|
CB2 Receptor
The cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), is a G protein-coupled receptor from the cannabinoid receptor family that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR2'' gene. It is closely related to the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), which is largely responsible for the efficacy of endocannabinoid-mediated presynaptic-inhibition, the psychoactive properties of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active agent in cannabis, and other phytocannabinoids (plant cannabinoids). The principal endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor is 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). CB2 was cloned in 1993 by a research group from Cambridge looking for a second cannabinoid receptor that could explain the pharmacological properties of tetrahydrocannabinol. The receptor was identified among cDNAs based on its similarity in amino-acid sequence to the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) receptor, discovered in 1990. The discovery of this receptor helped provide a molecular explanation for the established effects of cannabinoids on the immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK-ERK Pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway (also known as the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway) is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. The signal starts when a signaling molecule binds to the receptor on the cell surface and ends when the DNA in the nucleus expresses a protein and produces some change in the cell, such as cell division. The pathway includes many proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), originally called extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), which communicate by adding phosphate groups to a neighboring protein ( phosphorylating it), thereby acting as an "on" or "off" switch. When one of the proteins in the pathway is mutated, it can become stuck in the "on" or "off" position, a necessary step in the development of many cancers. In fact, components of the MAPK/ERK pathway were first discovered in cancer cells, and drugs that reverse the "on" or "off" switch are be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and the ribosome creates the protein utilizing amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
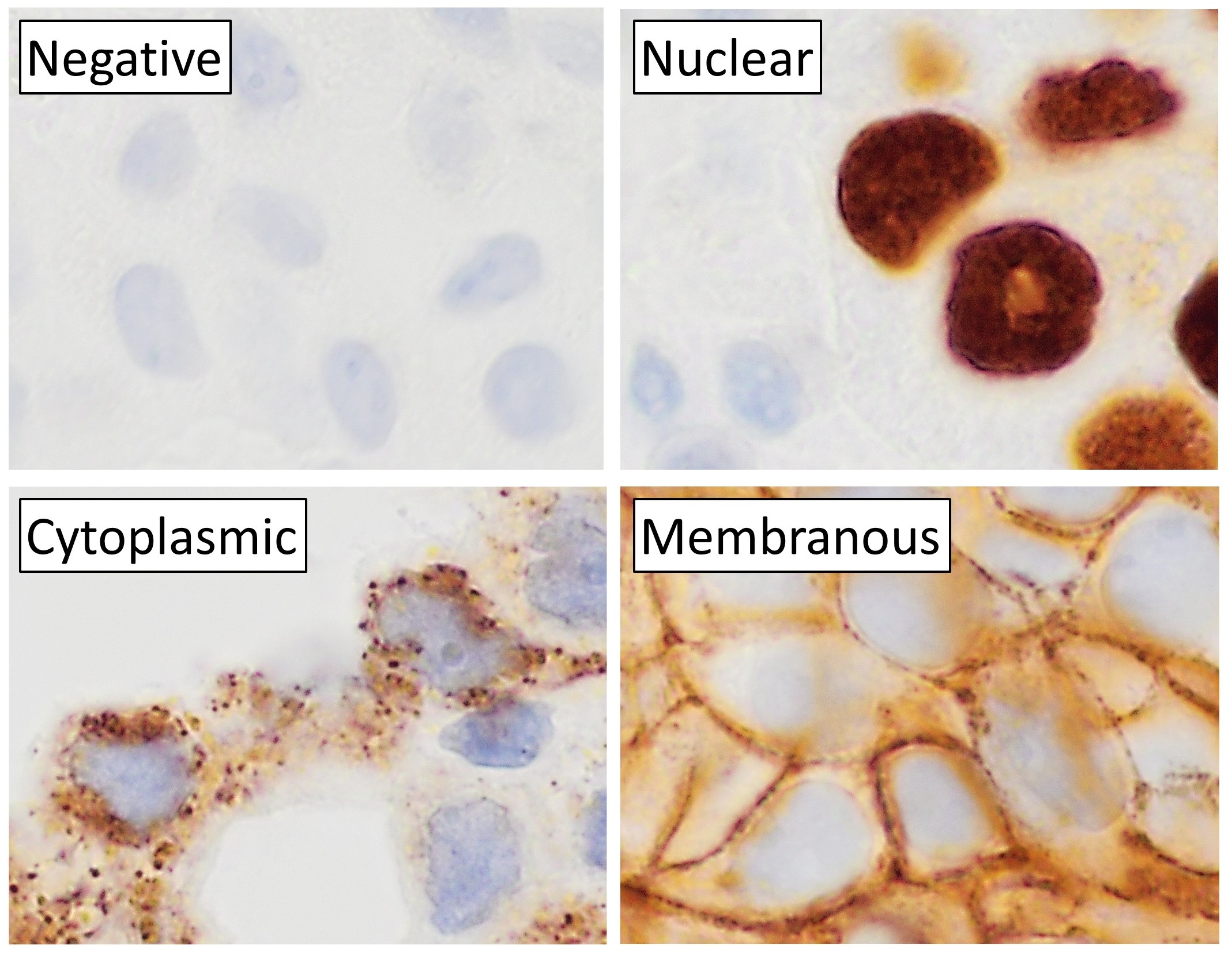
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Selectivity
Functional selectivity (or agonist trafficking, biased agonism, biased signaling, ligand bias, and differential engagement) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a reference ligand (often the endogenous hormone or peptide) at the same receptor. Functional selectivity can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways. To which degree each pathway is activated thus depends on which ligand binds to the receptor. Functional selectivity, or biased signaling, is most extensively characterized at G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). A number of biased agonists, such as those at muscarinic M2 receptors tested as analgesics or antiproliferative drugs, or those at opioid receptors that mediate pain, show potential at various receptor families to increase beneficial properties while reducing side effects. For example, pre-clinical studies with G protein biased agonists at the μ-opioid receptor show equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-arachidonoyl-dopamine
''N''-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an endocannabinoid that acts as an agonist of the CB1 receptor and the transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) ion channel. NADA was first described as a putative endocannabinoid (agonist for the CB1 receptor) in 2000 and was subsequently identified as an endovanilloid (agonist for TRPV1) in 2002. NADA is an endogenous arachidonic acid based lipid found in the brain of rats, with especially high concentrations in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and striatum. It activates the TRPV1 channel with an EC50 of approximately of 50 nM which makes it the putative endogenous Endogeny, in biology, refers to the property of originating or developing from within an organism, tissue, or cell. For example, ''endogenous substances'', and ''endogenous processes'' are those that originate within a living system (e.g. an ... TRPV1 agonist. In mice, NADA was shown to induce the tetrad of physiological paradigms associated with cannabinoids: hypothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virodhamine
Virodhamine (''O''-arachidonoyl ethanolamine; O-AEA) is an endocannabinoid and a nonclassic eicosanoid, derived from arachidonic acid. ''O''-Arachidonoyl ethanolamine is arachidonic acid and ethanolamine joined by an ester linkage, the opposite of the amide linkage found in anandamide. Based on this opposite orientation, the molecule was named virodhamine from the Sanskrit word ''virodha'', which means opposition. It acts as an antagonist of the CB1 receptor and agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ... of the CB2 receptor. Concentrations of virodhamine in the human hippocampus are similar to those of anandamide, but they are 2- to 9-fold higher in peripheral tissues that express CB2. Virodhamine lowers body temperature in mice, demonstrating cannabinoid act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-arachidonoyl Glycerol
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is an endocannabinoid, an endogenous agonist of the CB1 receptor and the primary endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor. It is an ester formed from the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid and glycerol. It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system, with cannabinoid neuromodulatory effects. It has been found in maternal bovine and human milk. The chemical was first described in 1994–1995, although it had been discovered some time before that. The activities of phospholipase C (PLC) and diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) mediate its formation. 2-AG is synthesized from arachidonic acid-containing diacylglycerol (DAG). Occurrence 2-AG, unlike anandamide (another endocannabinoid), is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system; it is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in mouse and rat brain (~5–10 nmol/g tissue). Detection of 2-AG in brain tissue is complicated by the relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachidonoylethanolamine
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ''ananda'' ( आनन्द), meaning "joy, bliss, delight," plus amide. Anandamide, the first discovered endocannabinoid, engages with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the same cannabinoid receptors that THC found in cannabis acts on. Anandamide can be found within tissues in a wide range of animals. It has also been found in plants, such as the cacao tree. Anandamide is derived from the non-oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid. It is synthesized from ''N''-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways. It is degraded primarily by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme, which converts anandamide into ethanolamine and arachidonic acid. As such, inhibitors of FAAH lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, quinolines, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |