|
Boulifa
Si Amar u Said Boulifa ( – 8 June 1931) was an Algerian Kabyle Berberologist and teacher. Biography Boulifa was born around 1865 in Adni village in the Irjen tribe, within the Kabyle People, Kabyle tribal confederation of At Iraten in Kabylie, Greater Kabylia. His family, the Aït Belkacem ou Amar (), are a modest marabout family (hence the "Si" of his name). Boulifa is his patronymic name in the French Civil Register. His father, Amar, left him an orphan very young. But, lucky enough to be related by his mother to the At Ameur, Tamazirt (city), Tamazirt's powerful family of Caids. Si Moula, his maternal uncle, thus sent him to the first arabic-french school opened in Kabylia in 1873, for which the candidates were then rare. This primary school was opened in Tamazirt in 1873. This combination of circumstances will be decisive for the rest of his life since he quickly committed to the career of teacher, the only way of promotion that could then be offered to a young Kabyle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabyle People
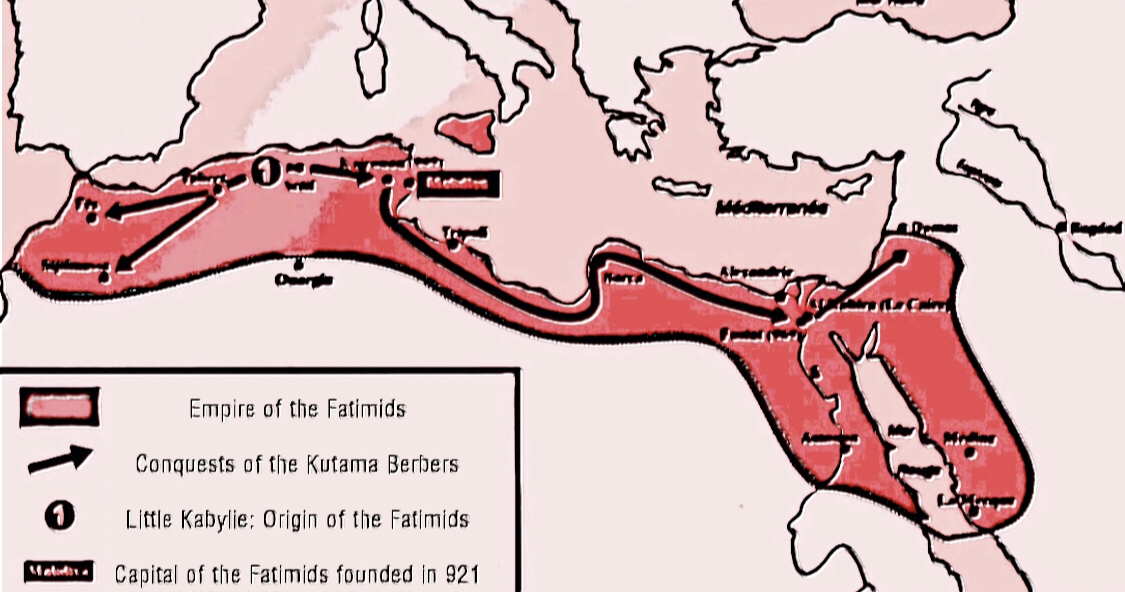
The Kabyle people ( kab, Izwawen or ''Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', ) are a Berber ethnic group indigenous to Kabylia in the north of Algeria, spread across the Atlas Mountains, east of Algiers. They represent the largest Berber-speaking population of Algeria and the second largest in North Africa. Many of the Kabyles have emigrated from Algeria, influenced by factors such as the Algerian Civil War, cultural repression by the central Algerian government, and overall industrial decline. Their diaspora has resulted in Kabyle people living in numerous countries. Large populations of Kabyle people settled in France and, to a lesser extent, Canada (mainly Québec) and United States. The Kabyle people speak Kabyle, a Berber language. Since the Berber Spring of 1980, they have been at the forefront of the fight for the official recognition of Berber languages in Algeria. History Fatimid Caliphate Between 902 and 909 the Fatimid state had been founded by the Kutama Berbers from L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabyle People
The Kabyle people ( kab, Izwawen or ''Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', ) are a Berber ethnic group indigenous to Kabylia in the north of Algeria, spread across the Atlas Mountains, east of Algiers. They represent the largest Berber-speaking population of Algeria and the second largest in North Africa. Many of the Kabyles have emigrated from Algeria, influenced by factors such as the Algerian Civil War, cultural repression by the central Algerian government, and overall industrial decline. Their diaspora has resulted in Kabyle people living in numerous countries. Large populations of Kabyle people settled in France and, to a lesser extent, Canada (mainly Québec) and United States. The Kabyle people speak Kabyle, a Berber language. Since the Berber Spring of 1980, they have been at the forefront of the fight for the official recognition of Berber languages in Algeria. History Fatimid Caliphate Between 902 and 909 the Fatimid state had been founded by the Kutama Berbers from L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustapha Pacha Hospital
Centre Hospitalo-Universitair Mustapha Pacha (French: Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire Mustapha d'Alge) was founded in 1854 in the town of Moustapha (now Sidi M'Hamed) and is the largest hospital in Algeria. This hospital center is one of 14 Centre Hospitalo-Universitair under the Algerian Ministry of Health, Population and Hospital Reform. History The hospital was established by a legacy of a rich settler named Fortin, a native of Ivry, in the city of Algiers. In his will of 19 September 1840, he donated a sum of 1.2 million francs for the erection of a civilian hospital in Mustapha. At its inception in 1854, it was a military hospital with a barracks on 8 hectares. On 21 May 1855, the civilian doctors courses were open to students, and on 18 January 1859, official courses were inaugurated in the framework of the new School of Medicine of Algiers founded in 1857. After 1877, 14 pavilions were built to plans by the architect Jules Voinot. The first services were those of Pediat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Algerian People
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Deaths
Events January * January 2 – South Dakota native Ernest Lawrence invents the cyclotron, used to accelerate particles to study nuclear physics. * January 4 – German pilot Elly Beinhorn begins her flight to Africa. * January 22 – Sir Isaac Isaacs is sworn in as the first Australian-born Governor-General of Australia. * January 25 – Mohandas Gandhi is again released from imprisonment in India. * January 27 – Pierre Laval forms a government in France. February * February 4 – Soviet leader Joseph Stalin gives a speech calling for rapid industrialization, arguing that only strong industrialized countries will win wars, while "weak" nations are "beaten". Stalin states: "We are fifty or a hundred years behind the advanced countries. We must make good this distance in ten years. Either we do it, or they will crush us." The first five-year plan in the Soviet Union is intensified, for the industrialization and collectivization of agriculture. * February 10 – Official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1865 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – The New York Stock Exchange opens its first permanent headquarters at 10-12 Broad near Wall Street, in New York City. * January 13 – American Civil War : Second Battle of Fort Fisher: United States forces launch a major amphibious assault against the last seaport held by the Confederates, Fort Fisher, North Carolina. * January 15 – American Civil War: United States forces capture Fort Fisher. * January 31 ** The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution (conditional prohibition of slavery and involuntary servitude) passes narrowly, in the House of Representatives. ** American Civil War: Confederate General Robert E. Lee becomes general-in-chief. * February ** American Civil War: Columbia, South Carolina burns, as Confederate forces flee from advancing Union forces. * February 3 – American Civil War : Hampton Roads Conference: Union and Confederate leaders discuss peace terms. * Feb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outre-Mers
''Outre-mers. Revue d'Histoire'' is a semi-annual French journal, founded in 1913 under the title ''Revue de l'histoire des colonies françaises''. It publishes two double issues annually. References External links "Outre-Mers. Revue d'histoire" ''Persée (web portal), Persée''. Publications established in 1913 French-language journals History journals {{history-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopédie Berbère
''Encyclopédie berbère'' (English: ''Berber Encyclopaedia'') is a French-language encyclopaedia dealing with subjects related to the Berber peoples (''Imazighen'' in Berber language), published both in print editions and in a partial online version. It was launched in 1984 under the aegis of UNESCO and was originally published by Editions Edisud. Its first editor-in-chief was Gabriel Camps. After his death in 2002, he was succeeded by Salem Chaker, Professor of Berber languages at the Aix-Marseille University Aix-Marseille University (AMU; french: Aix-Marseille Université; formally incorporated as ''Université d'Aix-Marseille'') is a public research university located in the Provence region of southern France. It was founded in 1409 when Louis II o .... Up to 2013, volumes 1 to 36 (Oryx - Ozoutae) have been published online through OpenEdition.org. The online site allows part of the encyclopedia to be viewed in full text and in PDF and offers a search function to key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Method (education)
The direct method of teaching, which is sometimes called the natural method, and is often (but not exclusively) used in teaching foreign languages, refrains from using the learners' native language and uses only the target language. It was established in England around 1900 and contrasts with the grammar–translation method and other traditional approaches, as well as with C.J. Dodson's bilingual method. It was adopted by key international language schools such as Berlitz, Alliance Française and Inlingua in the 1970s and many of the language departments of the Foreign Service Institute of the U.S. State Department in 2012. In general, teaching focuses on the development of oral skills. Characteristic features of the direct method are: * teaching concepts and vocabulary through pantomiming, real-life objects and other visual materials * teaching grammar by using an inductive approach (i.e. having learners find out rules through the presentation of adequate linguistic forms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabyle Language
Kabyle () or Kabylian (; native name: ''Taqbaylit'' , ) is a Berber language spoken by the Kabyle people in the north and northeast of Algeria. It is spoken primarily in Kabylia, east of the capital Algiers and in Algiers itself, but also by various groups near Blida, such as the Beni Salah and Beni Bou Yaqob.(extinct?) Estimating the number of Berber speakers is very difficult and figures are often contested. Estimates of the number of Kabyle speakers globally range from three million in 2003 according to the ''International Encyclopedia of Linguistics'' and three million in 2015 in Algeria only to six to seven million worldwide in 2020 according to Asya Pereltsvaig and ''Ethnologue''. Kabyle has a significant Arabic, French, Latin, Greek, Phoenician and Punic substratum, and Arabic loanwords represent 35% of the total Kabyle vocabulary. Classification Kabyle is one of the Berber languages, a family within the Afroasiatic languages. It is believed to have broken off very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qanun (law)
Qanun is an Arabic word ( ar, قانون, translit=qānūn; ota, قانون, translit=kānūn, derived from grc, κανών, translit=kanōn, which is also the root for the modern English word "canon"). Qanun can refer to laws established by Muslim sovereigns, in particular the body of administrative, economic and criminal law promulgated by Ottoman sultans, in contrast to sharia, the body of law elaborated by Muslim jurists. It is thus frequently translated as "dynastic law." History The idea of ''qanun'' entered the Muslim World in the thirteenth century, borrowed from the Mongol Empire following their invasions. The 10th sultan of the Ottoman Empire, Suleiman was known in the Ottoman Empire as Suleiman Kanuni ("the Lawgiver"), due to the laws he promulgated. After the fall of the Abbasid Caliphate in 1258, a practice known to the Turks and Mongols transformed itself into Qanun, which gave power to caliphs, governors, and sultans alike to "make their own regulations fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |