|
Body Odor
Body odor or body odour (BO) is present in all animals and its intensity can be influenced by many factors (behavioral patterns, survival strategies). Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various diseases and physiological conditions. Though body odor has played an important role (and continues to do so in many life forms) in early humankind, it is generally considered to be an unpleasant odor amongst many human cultures. Causes In humans, the formation of body odors is caused by factors such as diet, sex, health, and medication, but the major contribution comes from bacterial activity on skin gland secretions. Humans have three types of sweat glands: eccrine sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Eccrine sweat glands are present from birth, while the latter two become activated during puberty. Among the different types of human skin glands, body odor is primarily the result of the apocrine sweat glands, which secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipases
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms. Structure and catalytic mechanism Classically, lipases catalyse the hydrolysis of triglycerides: :triglyceride + H2O → fatty acid + diacylglycerol :diacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + monacylglycerol :monacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + glycerol Lipases are serine hydrolases, i.e. they function by transesterification generating an acyl serine intermediate. Most lipases act at a specific position on the glycerol backbone of a lipid sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifestyle (sociology)
Lifestyle is the interests, opinions, behaviours, and behavioural orientations of an individual, group, or culture. The term was introduced by Austrian psychologist Alfred Adler in his 1929 book, ''The Case of Miss R.'', with the meaning of "a person's basic character as established early in childhood". The broader sense of lifestyle as a "way or style of living" has been documented since 1961. Lifestyle is a combination of determining intangible or tangible factors. Tangible factors relate specifically to demographic variables, i.e. an individual's demographic profile, whereas intangible factors concern the psychological aspects of an individual such as personal values, preferences, and outlooks. A rural environment has different lifestyles compared to an urban metropolis. Location is important even within an urban scope. The nature of the neighborhood in which a person resides affects the set of lifestyles available to that person due to differences between various neighborho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
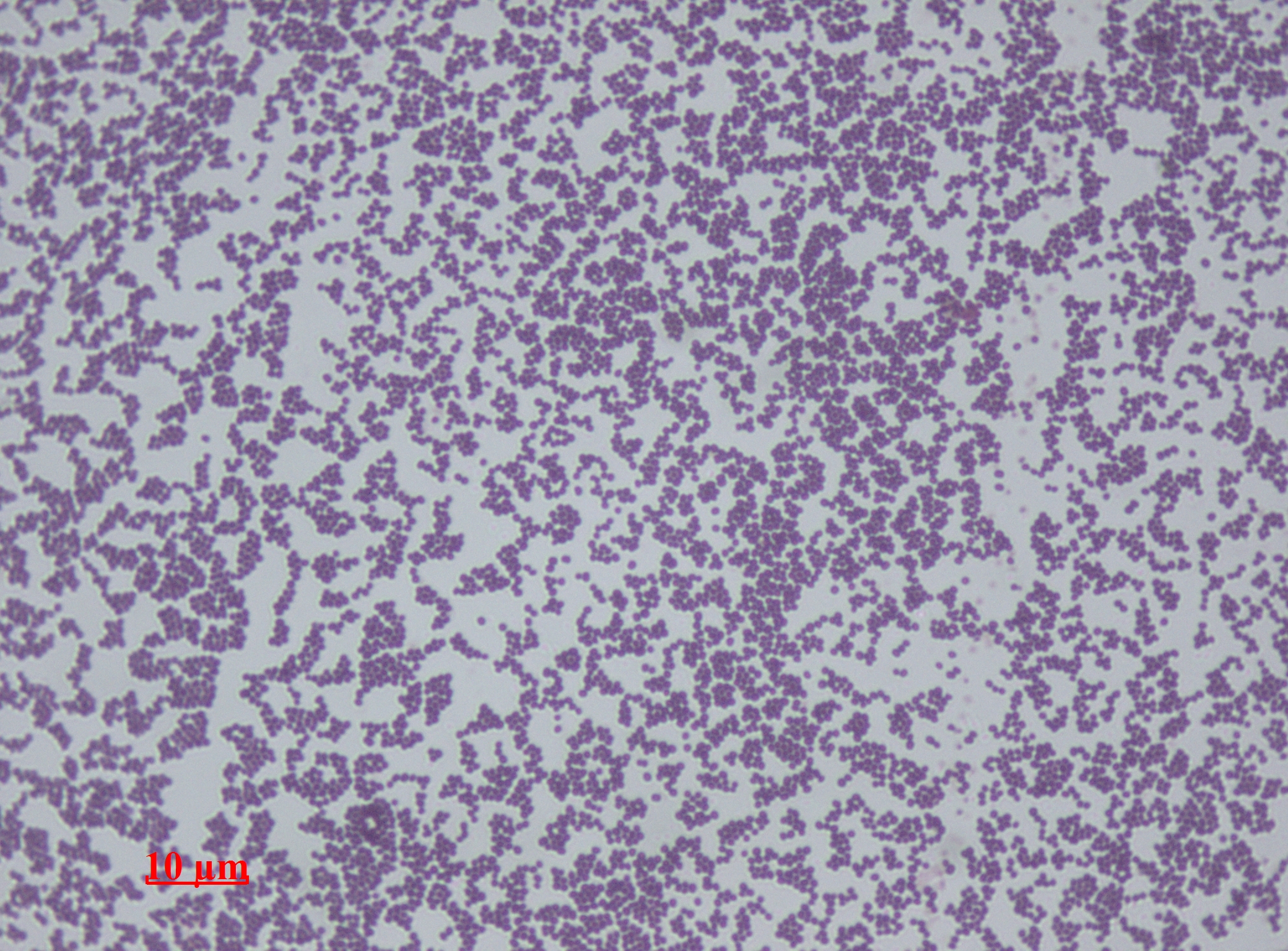
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus '' Staphylococcus''. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified salt tolerant strains of ''S. epid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for acetic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
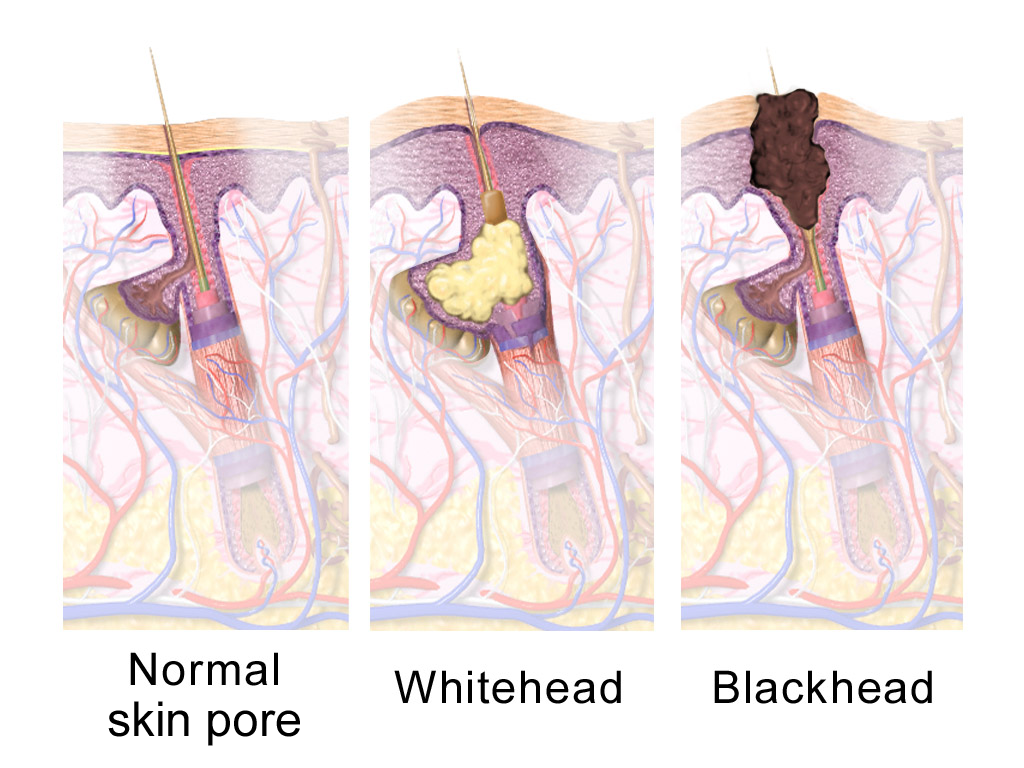
Sebaceous
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacteria
''Propionibacterium'' is a gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes. Its members are primarily facultative parasites and commensals of humans and other animals, living in and around the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and other areas of the skin. They are virtually ubiquitous and do not cause problems for most people, but propionibacteria have been implicated in acne and other skin conditions. One study found the ''Propionibacterium'' was the most prevalent human skin-associated genus of microorganisms. Members of the genus ''Propionibacterium'' are widely used in the production of vitamin B12, tetrapyrrole compounds, and propionic acid, as well as in the probiotics and cheese industries. The strain ''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' subsp. ''shermanii'' is used in cheesemaking to create CO2 bubbles that become "eyes"—round holes in the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
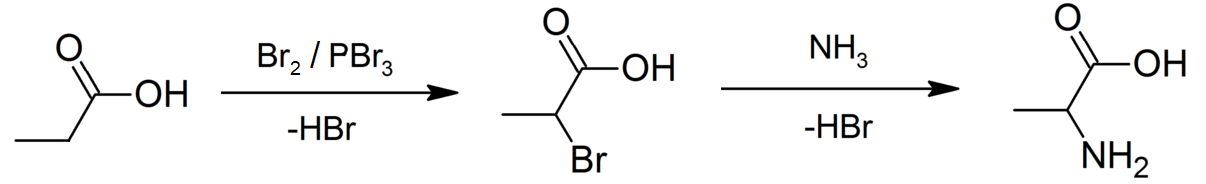
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Hominis
''Staphylococcus hominis'' is a coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus ''Staphylococcus'', consisting of Gram-positive, spherical cells in clusters. It occurs very commonly as a harmless commensal on human and animal skin and is known for producing thioalcohol compounds that contribute to body odour. Like many other coagulase-negative staphylococci, ''S. hominis'' may occasionally cause infection in patients whose immune systems are compromised, for example by chemotherapy or predisposing illness. Description Colonies of ''S. hominis'' are small, usually 1–2 mm in diameter after 24 hours' incubation at 35 °C, and white or tan in colour. Occasionally, strains are resistant to novobiocin and may be confused with other resistant species (e.g. '' S. saprophyticus''). It is one of only two species of ''Staphylococcus'' to display sensitivity to desferrioxamine, the other being '' S. epidermidis''. Unlike ''S. epidermidis'', ''S. hominis'' produces acid from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |