|
CHAMP (satellite)
Challenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) was a German satellite launched July 15, 2000 from Plesetsk, Russia and was used for atmospheric and ionospheric research, as well as other geoscientific applications, such as GPS radio occultation, gravity field determination, and studying the Earth's magnetic field. CHAMP was managed by GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ) Potsdam. The spacecraft is the first application of Astrium's "Flexbus" platform; GRACE was the second. A heavily modified version flew as the GOCE mission. Spacecraft Instruments An onboard BlackJack Global Positioning System (GPS) Flight Receiver, provided by JPL, enables the use of satellite to satellite tracking for vehicle positioning. To remove the effect of external, non-gravitational forces (e.g., atmospheric drag, solar radiation pressure) the satellite features an internal 3-axis STAR accelerometer. Independent verification of orbital position is enabled by a passive Laser Retro Reflector (LRR), which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravimetry
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest. Units of measurement Gravity is usually measured in units of acceleration. In the SI system of units, the standard unit of acceleration is 1 metre per second squared (abbreviated as m/s2). Other units include the cgs gal (sometimes known as a ''galileo'', in either case with symbol Gal), which equals 1 centimetre per second squared, and the '' g'' (''g''n), equal to 9.80665 m/s2. The value of the ''g''n is defined approximately equal to the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface (although the value of ''g'' varies by location). Gravimeters An instrument used to measure gravity is known as a gravimeter. For a small body, general relativity predicts gravitational effects indistinguishable from the effects of acceleration by the equivalence pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aerospace Centre
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. DLR also acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.261 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRACE And GRACE-FO
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of its science mission in October 2017. The GRACE Follow-On (GRACE-FO) is a continuation of the mission on near-identical hardware, launched in May 2018. By measuring gravity anomalies, GRACE showed how mass is distributed around the planet and how it varies over time. Data from the GRACE satellites is an important tool for studying Earth's ocean, geology, and climate. GRACE was a collaborative endeavor involving the Center for Space Research at the University of Texas at Austin, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the German Aerospace Center and Germany's National Research Center for Geosciences, Potsdam. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory was responsible for the overall mission management under the NASA ESSP (Earth System Science Pathfinder) progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Sounding Satellites
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Ranging Satellites
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances ( collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Which Reentered In 2010
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellites Of Germany
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by propulsion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 2000
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather satellite, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, Planetary science, planetary exploration, and Space transport, transportation of Human spaceflight, humans and cargo spacecraft, cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters outer space, space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Denmark
The Technical University of Denmark ( da, Danmarks Tekniske Universitet), often simply referred to as DTU, is a polytechnic university and school of engineering. It was founded in 1829 at the initiative of Hans Christian Ørsted as Denmark's first polytechnic, and it is today ranked among Europe's leading engineering institutions. It is located in the town Kongens Lyngby, north of central Copenhagen, Denmark. Along with École Polytechnique in Paris, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Eindhoven University of Technology, Technical University of Munich and Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, DTU is a member of EuroTech Universities Alliance. History DTU was founded in 1829 as the "College of Advanced Technology" (Danish: Den Polytekniske Læreanstalt). The Physicist Hans Christian Ørsted, at that time a professor at the University of Copenhagen, was one of the driving forces behind this initiative. He was inspired by the École Polytechnique in Paris, Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
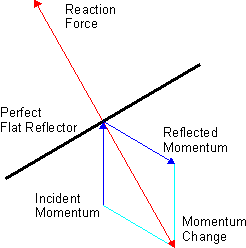
Satellite Laser Ranging
In satellite laser ranging (SLR) a global network of observation stations measures the round trip time of flight of ultrashort pulses of light to satellites equipped with retroreflectors. This provides instantaneous range measurements of millimeter level precision which can be accumulated to provide accurate measurement of orbits and a host of important scientific data. The laser pulse can also be reflected by the surface of a satellite without a retroreflector, which is used for tracking space debris. Satellite laser ranging is a proven geodesy, geodetic technique with significant potential for important contributions to scientific studies of the earth/atmosphere/ocean system. It is the most accurate technique currently available to determine the geocentric position of an Earth satellite, allowing for the precise calibration of radar altimeters and separation of long-term instrumentation drift from secular changes in ocean topography. Its ability to measure the variations ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |