|
C.E. Hooper
The C. E. Hooper Company was an American company which measured radio and television ratings during the Golden Age of Radio. Founded in 1934 by Claude E. Hooper (1898–1954), the company provided information on the most popular radio shows of the era. Claude E. Hooper became well known for his radio audience measurement systems, Hooper Ratings or "Hooperatings". Before beginning work in radio measurement, Hooper was an auditor of magazine circulation. Hooper worked within the market research organization of Daniel Starch until 1934, when he left to start a research company with colleague Montgomery Clark, Clark-Hooper. In the fall of 1934, the company launched syndicated radio measurement services in 16 cities. Clark left the business in 1938 and Hooper continued the firm as C. E. Hooper, Inc. The survey method employed by Hooper was designed with the help of George Gallup (see Gallup Poll), whose input Hooper later acknowledged as key. It differed from the method being used by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. The medium is capable of more than "radio broadcasting", which refers to an audio signal sent to radio receivers. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
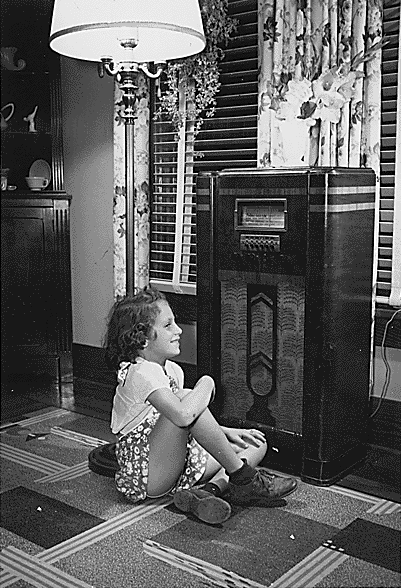
Golden Age Of Radio
The Golden Age of Radio, also known as the old-time radio (OTR) era, was an era of radio in the United States where it was the dominant electronic home entertainment medium. It began with the birth of commercial radio broadcasting in the early 1920s and lasted through the 1950s, when television superseded radio as the medium of choice for scripted programming, variety and dramatic shows. Radio was the first broadcast medium, and during this period people regularly tuned in to their favorite radio programs, and families gathered to listen to the home radio in the evening. According to a 1947 C. E. Hooper survey, 82 out of 100 Americans were found to be radio listeners. A variety of new entertainment formats and genres were created for the new medium, many of which later migrated to television: radio plays, mystery serials, soap operas, quiz shows, talent shows, daytime and evening variety hours, situation comedies, play-by-play sports, children's shows, cooking show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Starch
Daniel Starch (1883–1979) was an American psychologist and marketing researcher. He is considered to be one of the pioneers of marketing and consumer research in the early 20th century. Life Starch received a BS in mathematics and psychology from Morningside College in Iowa. After that, he moved for postgraduation studies to the University of Iowa, where he completed his PhD in psychology in 1906. The advisor of his thesis was Charles E. Seashore. After that, he worked briefly as a lecturer in Iowa and then went on to teach at Wellesley College in Massachusetts while pursuing further studies at Harvard University. In 1908, he became a professor at the University of Wisconsin A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ... where he stayed until 1919. From 1920 to 1926 he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gallup
George Horace Gallup (November 18, 1901 – July 26, 1984) was an American pioneer of survey sampling techniques and inventor of the Gallup poll, a statistics, statistically-based survey sampling, survey sampled measure of opinion polls, public opinion. Life and career George Gallup, Jr., was born in Jefferson, Iowa, the son of Nettie Quella (Davenport) and George Henry Gallup, a dairy farmer. As a teen, "Ted" would deliver milk and used his earnings to start a newspaper at his high school. He attended the University of Iowa, earning his B.A. in 1923, his M.A. in 1925 and his Ph.D. in 1928. While there he was a member of the Iowa Beta chapter of the Sigma Alpha Epsilon fraternity, and edited of ''The Daily Iowan'', the campus newspaper. He then moved first to Des Moines, Iowa, where he served until 1931 as head of the Department of Journalism at Drake University, then to Evanston, Illinois, as a professor of journalism and advertising at Northwestern University. He moved t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallup Poll
Gallup, Inc. is an American multinational analytics and advisory company based in Washington, D.C. Founded by George Gallup in 1935, the company became known for its public opinion polls conducted worldwide. Gallup provides analytics and management consulting to organizations globally. In addition the company offers educational consulting, the CliftonStrengths assessment and associated products, and business and management books published by its Gallup Press unit. Organization Gallup is a private employee-owned company based in Washington, D.C., founded by George Gallup in 1939. Headquartered in The Gallup Building, it maintains between 30 and 40 offices globally, in locations including in New York City, London, Berlin, Sydney, Singapore, and Abu Dhabi, and has approximately 1,500 employees. In 2022, Jon Clifton became Gallup's CEO, replacing his father, Jim Clifton, who had been the CEO since 1998. Gallup, Inc. has no affiliation with Gallup International, a Swiss-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACNielsen
NIQ (also known as NielsenIQ, formerly known as ACNielsen or AC Nielsen) is a global marketing research firm, with worldwide headquarters in Chicago, Illinois, United States. The company has approximately 30,000 employees and operates in more than 100 countries. NIQ acquired German market research firm GfK in 2023. Until March 2021, it was a part of Nielsen Holdings. Nielsen Holdings divested its consumer intelligence (by then known as NielsenIQ) business to private equity firm Advent International. The business later rebranded to NIQ. Activities A market research tool is the Homescan program where sample members track and report all grocery and retail purchases, allowing purchasing patterns to be related to household demographics. Homescan covers several countries including Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 2004, ACNielsen chose the CipherLab CPT-8001 as its data collection terminal for the Homescan program throughout Asia. The Homescan pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossley Ratings
The Crossley ratings (or Crossleys) were an audience measurement system created to determine the audience size of radio broadcasts beginning in 1930. Developed by Archibald Crossley, the ratings were generated using information collected by telephone surveys to random homes. In 1930, Crossley spearheaded the formation of the Cooperative Analysis of Broadcasting (CAB). The first national ratings service, CAB was supported by subscription and was at first available only to advertisers. Crossley's method of data collection essentially consisted of calling random households in selected cities and asking the respondent to recall what radio programs had been listened to at an earlier point: the previous day in Crossley's first surveys, later modified to a few hours earlier. The survey also divided the day into four listening periods (later known as dayparts), thus uncovering the fact that most radio listening at the time occurred in the evenings. In the industry, the method was known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Price (cartoonist)
George Price (June 9, 1901 – January 12, 1995) was an American cartoonist who was born in Fort Lee, New Jersey. After doing advertising artwork in his youth, Price started doing cartoons for ''The New Yorker'' magazine in 1929. He continued contributing to the ''New Yorker'' well into his eighties, displaying a talent for both graphic innovation (many of his cartoons consisted of a single, unending line) and for a wit that somehow combined the small issues of domestic life with a topical sensibility. Born on June 9, 1901, in the Coytesville section of Fort Lee, New Jersey, Price lived in nearby Tenafly and died on January 12, 1995, at Englewood Hospital and Medical Center.Collins, Glenn"George Price, 93, Cartoonist of Oddities, Dies" ''The New York Times ''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. It was founded on February 21, 1925, by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a reporter for ''The New York Times''. Together with entrepreneur Raoul H. Fleischmann, they established the F-R Publishing Company and set up the magazine's first office in Manhattan. Ross remained the editor until his death in 1951, shaping the magazine's editorial tone and standards. ''The New Yorker''s fact-checking operation is widely recognized among journalists as one of its strengths. Although its reviews and events listings often focused on the Culture of New York City, cultural life of New York City, ''The New Yorker'' gained a reputation for publishing serious essays, long-form journalism, well-regarded fiction, and humor for a national and international audience, including work by writers such as Truman Capote, Vladimir Nabokov, and Alice Munro. In the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidecar
A sidecar is a one-wheeled device attached to the side of a motorcycle, Scooter (motorcycle), scooter, or bicycle, making the whole a three-wheeled vehicle. The combination of a motorcycle with a sidecar is sometimes called a ''rig'', ''outfit'', or ''hack''. History Jean Bertoux, a French army officer, secured a prize offered by a French newspaper in 1893 for the best method of carrying a passenger on a bicycle. The sidecar wheel was mounted on the same lateral plane as the bicycle's rear and was supported by a triangulation of tubes from the bicycle. A sprung seat with back rest was mounted above the cross-member and a footboard hung below. A sidecar appeared in a cartoon by George Moore in the January 7, 1903, issue of the British newspaper ''Motor Cycling (magazine), Motor Cycling''. Three weeks later, a provisional patent was granted to Mr. W. J. Graham of Graham Brothers, Enfield, Middlesex. He partnered with Jonathan A. Kahn to begin production. One of Britain's oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Morgan (humorist)
Henry Morgan (born Henry Lerner von Ost Jr.; March 31, 1915 – May 19, 1994) was an American humorist. He first became familiar to radio audiences in the 1930s and 1940s as a barbed but often self-deprecating satirist. In the 1950s and later he was a regular and cantankerous panelist on the game show '' I've Got a Secret'' as well as other game and talk shows. Early life and education Morgan's parents divorced when he and his brother, Roger, were young. He grew up in Washington Heights, Manhattan, attended the High School of Commerce for two years, then went to the Harrisburg Academy in Pennsylvania, where he graduated in 1931. Radio Morgan began his radio career as a page at New York City station WMCA in 1932, after which he held a number of radio jobs, including announcing. He strenuously objected to the professional name Morgan but was told that his birth name of von Ost was exotic and difficult to pronounce despite the fame of successful announcers Harry von Zell and West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |