|
CARE Principles For Indigenous Data Governance
The CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance are a set of principles intended to guide open data projects in engaging Indigenous Peoples rights and interests. CARE was created in 2019 by the International Indigenous Data Sovereignty Interest Group, a group that is a part of the Research Data Alliance. It outlines collective rights related to open data in the context of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples and Indigenous data sovereignty. CARE is an acronym which stands for Collective Benefit, Authority to Control, Responsibility, Ethics. The CARE Principles are 'people and purpose-oriented, reflecting the crucial role of data in advancing Indigenous innovation and self-determination', and intended as a complement to the data-oriented perspective of other standards such as FAIR data (findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable). The CARE principles have been embedded into the Beta version of Standardised Data on Initiatives (STARDIT). CARE pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Open Data
Open data are data that are openly accessible, exploitable, editable and shareable by anyone for any purpose. Open data are generally licensed under an open license. The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other "open(-source)" movements such as open-source software, open-source hardware, open content, open specifications, open education, open educational resources, open government, open knowledge, open access (publishing), open access, open science, and the open web. The growth of the open data movement is paralleled by a rise in intellectual property rights. The philosophy behind open data has been long established (for example in the Merton thesis, Mertonian tradition of science), but the term "open data" itself is recent, gaining popularity with the rise of the Internet and World Wide Web and, especially, with the launch of open-data government initiatives Data.gov, Data.gov.uk and Data.gov.in. Open data can be linked data—referred to as linked open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Indigenous Peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model. Estimates of the population of Indigenous peoples range from 250 million to 600 million. There are some 5,000 distinct Indigenous peoples spread across every inhabited climate zone and inhabited continent of the world. Most Indigenous peoples are in a minority in the state or traditional territory they inhabit and have experienced domination by other groups, especially non-Indigenous peoples. Although many Indigenous peoples have experienced colonization by settlers from European nations, Indigenous identity is not determined by Western colonization. The rights of Indigenous peoples are outlined in national legislation, treaties and international law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Research Data Alliance
The Research Data Alliance (RDA) is a global research community-driven organization started in 2013 by the European Commission, the US National Science Foundation and National Institute of Standards and Technology, and the Australian Department of Industry, Innovation, Climate Change, Science, Research and Tertiary Education, Department of Innovation. Its mission is to build the social and technical bridges to enable open sharing and re-use of data.Research Data Alliance (2018"About RDA" Web Page. Accessed 2018-04-27 The RDA vision is researchers and innovators openly sharing and resuing data across technologies, disciplines, and countries to address the grand challenges of society. In its initial years, the RDA was major recipient of support in the form of grants from its constituent members' governments. Since 2017, the RDA is sustained by its Organisational and Regional members. As of March 2025, the RDA has over 15,000 individual members from over 150 countries.Research Data A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
United Nations Declaration On The Rights Of Indigenous Peoples
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film * ''The United'' (film), an unreleased Arabic-language film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe * "United (Who We Are)", a song by XO-IQ, featured in the television se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty means that data generated within a country’s borders is governed by that nation’s laws and regulatory frameworks; this ensures local control over data access, storage, and usage. In other words, a country is able to control and access the data that is generated in its territories. .An example of a nation's data sovereignty policy would be Australia’s Privacy Act 1988, which established the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) that regulate the handling of personal information by government agencies and private sector organizations. The APP contains 13 principles for how all personal or organizational data in Australia is meant to be kept. For many countries, the issue of data sovereignty is presented as an issue of national security with concerns over being able to protect citizens' personal data. Data can be used to help improve medical care, reinforce national security as well as have a positive impact on many economic and social infrastructures but may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage. Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law, binding, as such, on the United Nations as an authoritative interpretation of the Charter of the United Nations, Charter's norms. The principle does not state how the decision is to be made, nor what the outcome should be (whether independence, federation, protectorate, protection, some form of autonomy or full Cultural assimilation, assimilation), and the right of self-determination does not necessarily include a right to an independent state for every ethnic group within a former colonial territory. Further, no right to secession is recognized under international law. The concept emerged with the rise of nationalism in the 19th century and came into prominent use in the 1860s, spreading rapidly thereafter. During and after World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
FAIR Data
FAIR data is data which meets the FAIR principles of findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability (FAIR). The acronym and principles were defined in a March 2016 paper in the journal '' Scientific Data'' by a consortium of scientists and organizations. The FAIR principles emphasize machine-actionability (i.e., the capacity of computational systems to find, access, interoperate, and reuse data with none or minimal human intervention) because humans increasingly rely on computational support to deal with data as a result of the increase in the volume, complexity, and rate of production of data. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License The abbreviation is sometimes used to indicate that the dataset or database in question complies with the FAIR principles and also carries an explicit data‑capable open license. FAIR principles published by GO FAIR Acceptance and implementation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
First Nations Principles Of OCAP
The First Nations principles of OCAP® establish an Indigenous data governance standard for how First Nations' data and information should be collected, protected, used, and shared. OCAP® is an acronym for the principles of ownership, control, access, and possession. The principles were established in 1998 by Canadian First Nations leadership and are a trademark of the Canadian non-profit the First Nations Information Governance Centre (FNIGC). OCAP® The OCAP® principles are a set of standards for First Nations' information governance which are intended to support First Nations' path to data sovereignty. OCAP® principles also apply when conducting research using First Nations' data, particularly informing data collection and management. Ownership refers to the relationship of First Nations to their cultural knowledge, data, and information. This principle states that a community or group owns information collectively in the same way that an individual owns their personal info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty means that data generated within a country’s borders is governed by that nation’s laws and regulatory frameworks; this ensures local control over data access, storage, and usage. In other words, a country is able to control and access the data that is generated in its territories. .An example of a nation's data sovereignty policy would be Australia’s Privacy Act 1988, which established the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) that regulate the handling of personal information by government agencies and private sector organizations. The APP contains 13 principles for how all personal or organizational data in Australia is meant to be kept. For many countries, the issue of data sovereignty is presented as an issue of national security with concerns over being able to protect citizens' personal data. Data can be used to help improve medical care, reinforce national security as well as have a positive impact on many economic and social infrastructures but may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
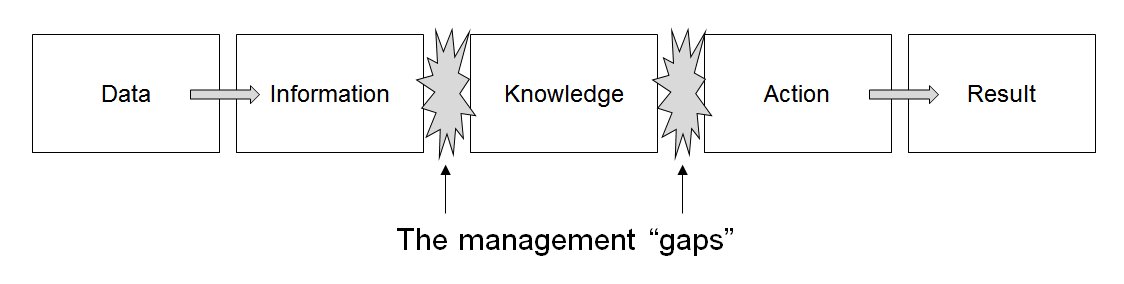 |
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making. Concept The concept of data management emerged alongside the evolution of computing technology. In the 1950s, as computers became more prevalent, organizations began to grapple with the challenge of organizing and storing data efficiently. Early methods relied on punch cards and manual sorting, which were labor-intensive and prone to errors. The introduction of database management systems in the 1970s marked a significant milestone, enabling structured storage and retrieval of data. By the 1980s, relational database models revolutionized data management, emphasizing the importance of data as an asset and fostering a data-centric mindset in business. This era also saw the rise of data governance practices, which prioritized the organization and regulation of data to ensure quality and complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |