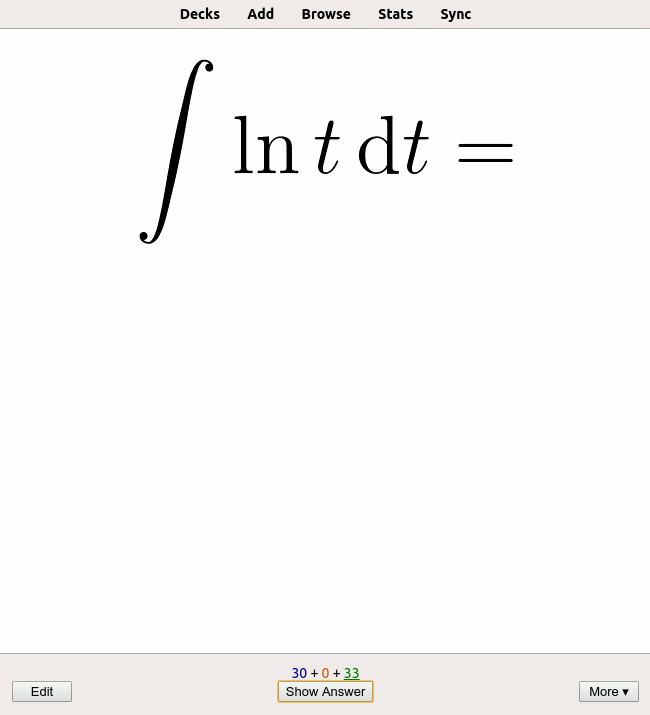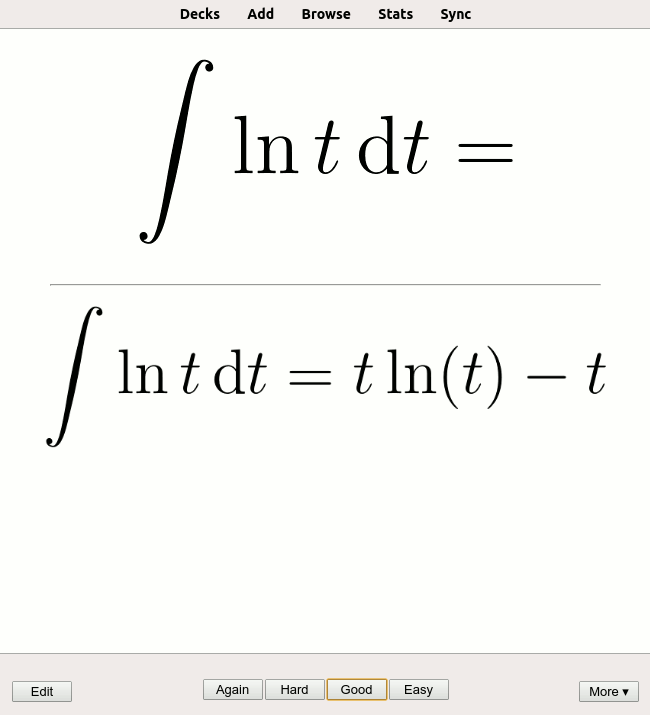|
Cambridge Mathematical Tripos
The Mathematical Tripos is the mathematics course that is taught in the Faculty of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge. Origin In its classical nineteenth-century form, the tripos was a distinctive written examination of undergraduate students of the University of Cambridge. Prior to 1824, the Mathematical Tripos was formally known as the "Senate House Examination". From about 1780 to 1909, the "Old Tripos" was distinguished by a number of features, including the publication of an order of merit of successful candidates, and the difficulty of the mathematical problems set for solution. By way of example, in 1854, the Tripos consisted of 16 papers spread over eight days, totaling 44.5 hours. The total number of questions was 211. It was divided into two parts, with Part I (the first three days) covering more elementary topics. The actual marks for the exams were never published, but there is reference to an exam in the 1860s where, out of a total possible mark of 17,000, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate House, Cambridge
The Senate House is a 1720s building of the University of Cambridge in England, used formerly for meetings of its academic senate, senate and now mainly for graduation ceremonies. Location and construction The building, which is situated in the centre of the city between King's College, Cambridge, King's and Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, Gonville and Caius Colleges, was designed by architect James Gibbs, based to an unclear extent on designs by the gentleman-architect James Burrough (architect), Sir James Burrough, and built in 1722–1730 by Gibbs in a neo-classical style using Portland stone. The ceremony to lay the first stone was performed by Thomas Crosse (priest), Thomas Crosse, then List of Vice-Chancellors of the University of Cambridge, Vice-Chancellor, on 22 June 1722.Cooper, Charles Henry (1866) "Memorials of Cambridge (Volume 3)", Cambridge: Wm Metcalfe. The site was previously used for houses, which were purchased by an act of Parliament, dated 11 June 172 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Physics
Mathematical physics is the development of mathematics, mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The ''Journal of Mathematical Physics'' defines the field as "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and for the formulation of physical theories". An alternative definition would also include those mathematics that are inspired by physics, known as physical mathematics. Scope There are several distinct branches of mathematical physics, and these roughly correspond to particular historical parts of our world. Classical mechanics Applying the techniques of mathematical physics to classical mechanics typically involves the rigorous, abstract, and advanced reformulation of Newtonian mechanics in terms of Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics (including both approaches in the presence of constraints). Both formulations are embodied in analytical mechanics and lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrangler (University Of Cambridge)
At the University of Cambridge in England, a "Wrangler" is a student who gains first-class honours in the Mathematical Tripos competition. The highest-scoring student is the Senior Wrangler, the second highest is the Second Wrangler, and so on. By contrast, the person who achieves the lowest exam marks while still earning a third-class honours degree (that is, while still earning an honours degree at all) is known as the Wooden spoon (award), wooden spoon. History Until 1909, the university made the rankings public. Since 1910, it has publicly revealed only the class of degree gained by each student. An examiner reveals the identity of the Senior Wrangler "unofficially" by tipping his hat when reading out the person's name, but other rankings are communicated to each student privately. Therefore, the names of only some 20th-century Senior Wrangler (University of Cambridge)#Senior Wranglers since 1910, Senior Wranglers (such as Crispin Nash-Williams, Christopher Budd (mathematicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theorem
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement (logic), statement that has been Mathematical proof, proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems. In mainstream mathematics, the axioms and the inference rules are commonly left implicit, and, in this case, they are almost always those of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice (ZFC), or of a less powerful theory, such as Peano arithmetic. Generally, an assertion that is explicitly called a theorem is a proved result that is not an immediate consequence of other known theorems. Moreover, many authors qualify as ''theorems'' only the most important results, and use the terms ''lemma'', ''proposition'' and ''corollary'' for less important theorems. In mathematical logic, the concepts of theorems and proofs have been formal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Mathematics And Its Applications
The Institute of Mathematics and its Applications (IMA) is the UK's chartered professional body for mathematicians and one of the UK's learned societies for mathematics (another being the London Mathematical Society). The IMA aims to advance mathematics and its applications, promote and foster research and other enquiries directed the advancement, teaching and application of mathematics, to seek to establish and maintain high standards of professional conduct for members and to seek to promote, encourage and guide the development of education and training in mathematics.Listing Charity Commission History In 1959, the need for a professional and learned body for mat ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved distinction in both poetry and mathematics. The breadth of Whewell's endeavours is his most remarkable feature. In a time of increasing specialisation, Whewell belonged in an earlier era when natural philosophers investigated widely. He published work in mechanics, physics, geology, astronomy, and economics, while also composing poetry, writing a Bridgewater Treatise, translating the works of Goethe, and writing sermons and Theology, theological tracts. In mathematics, Whewell introduced what is now called the Whewell equation, defining the shape of a curve without reference to an arbitrarily chosen coordinate system. He also organized thousands of volunteers internationally to study ocean tides, in what is now considered one of the first citizen science projects. He received the Royal Medal for this work in 1837. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptical Integral
In integral calculus, an elliptic integral is one of a number of related functions defined as the value of certain integrals, which were first studied by Giulio Fagnano and Leonhard Euler (). Their name originates from their originally arising in connection with the problem of finding the arc length of an ellipse. Modern mathematics defines an "elliptic integral" as any function which can be expressed in the form f(x) = \int_^ R \, dt, where is a rational function of its two arguments, is a polynomial of degree 3 or 4 with no repeated roots, and is a constant. In general, integrals in this form cannot be expressed in terms of elementary functions. Exceptions to this general rule are when has repeated roots, or when contains no odd powers of or if the integral is pseudo-elliptic. However, with the appropriate reduction formula, every elliptic integral can be brought into a form that involves integrals over rational functions and the three Legendre canonical forms, als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus De Morgan
Augustus De Morgan (27 June 1806 – 18 March 1871) was a British mathematician and logician. He is best known for De Morgan's laws, relating logical conjunction, disjunction, and negation, and for coining the term "mathematical induction", the underlying principles of which he formalized. De Morgan's contributions to logic are heavily used in many branches of mathematics, including set theory and probability theory, as well as other related fields such as computer science. Biography Childhood Augustus De Morgan was born in Madurai, in the Carnatic Sultanate, Carnatic region of India, in 1806. His father was Lieutenant-Colonel John De Morgan (1772–1816), who held various appointments in the service of the East India Company, and his mother, Elizabeth (née Dodson, 1776–1856), was the granddaughter of James Dodson (mathematician), James Dodson, who computed a table of anti-logarithms (inverse logarithms). Augustus De Morgan became blind in one eye within a few months of his bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rote Learning
Rote learning is a memorization technique based on repetition. The method rests on the premise that the recall of repeated material becomes faster the more one repeats it. Some of the alternatives to rote learning include meaningful learning, associative learning, spaced repetition and active learning. Versus critical thinking Rote learning is widely used in the mastery of foundational knowledge. Examples of school topics where rote learning is frequently used include phonics in reading, the periodic table in chemistry, multiplication tables in mathematics, anatomy in medicine, cases or statutes in law, basic formulae in any science, etc. By definition, rote learning eschews comprehension, so by itself it is an ineffective tool in mastering any complex subject at an advanced level. For instance, one illustration of rote learning can be observed in preparing quickly for exams, a technique which may be colloquially referred to as " cramming". Rote learning is sometimes dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism achieved the Unification (physics)#Unification of magnetism, electricity, light and related radiation, second great unification in physics, where Unification (physics)#Unification of gravity and astronomy, the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton. Maxwell was also key in the creation of statistical mechanics. With the publication of "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric force, electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. (Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |