|
Brasilodontidae
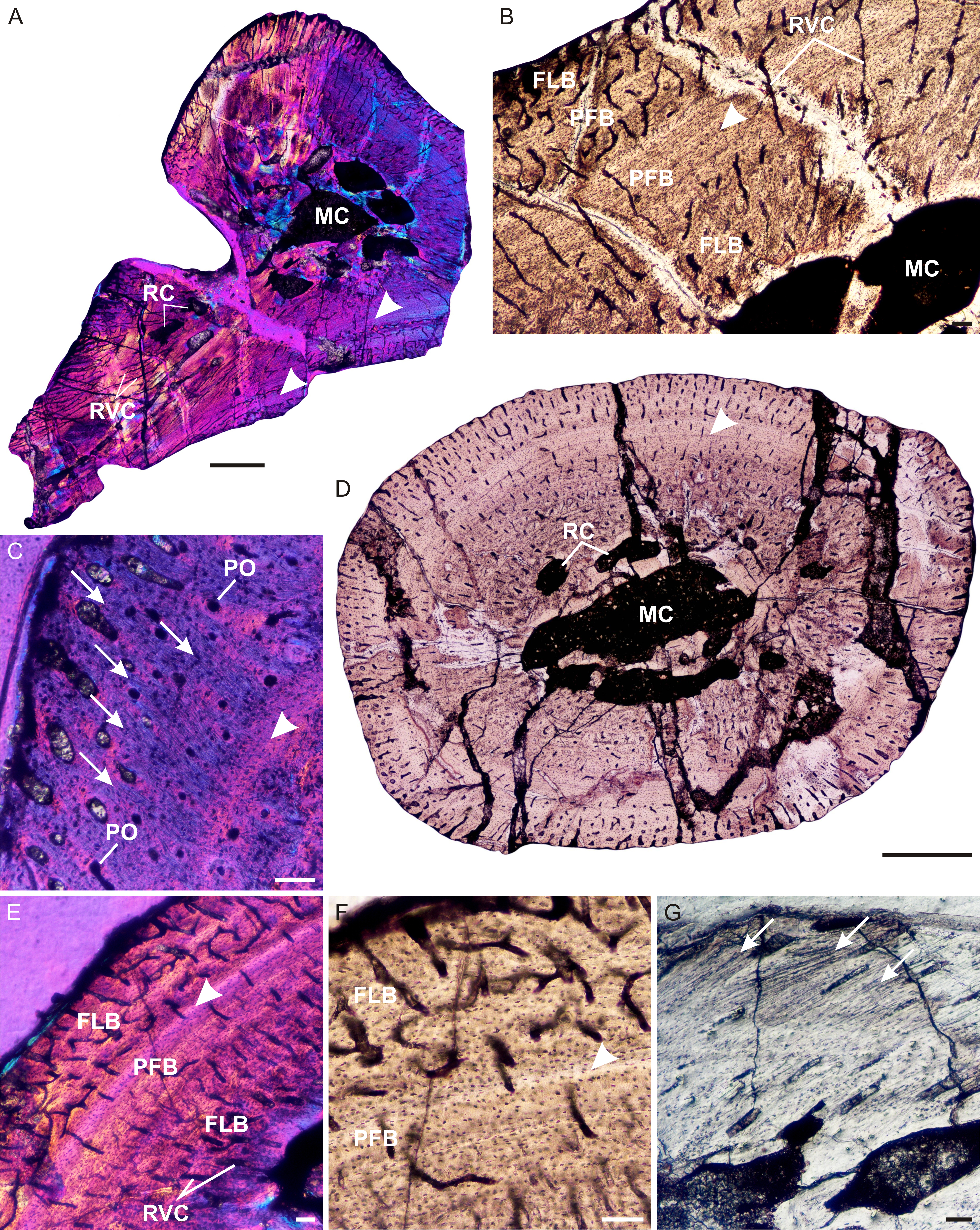
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at around . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. Discovery and naming The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilitherium
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at around . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. Discovery and naming The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilodontidae
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at around . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. Discovery and naming The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilodon Localities
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at around . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. Discovery and naming The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicynodon
''Brasilodon'' ("tooth from Brazil") is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of ''Brasilodon'' has been estimated at around . Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''B. quadrangularis''. ''Brasilodon'' belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, ''Brasilitherium'' and ''Minicynodon'', are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Brasilodon''. Discovery and naming The first three specimens referred to ''Brasilodon quadrangularis'' were found at the Linha São Luiz site, a quarry near the town of Faxinal do Soturno in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The rocks where ''Brasilodon'' was found belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynodont
The cynodonts () (clade Cynodontia) are a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts had a wide variety of lifestyles, including carnivory and herbivory. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extinct ancestors and close relatives, having evolved from advanced probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. All other cynodont lines went extinct, with the last known non-mammalian cynodont group, the Tritylodontidae, having its youngest records in the Early Cretaceous. Description Early cynodonts have many of the skeletal characteristics of mammals. The teeth were fully differentiated and the braincase bulged at the back of the head. Outside of some crown-group mammals (notably the therians), all cynodonts probably laid eggs. The temporal fenestrae were much larger than those of their ancestors, and the widening of the zygomatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prozostrodon
''Prozostrodon'' is an extinct genus of advanced cynodonts that was closely related to the ancestors of mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated middle to late Triassic. It was originally described as a species of ''Thrinaxodon'' and was probably fairly similar to that genus in overall build. The holotype has a skull length of 6.7 cm, indicating the whole animal may have been the size of a cat, though there is some doubt as to whether the find represents an adult individual. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a small carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey. Later analysis indicated ''Prozostrodon'' was more closely related to the mammals than to the ''Thrinaxodon'' species, and it was given its own genus. Cladistic analysis indicates its closest relatives gave rise to the first mammaliaforms and therefore to the crown group mammals. The holotype of ''Prozostrodon'' was found in the Geopark of Paleorrota, Santa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Below the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptionally strong jaw muscles. The sagittal crest serves primarily for attachment of the temporalis muscle, which is one of the main chewing muscles. Development of the sagittal crest is thought to be connected to the development of this muscle. A sagittal crest usually develops during the juvenile stage of an animal in conjunction with the growth of the temporalis muscle, as a result of convergence and gradual heightening of the temporal lines. Function A sagittal crest tends to be present on the skulls of adult animals that rely on powerful biting and clenching of their teeth, usually as a part of their hunting strategy. Skulls of some dinosaur species, including tyrannosaurs, possessed well developed sagittal crests. Among mammals, dogs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefrontal Bone
The prefrontal bone is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls. It first evolved in the sarcopterygian clade Rhipidistia, which includes lungfish and the Tetrapodomorpha. The prefrontal is found in most modern and extinct lungfish, amphibians and reptiles. The prefrontal is lost in early mammaliaforms and so is not present in modern mammals either. In dinosaurs The prefrontal bone is a very small bone near the top of the skull, which is lost in many groups of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs and is completely absent in their modern descendants, the birds. Conversely, a well developed prefrontal is considered to be a primitive feature in dinosaurs. The prefrontal makes contact with several other bones in the skull. The anterior part of the bone articulates with the nasal bone and the lacrimal bone. The posterior part of the bone articulates with the frontal Front may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''The Front'' (194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postorbital Bone
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some vertebrates, the postorbital is fused with the postfrontal to create a postorbitofrontal. Birds have a separate postorbital as an embryo, but the bone fuses with the frontal Front may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film * ''The Front'', 1976 film Music *The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ea ... before it hatches. References * Roemer, A. S. 1956. ''Osteology of the Reptiles''. University of Chicago Press. 772 pp. Skull {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and '' Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', the middle Muschelkalk (shell-bearing limestone) and the upper Keuper (coloured clay). The Late Triassic Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postorbital Bar
The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strepsirrhine primates and the hyrax, while haplorhine primates have evolved fully enclosed sockets. One theory for this evolutionary difference is the relative importance of vision to both orders. As haplorrhines ( tarsiers and simians) tend to be diurnal, and rely heavily on visual input, many strepsirrhines are nocturnal and have a decreased reliance on visual input. Postorbital bars evolved several times independently during mammalian evolution and the evolutionary histories of several other clades. Some species, such as Tarsiers, have a postorbital septum. This septum can be considered as joined processes with a small articulation between the frontal bone, the zygomatic bone and the alisphenoid bone and is therefore different from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |