|
Burgundofaro
Saint Faro (or Burgundofaro; died 675 AD), Count of Guînes, was bishop of Meaux. The family to which Faro belonged is known as the Faronids and is named after him. He is canonized as a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church. History Burgundofaro was of an ancient noble Burgundian family. His father, Ageneric, was one of the principal lords at the Court of Theodebert II.Monks of Ramsgate. "Faro". ''Book of Saints'' 1921. CatholicSaints.Info. 23 February 2013 His brothers were , count of Guines, |
Bishop Of Meaux
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Meaux (Latin: ''Dioecesis Meldensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Meaux'') is a diocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in France. The diocese comprises the entire department of Seine-et-Marne. It was suffragan of the Archdiocese of Sens until 1622, and subsequently of Archdiocese of Paris. History Creation The present Diocese of Meaux is made up of the greater part of the former Diocese of Meaux, a large part of the former Diocese of Sens, a part of the former Diocese of Paris, and a few parishes of the former Dioceses of Troyes, Soissons and Senlis. Hildegar, who lived in the ninth century, says in his "Life of St. Faro" (Burgundofaro), that this bishop was the twentieth since St. Denis. According to the tradition accepted by Hildegaire, St. Denis was the first bishop of Meaux, and was succeeded by his disciple Saint Saintin, who in turn was succeeded by St. Antoninus; and another saint, named Rigomer, occupied the See of Meaux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Guînes
The County of Guînes, was a Flemish fief and later French fief in the Middle Ages. The county was split from the County of Boulogne in about 988. Counts *?-c.965 - Siegfried, Count of Guînes **Although he never seemed to be formally designated as Count, he is historically referred to as such. *c.965-? - Ardolf, Count of Guînes * Raoul, Count of Guînes (son of Ardolf), also known as Ralph or Rodolphe * Eustace, Count of Guînes (son of Raoul) * Baldwin I, Count of Guînes (son of Eustace), also known as Baudouin * Robert Manasses, Count of Guînes (son of Baldwin I) *1138-1146 - Aubrey de Vere - jure exoris *?-1169 - Arnoul I, Count de Guînes (son of Gisela of Guînes, daughter of Baldwin I) *1169-1205 - Baldwin II, Count of Guînes *1205-1220 - Arnold II of Guînes *1220-1244 - Baldwin III, Count of Guînes *1244-? - Arnould III, Count of Guînes * Baldwin IV, Count of Guînes *1294–1302 - John II of Brienne, Count of Guînes *1302–1344 - Raoul I of Brienne, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Frankish Saints
The 7th century is the period from 601 (DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
675 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 675 ( DCLXXV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 675 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Europe * King Childeric II is murdered by a band of dissatisfied Neustrians, along with his wife Bilichild and 5-year-old son Dagobert, while hunting in the forest of Livry (present-day Lognes) near Chelles. * Theuderic III retakes the throne of his elder brother Childeric II. He inherits the Frankish kingdoms of Neustria and Burgundy. * Clovis III, an illegitimate son of Chlothar III, is proclaimed king of Austrasia by the Austrasian nobles. Britain * King Wulfhere of Mercia dies after a 17-year reign, in which he has extended his sway over much of England south of the Humber River, including Essex, Surrey, and part of Wessex north of the Thames. Wul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishops Of Meaux
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibility by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Burgundian Bishops
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Fiacre
Saint Fiacre ( ga, Fiachra, la, Fiacrius) is the name of three different Irish saints, the most famous of which is Saint Fiacre of Breuil (c. AD 600 – 18 August 670), the Catholic priest, abbot, hermit, and gardener of the seventh century who was famous for his sanctity and skill in curing infirmities. He emigrated from his native Ireland to France, where he constructed for himself a hermitage together with a vegetable and herb garden, oratory, and hospice for travellers. He is the patron saint of gardeners. Saint Fiacre of Breuil Name is an ancient pre- Christian, Irish name. It has been interpreted to denote "battle king" or to derive from ("raven"). The name is found in ancient Irish folklore and stories such as the '' Children of Lir''. The appellation "of Breuil" can in present times be misleading: the site of the hermitage, garden, oratory, and hospice of Saint Fiacre was in the place denominated "Brogillum" in ancient times and later renamed "Breuil", for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gormond Et Isembart
''Gormond et Isembart'' (English: "Gormond and Isembart") is an Old French ''chanson de geste'' from the second half of the eleventh or first half of the twelfth century.Hasenohr, 554-555.Holmes, 90-92. Along with ''The Song of Roland'' and the '' Chanson de Guillaume'', it is one of the three ''chansons de geste'' whose composition incontestably dates from before 1150;Hasenohr, 239. it may be slightly younger than ''The Song of Roland'' and, according to one expert, may date from as early as 1068. The poem tells the story of a rebellious young French lord, Isembart, who allies himself with a Saracen king, Gormond, renounces his Christianity, and battles the French king. The poem is sometimes grouped with the '' Geste de Doon de Mayence'' or "rebellious vassal cycle" of ''chansons de geste''. The text The extant work only survives in a fragment (two parchment sheets that had been used as a binding of a book) of 661 octosyllable (unusual for a ''chanson de geste'') verses in asson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wissant
Wissant (; from nl, Witzand, lang, “white sand”) is a seaside commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. Geography Wissant is a fishing port and farming village located approximately north of Boulogne, west-southwest of Calais, southeast of Dover, west-southwest of Dunkirk, from the Belgian coast, north of Le Havre, northeast of Brest, and north of Paris, at the junction of the D238 and the D940 roads, on the English Channel coast. History Located at the eastern end of a lagoon formed by a storm-breach of the coastal dunes, probably in the mid-10th century, Wissant has been a fishing village for a millennium: along with Audresselles it is the last fishing village in France to use a traditional method of fishing using a wooden boat called a '' flobart'' and was in the Middle Ages a major port for embarkation for England: In a mid-11th century ''Life of St. Vulganius'', Wissant was specified, probably anachronistically, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
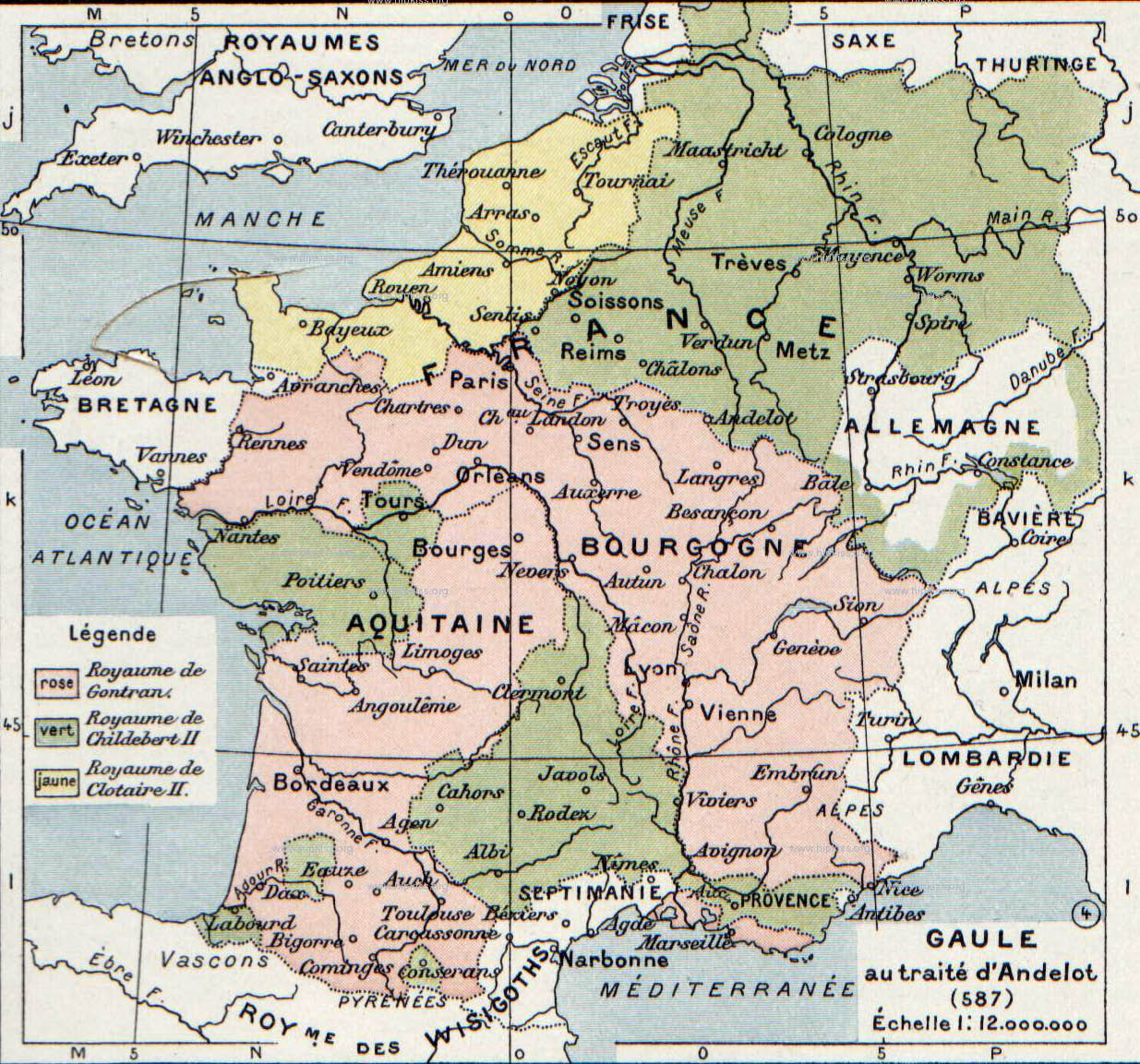
Clotaire II
Chlothar II, sometime called "the Young" (French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629), was king of Neustria and king of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, Neustria was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution in an especially brutal manner in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing erosion of royal power to the French nobility and the church against a backdrop of feuding among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodobert II
Theudebert II () (c.585-612), King of Austrasia (595–612 AD), was the son and heir of Childebert II. He received the kingdom of Austrasia plus the cities (''civitates'') of Poitiers, Tours, Le Puy-en-Velay, Bordeaux, and Châteaudun, as well as the Champagne, the Auvergne, and Transjurane Alemannia. During his early years, his grandmother Brunhilda ruled for Theudebert and his brother Theuderic II, who had received the realm of Burgundy. After the two brothers reached adulthood, they were often at war, with Brunhilda siding with Theuderic. In 599, Theuderic defeated Theudebert at Sens, but then the two brothers allied against their cousin Chlothar II and defeated him at Dormelles (near Montereau), thereby laying their hands on a great portion of Neustria (600–604). At this point, however, the two brothers took up arms against each other; Theuderic defeated Theudebert at Étampes. In 605, Theudebert refused to aid his brother whose kingdom was invaded by Clothar II. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |