|
Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero
Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero (CSRZ) is an optical line code. In CSRZ the field intensity drops to zero between consecutive bits ( RZ), and the field phase alternates by π radians between neighbouring bits, so that if the phase of the signal is e.g. 0 in even bits (bit number 2''n''), the phase in odd bit slots (bit number 2''n''+1) will be π, the phase alternation amplitude. In its standard form CSRZ is generated by a single Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM), driven by two sinusoidal waves at half the bit rate BR, and in phase opposition. This gives rise to characteristically broad pulses (duty cycle 67%). The signal format Alternate-Phase Return-to-Zero (APRZ) can be viewed as a generalisation of CSRZ in which the phase alternation can take up any value ''ΔΦ'' (and not necessarily only π) and the duty cycle is also a free parameter. CSRZ can be used to generate specific optical modulation formats, e.g. CSRZ- OOK, in which data is coded on the intensity of the signal usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Code
In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmission (telecommunications), transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are Unipolar encoding, unipolar, Polar encoding, polar, Bipolar encoding, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return-to-zero
Return-to-zero (RZ or RTZ) describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format. The "zero" between each bit is a neutral or rest condition, such as a zero amplitude in pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM), zero phase shift in phase-shift keying (PSK), or mid-frequency in frequency-shift keying (FSK). That "zero" condition is typically halfway between the significant condition representing a 1 bit and the other significant condition representing a 0 bit. Although return-to-zero (RZ) contains a provision for synchronization, it still has a DC component resulting in “baseline wander” during long strings of 0 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternate-Phase Return-to-Zero
Alternate-Phase Return-to-Zero (APRZ) is an optical line code. In APRZ the field intensity drops to zero between consecutive bits, and the field phase alternates between neighbouring bits, so that if the phase of the signal is, for example, 0 in even bits (bit number 2''n''), the phase in odd bit slots (bit number 2''n''+1) will be ''ΔΦ'', the phase alternation amplitude. Special cases Return-to-zero can be seen as a special case of APRZ in which ''ΔΦ''=0, while Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero (CSRZ) can be viewed as a special case of APRZ in which ''ΔΦ''=π (and the duty cycle is 67%, at least in the standard form of CSRZ). APRZ can be used to generate specific optical modulation formats, for example, APRZ-OOK, in which data is coded on the intensity of the signal using a binary scheme (light on=1, light off=0). APRZ is often used to designate APRZ-OOK. Characteristics The characteristic properties of an APRZ signal are those to have a spectrum similar to that of an RZ s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
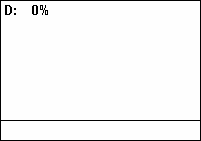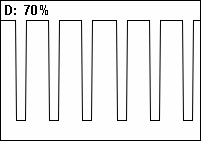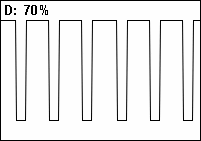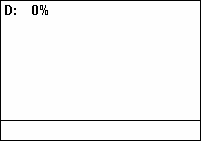
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. The duty factor for periodic signal expresses the same notion, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filter (optics)
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter. Filters mostly belong to one of two categories. The simplest, physically, is the absorptive filter; then there are interference or dichroic filters. Many optical filters are used for optical imaging and are manufactured to be transparent; some used for light sources can be translucent. Optical filters selectively transmit light in a particular range of wavelengths, that is, colours, while absorbing the remainder. They can usually pass long wavelengths only (longpass), short wavelengths only (shortpass), or a band of wavelengths, blocki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Dispersion
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum. Spectrum has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad range of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Codes
Line most often refers to: * Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity * Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * Lines (film), ''Lines'' (film), a 2016 Greek film * The Line (2017 film), ''The Line'' (2017 film) * The Line (2009 film), ''The Line'' (2009 film) * ''The Line'', a 2009 independent film by Nancy Schwartzman Podcasts * The Line (podcast), ''The Line'' (podcast), 2021 by Dan Taberski Literature * Line (comics), a term to describe a subset of comic book series by a publisher * Line (play), ''Line'' (play), by Israel Horovitz, 1967 * Line (poetry), the fundamental unit of poetic composition * Lines (poem), "Lines" (poem), an 1837 poem by Emily Brontë * The Line (memoir), ''The Line'' (memoir), by Arch and Martin Flanagan * The Line (play), ''The Line'' (play), by Timberlake Wertenbaker, 2009 Music Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |