|
Bhuvanaikabahu VI Of Kotte
Bhuvanekabahu VI of Kotte (, ), also known as Sapumal Kumaraya and Chempaka Perumal, was an adopted son of Parakramabahu VI, whose principal achievement was the conquest of Jaffna Kingdom in 1447 or 1450.Gnanaprakasar, S ''A critical history of Jaffna'', p.103 Bhuvanaikabahu was apparently summoned south after the demise of his adopted father. He then ruled for 17 years. According to ''Rajavaliya'', he killed the grandson of Parakrama Bahu VI, namely Vira Parakrama Bahu or Jaya Bahu (1468 – c. 1470). Do Couto, however, who was well-informed, says after a few years' reign the king died and his half-witted son was put on the throne by his aunt, who two years later finding herself unable to rule sent for Sapumal Kumaraya from Jaffna. Origin theories There are number of theories as to his ethnic origin and the reason for the rebellion against his rule. According to John Holt, he was an ethnic Tamil from the eastern part of the island, whereas other sources say that he may have c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Kotte
The Kingdom of Kotte ( si, කෝට්ටේ රාජධානිය, Kottay Rajadhaniya), named after its capital, Kotte, was a Sinhalese kingdom that flourished in Sri Lanka during the 15th century. Kotte, under the rule of Ming-backed Parakramabahu VI, conquered the Jaffna kingdom and the Vanni principalities, and brought the country under one flag. It led to a punitive invasion against the Vijayanagar dynasty and captured a port, which was converted to a trade route. The Kotte Kingdom was largely dissolved during the Sinhalese-Portuguese War, as it faced attacks from rival Sinhalese kingdoms, the Kingdom of Sitawaka and Kingdom of Kandy. Dom João Dharmapala handed it over to the Portuguese, thus leading to the formation of Ceylon. The remainder was annexed into Sitwaka and Kandy. Etymology The term ''Kotte'' is said to have derived from the Sinhalese word ''kotta'' (කෝට්ට) and Tamil word ''kōttei'' which mean fortress.The word ''Kotte'' was introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Sebastian
Anton Sebastianpillai FRCP (23 January 1945 – 4 April 2020), was a British historian, author (writing as Anton Sebastian) and consultant geriatrician, of Sri Lankan Tamil origin. Biography He had his primay and secondary education at St Sylvester's College, Kandy and trained at Peradeniya Medical School, in Sri Lanka, qualifying in 1967. He gave talks to the Foreign Correspondents' Club, New Delhi, India, and gave the 'Millennium Oration' of the Sri Lanka Medical Association of North America. He died on 4 April 2020, at Kingston Hospital, London, after contracting COVID-19 while working there. He had been admitted to the hospital's intensive care unit on 31 March and was aged 75. He was a bibliophile, with a collection of rare books on Sri Lanka and on medical history. Works As Anton Sebastian he wrote a number of reference works: * * * * His ''Dictionary of the History of Medicine'' won a British Medical Association The British Medical Association (BMA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectuals
An intellectual is a person who engages in critical thinking, research, and reflection about the reality of society, and who proposes solutions for the normative problems of society. Coming from the world of culture, either as a creator or as a mediator, the intellectual participates in politics, either to defend a concrete proposition or to denounce an injustice, usually by either rejecting or producing or extending an ideology, and by defending a system of values. Etymological background "Man of letters" The term "man of letters" derives from the French term '' belletrist'' or ''homme de lettres'' but is not synonymous with "an academic". A "man of letters" was a literate man, able to read and write, as opposed to an illiterate man in a time when literacy was rare and thus highly valued in the upper strata of society. In the 17th and 18th centuries, the term ''Belletrist(s)'' came to be applied to the ''literati'': the French participants in—sometimes referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryacakravarti Dynasty
The Arya Chakravarti dynasty ( ta, ஆரியச் சக்கரவர்த்திகள் வம்சம், Sinhalese: ආර්ය චක්රවර්තී රාජවංශය) were kings of the Jaffna Kingdom in Sri Lanka. The earliest Sri Lankan sources, between 1277 and 1283, mention a military leader of this name as a minister in the services of the Pandyan Empire; he raided the western Sri Lankan coast and took the politically significant relic of the Buddha's tooth from the Sinhalese capital city of Yapahuwa. Political and military leaders of the same family name left a number of inscriptions in the modern-day Tamil Nadu state, with dates ranging from 1272 to 1305, during the late Pandyan Empire. According to contemporary native literature, such as ''Cekaracecekaramalai'', the family also claimed lineage from the Tamil Brahmins of the prominent Hindu pilgrimage temple of Rameswaram in the modern Ramanathapuram District of India. They ruled the Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirunelveli
Tirunelveli (, ta, திருநெல்வேலி, translit=Tirunelveli) also known as Nellai ( ta, நெல்லை, translit=Nellai) and historically (during British rule) as Tinnevelly, is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirunelveli District. It is the sixth-largest municipal corporation in the state after Chennai, Coimbatore, Madurai, Tiruchirappalli and Salem. Tirunelveli is located southwest of the state capital Chennai, away from Thoothukudi, and from Kanyakumari. The downtown is located on the west bank of the Thamirabarani River; its twin Palayamkottai is on the east bank. Palayamkottai is called the Oxford of South India as it is a hub of many schools and colleges. It boasts several important government offices. Tirunelveli is an ancient city, recorded to be more than two millennia old. It has been ruled at different times by the Early Pandyas, the Cheras, the Medieval Cholas and Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
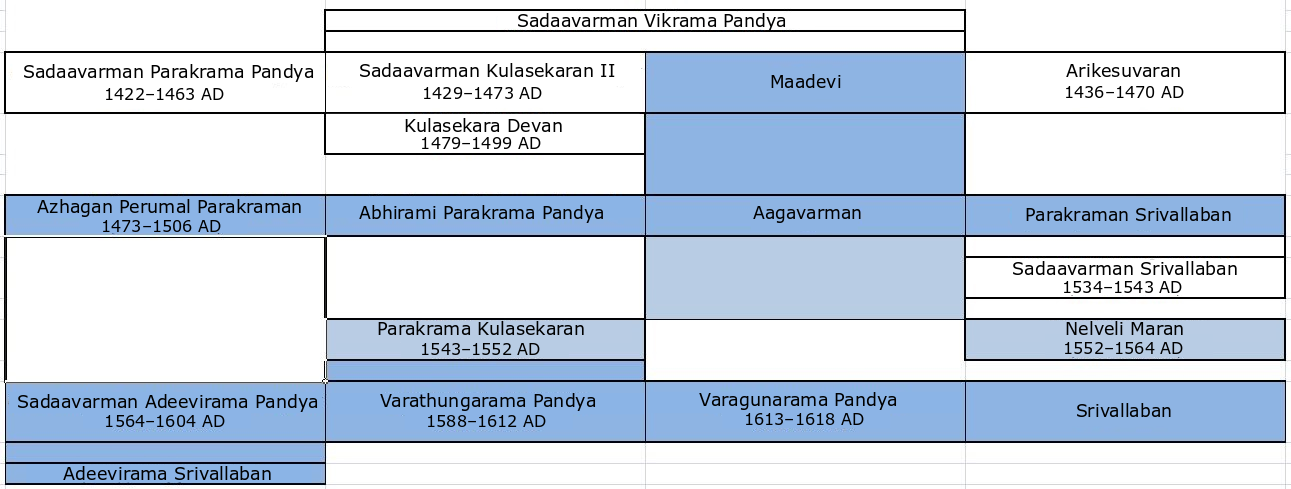
Tenkasi Pandyas
Tenkasi Pandyas were the Pandya kings from Sadaavarman Parakrama Pandya to his successors who ruled with Tenkasi as their capital. With the invasion of the Sultanates, Vijayanagaras, and Nayakars from the fourteenth century onwards, the Pandyas lost their traditional capital of Madurai and shifted to cities like Tenkasi and Tirunelveli.Karashima, Noburu. 2014. 'The Fall of the Old States', in ''A Concise History of South India: Issues and Interpretations'', ed. Noburu Karashima, pp. 173–74. New Delhi: Oxford University Press. Tenkasi was the last capital of the Pandyas. All the Pandyas from Sadaavarman Parakrama Pandya and his next generations were crowned in the Adheenam Mutt in Kasi Viswanathar temple. During the same period, some Pandyas ruled with Tirunelveli as their capital. Kayatharu, Vadakkuvalliyur, and Ukkirankottai are some of their major cities. Inscriptions on them are found in Tenkasi's Kasi Viswanathar temple, Brahmadesam, Cheranmadevi, Ambasamudram, Kal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus '' Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfast cereals, snack foods, bagels, teas, and traditional foods. The aroma and flavour of cinnamon derive from its essential oil and principal component, cinnamaldehyde, as well as numerous other constituents including eugenol. Cinnamon is the name for several species of trees and the commercial spice products that some of them produce. All are members of the genus ''Cinnamomum'' in the family Lauraceae. Only a few ''Cinnamomum'' species are grown commercially for spice. '' Cinnamomum verum'' (AKA ''C. zeylanicum''), known as "Ceylon cinnamon" after its origins in Sri Lanka (formerly Ceylon), is considered to be "true cinnamon", but most cinnamon in international commerce is derived from four other species, usually and more correctly ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, comprising 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. Covering the southern part of the peninsular Deccan Plateau, South India is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse with two mountain ranges – the Western and Eastern Ghats – bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Tungabhadra, Periyar, Bharathappuzha, Pamba, Thamirabarani, Palar, and Vaigai rivers are important perennial rivers. The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major Dravidian languages: Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam and Kannada (all 4 of which are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vannimai
The Vanni chieftaincies or Vanni principalities was a region between Anuradhapura and Jaffna, but also extending to along the eastern coast to Panama and Yala, during the Transitional and Kandyan periods of Sri Lanka. The heavily forested land was a collection of chieftaincies of principalities that were a collective buffer zone between the Jaffna Kingdom, in the north of Sri Lanka, and the Sinhalese kingdoms in the south. Traditionally the forest regions were ruled by Vedda rulers. Later on, the emergence of these chieftaincies were a direct result of the breakdown of central authority and the collapse of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa in the 13th century, as well as the establishment of the Jaffna Kingdom in the Jaffna Peninsula. Control of this area was taken over by dispossessed Sinhalese nobles and chiefs of the South Indian military of Māgha of Kalinga (1215–1236), whose 1215 invasion of Polonnaruwa led to the kingdom's downfall. Sinhalese chieftaincies would lay on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanniar (Sri Lanka)
Vanniar or Vanniyar (, ) was a title borne by chiefs in medieval Sri Lanka who ruled in the Vannimai, Chiefdom of Vavuni regions as tribute payers to the Jaffna kingdom, Jaffna vassal state. There are a number of origin theories for the feudal chiefs, coming from an indigenous formation. The most famous of the Vavni chieftains was Pandara Vannian, known for his resistance against the British colonial power. Etymology The word ''Vanni'' may have been a derivation of the Tamil language, Tamil word ''vanam'', meaning "forest", with Vanniar meaning "person from the forest". History Medieval Tamil chronicles such as the 18th-century ''Yalpana Vaipava Malai'' and stone inscriptions like Konesar Kalvettu recount that the Chola royal Kankan, a descendant of the legendary King Manu Needhi Cholan of Thiruvarur, Chola Nadu, restored the Koneswaram temple at Trincomalee and the Kantalai tank after finding them in ruins. He visited the Munneswaram temple on the west coast, before settling an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanni (Sri Lanka)
The Vanni, also spelled Wanni, is the name given to the mainland area of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It covers the entirety of Mannar, Mullaitivu and Vavuniya Districts, and most of Kilinochchi District, and has an area of approximately . The population and infrastructure of the Vanni were devastated by the Sri Lankan Civil War. History Tamil feudal chiefs called Vanniar chiefs who have their origin here cultivated the Vanni in the first millennium of the Common Era governing what were called Vannimai, the Jaffna kingdom's land divisions located south of the Jaffna Peninsula in the present-day Northern, North Central and Eastern provinces of Sri Lanka. Geography Geographically, the Vanni is distinct from the Jaffna Peninsula, the other area of the Northern Province. Jaffna peninsula is irrigated by underground aquifers fed by wells whereas the Vanni has irrigation tanks fed by perennial rivers. Major rivers include: Akkarayan Aru, Aruvi Aru, Kanakarayan Aru, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinhalese People
Sinhalese people ( si, සිංහල ජනතාව, Sinhala Janathāva) are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the island of Sri Lanka. They were historically known as Hela people ( si, හෙළ). They constitute about 75% of the Sri Lankan population and number more than 16.2 million. The Sinhalese identity is based on language, cultural heritage and nationality. The Sinhalese people speak Sinhala, an insular Indo-Aryan language, and are predominantly Theravada Buddhists, although a minority of Sinhalese follow branches of Christianity and other religions. Since 1815, they were broadly divided into two respective groups: The 'Up-country Sinhalese' in the central mountainous regions, and the 'Low-country Sinhalese' in the coastal regions; although both groups speak the same language, they are distinguished as they observe different cultural customs. According to the Mahavamsa and the Dipavamsa, a third–fifth century treatise written in Pali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

.png)