|
CFU-Baso
CFU-Baso is a colony forming unit that gives rise to basophil Basophils are a type of white blood cell White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and f ...s. Some sources use the term "CFU-Bas". References Colony forming units Blood cells {{Cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the (midgestational) aorta-gonad-mesonephros region, through a process known as endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. In adults, haematopoiesis occurs in the red bone marrow, in the core of most bones. The red bone marrow is derived from the layer of the embryo called the mesoderm. Haematopoiesis is the process by which all mature blood cells are produced. It must balance enormous production needs (the average person produces more than 500 billion blood cells every day) with the need to regulate the number of each blood cell type in the circulation. In vertebrates, the vast majority of hematopoiesis occurs in the bone marrow and is derived from a limited number of hematopoietic stem cells that are multipotent and capable of extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
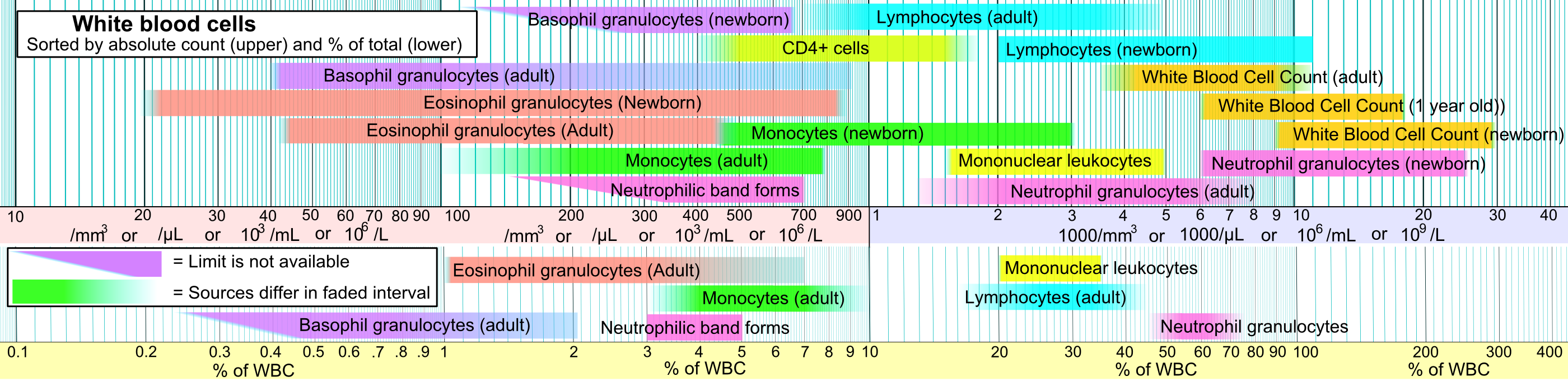
Basophil
Basophils are a type of white blood cell White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera .... Basophils are the least common type of granulocyte, representing about 0.5% to 1% of circulating white blood cells. They are the largest type of granulocyte. They are responsible for inflammatory reactions during immune response, as well as in the formation of acute and chronic allergic diseases, including anaphylaxis, asthma, atopic dermatitis and Hay Fever, hay fever. They also produce compounds that coordinate immune responses, including histamine and serotonin that induce inflammation, and heparin that prevents Coagulation, blood clotting, although there are less than that found in mast cell granules. Mast cells were once thought to be basophils that migrated from the blood into their r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Forming Units
In microbiology, a colony-forming unit (CFU, cfu or Cfu) is a unit which estimates the number of microbial cells (bacteria, fungi, viruses etc.) in a sample that are viable, able to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions. Counting with colony-forming units requires culturing the microbes and counts only viable cells, in contrast with microscopic examination which counts all cells, living or dead. The visual appearance of a colony in a cell culture requires significant growth, and when counting colonies, it is uncertain if the colony arose from a single cell or a group of cells. Expressing results as colony-forming units reflects this uncertainty. Theory The purpose of plate counting is to estimate the number of cells present based on their ability to give rise to colonies under specific conditions of temperature, time, and nutrient medium. Theoretically, one viable cell can give rise to a colony through replication. However, solitary cells are the exception i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |