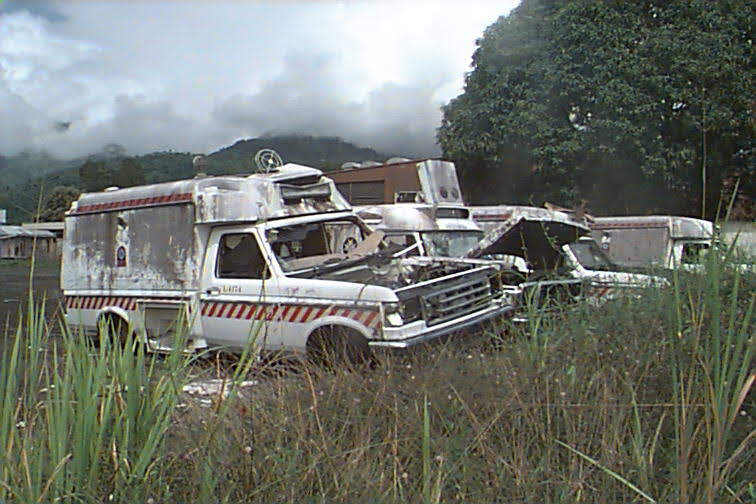
Carteret Islands
The Carteret Islands (also known as Carteret Atoll, originally known as Tulun or Kilinailau Islands/Atoll) are Papua New Guinea islands located north-east of Bougainville Island, Bougainville in the Oceania, South Pacific. The atoll has a scattering of low-lying islands called Han, Jangain, Yesila, Yolasa and Piul, in a horseshoe shape stretching in north-south direction, with a total land area of and a maximum elevation of above sea level. The group is made up of islands collectively named after the British navigator Philip Carteret, who was the first European to discover them, arriving in the sloop in 1767. , about one thousand people lived on the islands. Although the Carteret islanders’ ancestors have lived on the island for thousands of years. Han is the most significant island, with the others being small islets around the lagoon. The main settlement is at Weteili on Han. The island is near the edge of the large geologic formation called the Ontong Java Plateau. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
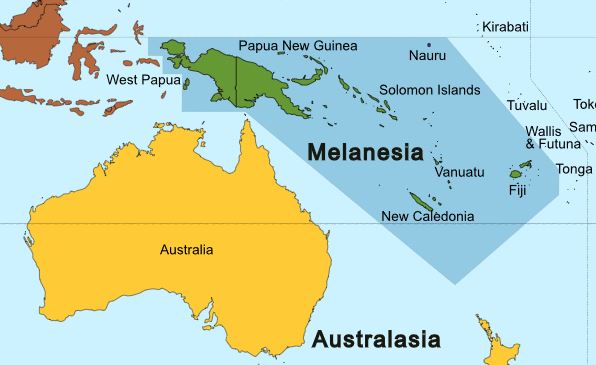
Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea. The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, and Papua New Guinea. It also includes the West New Guinea, Indonesian part of New Guinea, the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia, and the Torres Strait Islands. Almost all of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere; only a few small islands that are not politically considered part of Oceania—specifically the northwestern islands of Western New Guinea—lie in the Northern Hemisphere. The name ''Melanesia'' (in French, ''Mélanésie'') was first used in 1832 by French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville: he coined the terms ''Melanesia'' and ''Micronesia'' to go alongside the pre-existing ''Polynesia'' to designate what he viewed as the three main Ethnicity, ethnic and geographical regions forming the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buka Island
Buka Island is the second-largest island in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, in eastern Papua New Guinea. It is in Buka Rural LLG of North Bougainville District, with the Autonomous Region's and district's capital city of Buka, Bougainville, Buka on the island. The island is separated by the narrow Buka Passage from the northwestern coast of Bougainville Island, and has an area of approximately . Buka, Bougainville Island and the Tabar Group, Tabar Islands and their surrounding waters are identified as being part of the Solomon Archipelago terrestrial ecoregion and marine ecoregion. History Buka was first occupied by humans in the Paleolithic period, with evidence for human habitation at Kilu Cave some 30,000 years ago. British, Australian and American whaling ships visited the island in the nineteenth century for food, water and wood. The first on record was the ''Eliza'' in 1806, and the last known visit was by the ''Palmetto'' in 1881. The present inhabitants s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seawall
A seawall (or sea wall) is a form of coastal defense constructed where the sea, and associated coastal processes, impact directly upon the landforms of the coast. The purpose of a seawall is to protect areas of human habitation, conservation, and leisure activities from the action of tides, waves, or tsunamis. As a seawall is a static feature, it will conflict with the dynamic nature of the coast and impede the exchange of sediment between land and sea. Seawall designs factor in local climate, coastal position, wave regime (determined by wave characteristics and effectors), and value (morphological characteristics) of landform. Seawalls are hard engineering shore-based structures that protect the coast from erosion. Various environmental issues may arise from the construction of a seawall, including the disruption of sediment movement and transport patterns. Combined with a high construction cost, this has led to increasing use of other soft engineering coastal management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panguna Mine
The Panguna mine is a large copper mine located in Bougainville, Papua New Guinea. Panguna represents one of the largest copper reserves in Papua New Guinea and in the world, having an estimated reserve of one billion tonnes of ore copper and twelve million ounces of gold. The mine has been closed since 1989 and has ceased all production. History The discovery of vast copper ore deposits in Bougainville's Crown Prince Range led to the establishment of the copper mine in 1969 by Bougainville Copper Ltd (BCL), a subsidiary of the Australian company Conzinc Rio Tinto of Australia. The mine began production in 1972, with the support of the Papua New Guinea National Government as a 20% shareholder. In contrast to this, the Bougainvilleans received 0.5–1.25% share of the total profit. The site was at the time the world's largest open-pit copper/gold mine, generating 12% of PNG's GDP and over 45% of the nation's export revenue. Profits derived from the mine helped fund Papua New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bougainville Conflict
The Bougainville conflict, also known as the Bougainville Civil War, was a multi-layered armed conflict fought from 1988 to 1998 in the North Solomons Province of Papua New Guinea (PNG) between PNG and the secessionist forces of the Bougainville Revolutionary Army (BRA), and between the BRA and other armed groups on Bougainville. The conflict was described by Bougainvillean President John Momis as the largest conflict in Oceania since the end of World War II in 1945, with an estimated 15,000–20,000 Bougainvilleans dead, although lower estimates place the toll at around 1,000–2,000. Hostilities concluded under the Bougainville Peace Agreement in 1998. The national (PNG) government agreed to the founding of the Autonomous Bougainville Government and to certain rights and authorities that the autonomous government would have over what became known as Bougainville Province, which includes outlying small islands in addition to Bougainville Island itself. Background Bougain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Come Up (film)
''Sun Come Up'' is a 2010 documentary film on the effect of global warming on the Carteret Islands. The film showed at the 2010 Full Frame Documentary Film Festival on April 8. It was named as a nominee for the Academy Award for Best Documentary (Short Subject) at the 83rd Academy Awards on January 25, 2011, but lost to Strangers No More. References External links * ''Sun Come Up''at New Day Films New Day Films is a U.S. film distribution cooperative that primarily serves the non-theatrical market (colleges and universities, libraries, high schools, and community groups). Its filmmaker members come from across the US. The cooperative is memb ... The Love Story Behind Oscar Nominee 'Sun Come Up'NPR, February 26, 2011 2010 films American documentary films 2010 short documentary films Documentary films about global warming Films set in Papua New Guinea Kickstarter-funded documentaries 2010s American films {{climate-change-doc-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
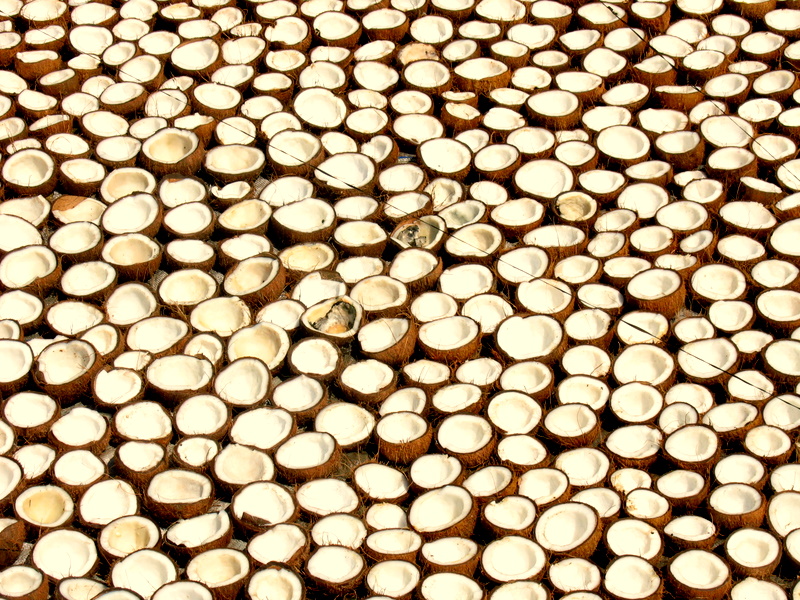
Copra
Copra (from ; ; ; ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copra is rich in lauric acid, making it an important commodity in the preparation of lauryl alcohol, soaps, fatty acids, cosmetics, etc. and thus a lucrative product for many coconut-producing countries. The palatable oil cake, known as copra cake, obtained as a residue in the production of copra oil is used in animal feeds. The ground cake is known as coconut or copra meal. Production Copra has traditionally been grated and ground, then boiled in water to extract coconut oil. It was used by Pacific island cultures and became a valuable commercial product for merchants in the South Seas and South Asia in the 1860s. Nowadays, coconut oil (70%) is extracted by crushing copra; the by-product is known as copra cake or copra meal (30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a Nut (fruit), nut. Originally native to Central Indo-Pacific, they are now ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics. The coconut tree provides food, fuel, cosmetics, folk medicine and building materials, among many other uses. The inner flesh of the mature seed, as well as the coconut milk extracted from it, forms a regular part of the diets of many people in the tropics and subtropics. Coconuts are distinct from other fruits because their endosperm contains a large quantity of an almost clear liquid, called "coconut water" or "coconut juice". Mature, ripe coconuts can be used as edible seeds, or processed for Coconut oil, oil and Coconut milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Culture of Africa, African, Oceania, Oceanic, East Asian, Southeast Asian and South Asian cultures (similar to Yam (vegetable), yams). Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Common names The English term '':wikt:taro#English, taro'' was :wikt:taro#Maori, borrowed from the Māori language when James Cook, Captain Cook first observed ''Colocasia'' plantations in New Zealand in 1769. The form ''taro'' or ''talo'' is widespread among Polynesian languages:*''talo'': taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – entry in the ''Polynesian Lexicon Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonata
Pulmonata or pulmonates is an informal group (previously an order, and before that, a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group includes many land and freshwater families, and several marine families. The taxon Pulmonata as traditionally defined was found to be polyphyletic in a molecular study per Jörger ''et al.'', dating from 2010. Pulmonata are known from the Carboniferous period to the present. Pulmonates have a single atrium and kidney, and a concentrated symmetrical nervous system. The mantle cavity is on the right side of the body, and lacks gills, instead being converted into a vascularised lung. Most species have a shell, but no operculum, although the group does also include several shell-less slugs. Pulmonates are hermaphroditic, and some groups possess love darts. Linnean taxonomy The taxonomy of this group according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Morrell
Benjamin Morrell (July 5, 1795 – ) was an American sea captain, explorer and trader who made a number of voyages, mainly to the Atlantic, the Southern Ocean and the Pacific Islands. In a ghost-written memoir, ''A Narrative of Four Voyages'', which describes his sea-going life between 1823 and 1832, Morrell included numerous claims of discovery and achievement, many of which have been disputed by geographers and historians, and in some cases have been proven false. He ended his career as a fugitive, having wrecked his ship and misappropriated parts of the salvaged cargo. Morrell had an eventful early career, running away to sea at the age of 17 and being twice captured and imprisoned by the British during the War of 1812. He subsequently sailed wikt:before the mast, before the mast for several years before being appointed as chief mate, and later as captain, of the New York sealer ''Wasp''. In 1823, he took ''Wasp'' for an extended voyage into subantarctic waters, and on his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus Gower
Admiral Sir Erasmus Gower (3 December 1742 – 21 June 1814) was a Royal Navy officer and colonial governor. Naval career Gower, aged 13, joined the Royal Navy in 1755 under the patronage of his uncle, Captain John Donkley. He was present at the Battle of Quiberon Bay under Admiral Edward Hawke, 1st Baron Hawke and served under Byron's command on from 1764 to 1766. He was promoted to lieutenant, serving with distinction under Commander Philip Carteret from 1766 to 1769. He then served in the Falkland Islands, West Indies, Mediterranean, the East and Newfoundland until 1792, when he declined a baronetcy and was knighted. In 1792, Gower was named Commander of the first British diplomatic mission to imperial China and sailed in the 64-gun HMS ''Lion''. This expedition was headed by Lord George Macartney. They were also accompanied by East Indiaman ''Hindostan'', chartered from the East India Company for the mission. Although the Macartney Embassy returned to London without ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |