|
Boven Digul
Boven Digoel Regency is a regency (''kabupaten'') in the northern part of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It is split off from Merauke Regency (of which it used to be a part) on 12 November 2002. The regency covers an area of , and the total population was 55,784 at the 2010 Census and 64,285 at the 2020 Census. The administrative centre is the town of Tanahmerah. Administrative districts The regency comprises twenty districts (''distrik''), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census and the 2020 Census.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. The table also includes the location of the district administrative centres and the number of administrative villages (rural ''desa'' and urban ''kelurahan'') in each district. History In the Dutch East Indies era, the present Boven Digoel Regency was known as ''Digul Atas'' (Upper Digul), located on the banks of the Digul River. Boven-Digoel was a Dutch prison camp in the Dutch East Indies at the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regencies And Cities Of Indonesia
Regency (Indonesia), Regencies (''kabupaten'') and City status in Indonesia#Kota, cities (''kota'') are the second-level subdivisions of Indonesia, administrative subdivision in Indonesia, immediately below the Provinces of Indonesia, provinces, and above the Districts of Indonesia, districts. Regencies are roughly equivalent to American County (United States), counties, although Lists of populated places in the United States, most cities in the United States are below the counties. Following the implementation of decentralization beginning on 1 January 2001, regencies and city municipalities became the key administrative units responsible for providing most governmental services. Each of regencies and cities has their own local government and legislative body. The difference between a regency and a city lies in demography, size, and economy. Generally, a regency comprises a rural area larger than a city, but also often includes various towns. A city usually has non-agricultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boven-Digoel Concentration Camp
Boven-Digoel was a Dutch concentration camp for political prisoners operated in the Dutch East Indies from 1927 to 1947. It was located in a remote area on the banks of the river Digul, in what is now Boven Digoel Regency in South Papua, Indonesia. The site was chosen in 1928 for the internal exile of Indonesians implicated in the 1926 and 1927 communist uprisings in Java and Sumatra.Robert Cribb, ‘Convict Exile and Penal Settlement in Colonial Indonesia’, Journal of Colonialism and Colonial History 18, no 3 (2017), online: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/cch.2017.0043 Indonesian nationalists not associated with the Indonesian Communist Party were subsequently also sent there. History The camp was located in an isolated part of New Guinea, and surrounded by hundreds of miles of impenetrable jungle and hostile Papua tribes, so that contact with the outside world, and escape, was next to impossible. It was notorious for its endemic malaria.Adrian Vickers, p.80. The Boven-Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West New Guinea Dispute
The West New Guinea dispute (1950–1962), also known as the West Irian dispute, was a diplomatic and political conflict between the Netherlands and Indonesia over the territory of Dutch New Guinea. While the Netherlands had ceded sovereignty over most of the Dutch East Indies to Indonesia on 27 December 1949 following an independence struggle, it retained control over its colony on the western half of New Guinea. The Indonesian government claimed this territory as well, on the basis that it had belonged to the Dutch East Indies and that the new Republic of Indonesia was the legitimate successor to the former Dutch colony. During the first phase of the dispute (1950–1954), Indonesia pursued bilateral negotiations with the Netherlands. During the second phase (1954–1958), Indonesia attempted to raise support for its territorial claims in the United Nations General Assembly.Soedjati Djiwandono, ''Konfrontasi Revisited'', pp.1–2 During the third phase (1960–1962), Indonesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Occupation Of The Dutch East Indies
The Empire of Japan occupied the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) during World War II from March 1942 until after the end of the war in September 1945. It was one of the most crucial and important periods in modern Indonesian history. In May 1940, Germany occupied the Netherlands, and martial law was declared in the Dutch East Indies. Following the failure of negotiations between the Dutch authorities and the Japanese, Japanese assets in the archipelago were frozen. The Dutch declared war on Japan following the 7 December 1941 Attack on Pearl Harbor. The Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies began on 10 January 1942, and the Imperial Japanese Army overran the entire colony in less than three months. The Dutch surrendered on 8 March. Initially, most Indonesians welcomed the Japanese as liberators from their Dutch colonial masters. The sentiment changed, however, as between 4 and 10 million Indonesians were recruited as forced labourers ('' romusha'') on economic deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tugu Muhammad Hatta Boven Digoel
Tugu may refer to: * National Monument (Malaysia) or ''Tugu Negara'', a monument in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia * Tugu Yogyakarta, a monument in Yogyakarta, Indonesia * Tugu Muda, a monument in Semarang, Indonesia * Tugu Keris, a monument in the shape of a kris in Klang, Malaysia * Heroes Monument or ''Tugu Pahlawan'', a monument in Surabaya, Indonesia * Mardijker Creole or ''Papiá Tugu'', an extinct Portuguese-based Jakartan creole * Tugu inscription, a stone inscription of Tarumanagara origins dating to the 5th century Locations * Tugu, Ghana, a community in the Tamale Metropolitan District, Northern Region, Ghana * Tugu Stadium, a stadium used by the Indonesian football club Persitara * Yogyakarta railway station, a train station in Yogyakarta, Indonesia commonly referred to as ''Stasiun Tugu'' * Kampung Tugu, a subdistrict of Koja, North Jakarta ** Tugu Church Tugu Church (Indonesian: ), is a Protestant church in Kampung Kurus (Kampung Kecil), Semper Barat Administrative Villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marco Kartodikromo
Marco Kartodikromo (1890 – 18 March 1932), also known by his pen name Mas Marco, was an Indonesian journalist and writer. Born to a low-ranking ''priyayi'' (noble) family in Blora, Dutch East Indies, Kartodikromo's first employment was with the national railway. Disgusted by the racism shown there, in 1911 he moved to Bandung and found work as a journalist for '' Medan Prijaji''. The following year he moved to Surakarta and worked with two publications, ''Saro Tomo'' and ''Doenia Bergerak''; he soon began to write pieces critical against the Dutch colonial government, which led to his arrest. After a period as a correspondent in the Netherlands, Kartodikromo continued his journalism and critique of the government; he also wrote several pieces of fiction. Involved with the Communist Party of Indonesia, after a 1926 communist-led revolt Kartodikromo was exiled to Boven-Digoel prison camp in Papua. He died in the camp of malaria in 1932. Kartodikromo, who preferred wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayuti Melik
Mohamad Ibnu Sayuti, known as Sayuti Melik (November 22, 1908 – February 27, 1989) was an Indonesian typist. He helped type a copy of the Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, which Sukarno proclaimed to Indonesia on August 17, 1945. He was the husband of Soerastri Karma Trimurti, a journalist and activist in the women's rights and Indonesian independence movements. Early life Melik was born in 1908 in Sleman, Yogyakarta. He went to Ongko Loro School in the village of Srowolan, and after that continued his education in Yogyakarta. His father had brought him up as a nationalist, a movement his father joined after the dutch government used his fields to grow tobacco on. However, he only first heard about the movement from his Dutch history teacher, HA Zurink, while studying in Solo in 1920. In his teenage years, he was interested in reading the Islam magazine titled "Movements of Islam". The newspaper was led by the left-leaning scholar KH Misbach, based in Kauman, Solo. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutan Syahrir
Sutan Sjahrir (5 March 1909 – 9 April 1966) was an Indonesian politician, and revolutionary independence leader, who served as the first Prime Minister of Indonesia, from 1945 until 1947. Previously, he was a key Indonesian nationalist organizer in the 1930s and 1940s. Unlike some of his colleagues, he did not support the Japanese during the Japanese occupation and fought in the resistance against them. He was considered to be an idealist and an intellectual. Born to a Minangkabau family, he studied at the University of Amsterdam, and later became a law student at the Leiden University. He became involved in Socialist politics, and Indonesia's struggle for independence, becoming a close associate of the older independence activist Mohammad Hatta, who would later become the first Vice President of Indonesia. During the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies, Sjahrir fought in the resistance. Towards independence on 17 August 1945, he was involved in the Rengasdengklok Inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
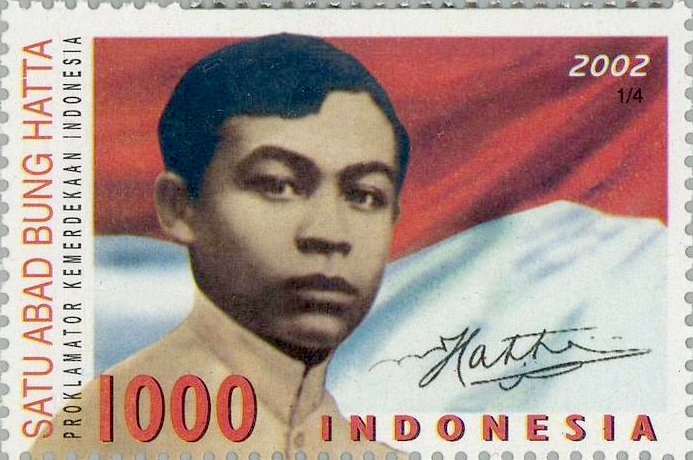
Mohammad Hatta
Mohammad Hatta (; 12 August 1902 – 14 March 1980) was an Indonesian statesman and nationalist who served as the country's first vice president. Known as "The Proclamator", he and a number of Indonesians, including the first president of Indonesia, Soekarno, fought for the independence of Indonesia from the Dutch. Hatta was born in Fort de Kock, Dutch East Indies (now Bukittinggi, Indonesia). After his early education, he studied in Dutch schools in the Dutch East Indies and studied in the Netherlands from 1921 until 1932. Early life, family, and early education Early life and family Hatta was born in Fort De Kock (now known as Bukittinggi) on 12 August 1902 into a prominent and strongly Islamic family. His grandfather, Sheikh Abdurrahman, was a respected Naqshbandi- Khalidi murshid in Batuhampar, near Payakumbuh. His father, Haji Mohammad Djamil, died when he was eight months old and he was left with his six sisters and his mother. As in the matrilineal society of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Indonesia
The Communist Party of Indonesia ( Indonesian: ''Partai Komunis Indonesia'', PKI) was a communist party in Indonesia during the mid-20th century. It was the largest non-ruling communist party in the world before its violent disbandment in 1965. The party had two million members in the 1955 elections, with 16 percent of the national vote and almost 30 percent of the vote in East Java. During most of the period immediately following independence until the eradication of the PKI in 1965, it was a legal party operating openly in the country. History Forerunners The Indies Social Democratic Association ( Dutch: ''Indische Sociaal-Democratische Vereeniging'', ISDV) was founded in 1914 by Dutch socialist Henk Sneevliet and another Indies socialist. The 85-member ISDV was a merger of the two Dutch socialist parties (the SDAP and the Socialist Party of the Netherlands), which would become the Communist Party of the Netherlands with Dutch East Indies leadership. The Dutch members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
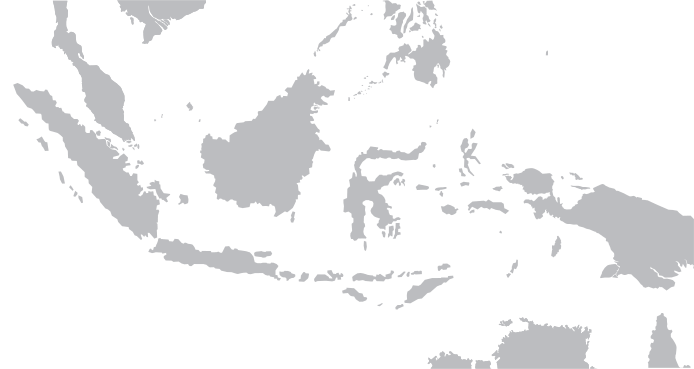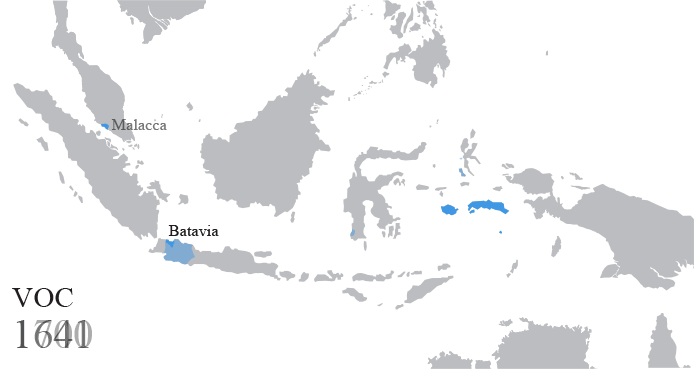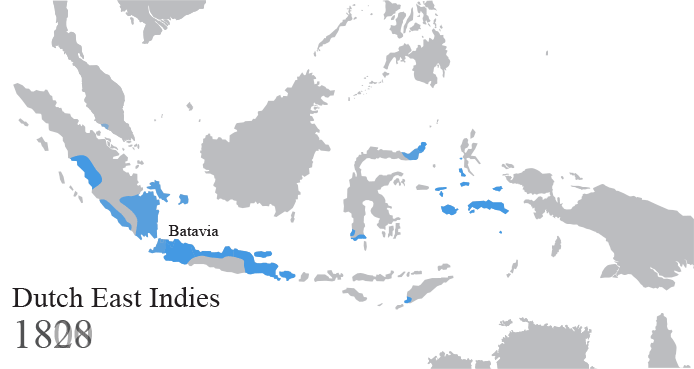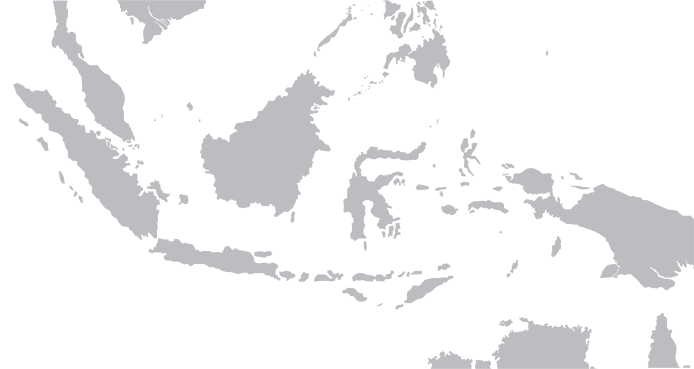
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |