|
Battle Of Congella
The Battle of Congella, beginning 23 May 1842, was between the British of the Cape colony and Voortrekkers or the Boer forces of the Natalia Republic. The Republic of Natalia sought an independent port of entry, free from British control and thus sought to conquer the Port Natal trading settlement which had been settled by mostly British merchants in modern-day KwaZulu-Natal. The battle ended in a British victory due to the heroic ride of Dick King for reinforcements. Background According to South African history, in the mid-1820s Shaka, king of the Zulu people swept through the countryside now known as KwaZulu-Natal, killing almost the entire native population of bushmen. Through his conquests, Shaka founded the first unified Zulu Kingdom. A few years later, the English colonists living in the coastal settlement of Port Natal (Durban) requested to be officially recognised by the Cape Government as a dependency of Britain. This was rejected, and as a result the colonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
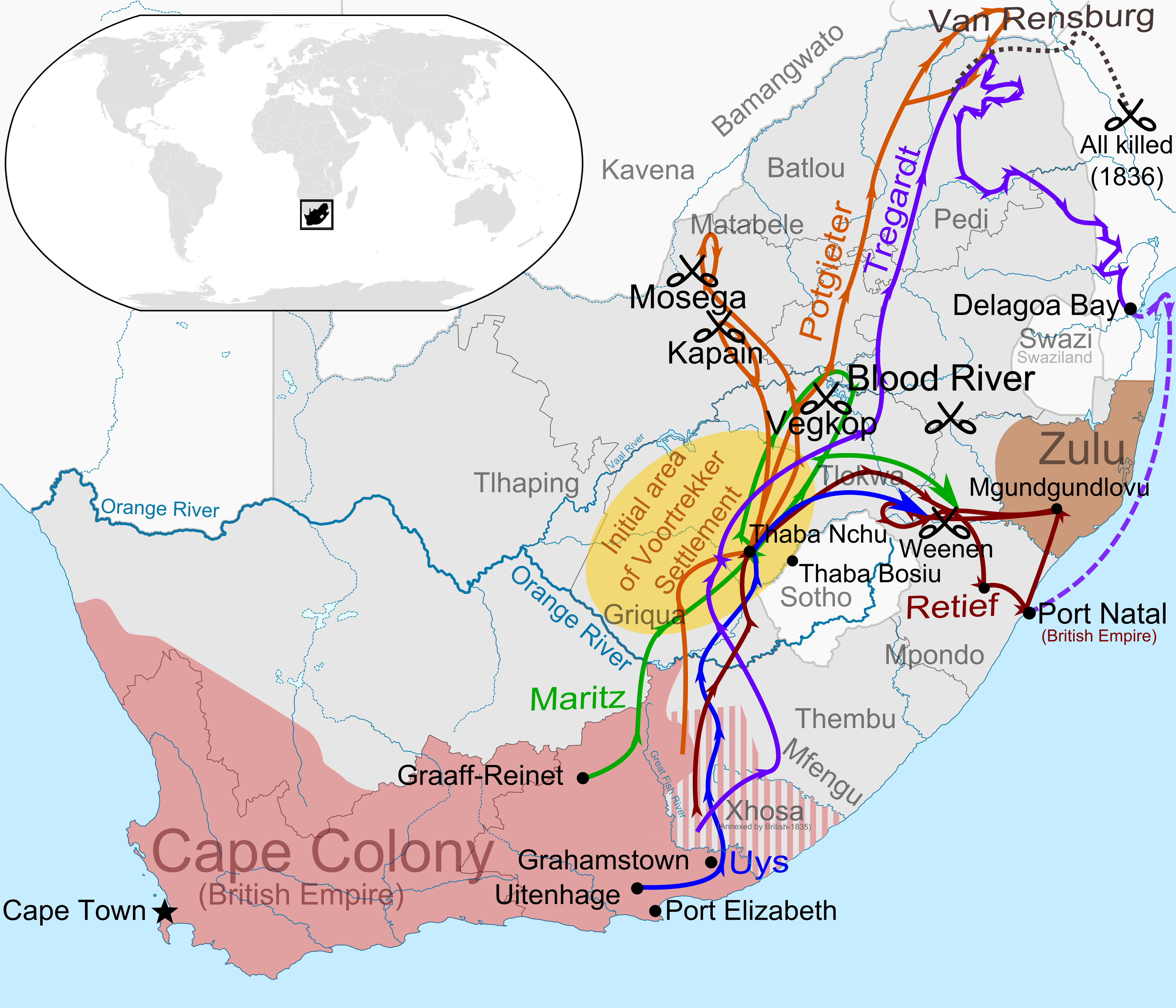
Great Trek
The Great Trek ( af, Die Groot Trek; nl, De Grote Trek) was a Northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as '' Boers'', and the British Empire. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers", "pathfinders" (literally "fore-trekkers") in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with three other colonies to form the Union of South Africa. The British colony was preceded by an earlier corporate colony that became an original Dutch colony of the same name, which was established in 1652 by the Dutch East India Company (VOC). The Cape was under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and under rule of the Napoleonic Batavia Republic from 1803 to 1806. The VOC lost the colony to Great Britain following the 1795 Battle of Muizenberg, but it was acceded to the Batavia Republic following the 1802 Treaty of Amiens. It was re-occupied by the British following the Battle of Blaauwberg in 1806, and British possession affirmed with the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814. The Cape of Good Hope then remained in the British Empire, becoming self-governi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outpost (military)
A military outpost is detachment of troops stationed at a distance from the main force or formation, usually at a station in a remote or sparsely populated location, positioned to stand guard against unauthorized intrusions and surprise attacks; and the station occupied by such troops, usually a small military base or settlement in an outlying frontier, limit, political boundary or in another country. Outposts can also be called miniature military bases based on size and number of troops it houses. Dictionary meaning: Outpost TheFreeDictionary; An online Dictionary and Thesaurus Recent military use Military outposts, most recently referred to as combat outposts (COPs), served as a cornerstone of counterinsurgency doctrine in Iraq and Afghanistan. These permanent or semi-permanent ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Flag
The national flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Jack, also known as the Union Flag. The design of the Union Jack dates back to the Act of Union 1801 which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The flag consists of the red cross of Saint George (patron saint of England (which also represents Wales)), edged in white, superimposed on the saltire of St Patrick (patron saint of Ireland), also edged in white, which are superimposed on the saltire of Saint Andrew (patron saint of Scotland). Wales is not represented in the Union Flag by Wales's patron saint, Saint David, because the flag was designed whilst Wales was part of the Kingdom of England. The flag proportions on land and the war flag used by the British Army have the proportions 3:5. The flag's height-to-length proportions at sea are 1:2. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grahamstown
Makhanda, also known as Grahamstown, is a town of about 140,000 people in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is situated about northeast of Port Elizabeth and southwest of East London. Makhanda is the largest town in the Makana Local Municipality, and the seat of the municipal council. It also hosts Rhodes University, the Eastern Cape Division of the High Court, the South African Library for the Blind (SALB), a diocese of the Anglican Church of Southern Africa, and 6 South African Infantry Battalion. Furthermore, located approximately 3 km south-east of the town lies the world renowned Waterloo Farm, the only estuarine fossil site in the world from 360 million years ago with exceptional soft-tissue preservation. The town's name-change from Grahamstown to Makhanda was officially gazetted on 29 June 2018. The town was officially renamed to Makhanda in memory of Xhosa warrior and prophet Makhanda ka Nxele. History Founding Makhanda was founded as Graha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territories that are not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governed colonies controlled by colonial settlers. The term colony originates from the ancient Roman '' colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'. Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''metropolis'' ("mother- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Natal
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from 25 October 2017. Retrieved 2021-03-05.The names and the naming of Durban Website ''natalia.org.za'' (pdf). Retrieved 2021-03-05. is the third most populous city in after and |
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually disappeared as the use of heavy armour declined, but ''musket'' continued as the generic term for smoothbore long guns until the mid-19th century. In turn, this style of musket was retired in the 19th century when rifled muskets (simply called rifles in modern terminology) using the Minié ball (invented by Claude-Étienne Minié in 1849) became common. The development of breech-loading firearms using self-contained cartridges (introduced by Casimir Lefaucheux in 1835) and the first reliable repeating rifles produced by Winchester Repeating Arms Company in 1860 also led to their demise. By the time that repeating rifles became common, they were known as simply "rifles", ending the era of the musket. Etymology According to the Online Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE, AusE, and IndE), is a male bovine trained and used as a draft animal. Oxen are commonly castrated adult male cattle; castration inhibits testosterone and aggression, which makes the males docile and safer to work with. Cows (adult females) or bulls (intact males) may also be used in some areas. Oxen are used for plowing, for transport (pulling carts, hauling wagons and even riding), for threshing grain by trampling, and for powering machines that grind grain or supply irrigation among other purposes. Oxen may be also used to skid logs in forests, particularly in low-impact, select-cut logging. Oxen are usually yoked in pairs. Light work such as carting household items on good roads might require just one pair, while for heavier work, further pairs would be added as necessary. A team used for a heavy load over difficult ground might exceed nine or ten pairs. Domestication Oxen are thought to have first been ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers
The Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers was an Irish line infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 until 1968. The regiment was formed in 1881 by the amalgamation of the 27th (Inniskilling) Regiment of Foot and the 108th Regiment of Foot. It saw service in the Second Boer War, the First World War and the Second World War. In 1968 it was amalgamated with the other regiments in the North Irish Brigade, the Royal Ulster Rifles, and the Royal Irish Fusiliers (Princess Victoria's) into the Royal Irish Rangers. History 1881 – 1914 On 1 July 1881 the 27th (Inniskilling) Regiment of Foot and the 108th Regiment of Foot were redesignated as the 1st and 2nd Battalions, The Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers, respectively. In 1903 the Regiment was granted a grey hackle for their fusilier raccoon-skin hats to commemorate the original grey uniforms of the Inniskilling Regiment. The regimental district comprised the City of Londonderry and the counties of Donegal, Londond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Seventh Coalition. One of these was a British-led coalition consisting of units from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover, Duchy of Brunswick, Brunswick, and Duchy of Nassau, Nassau, under the command of the Duke of Wellington (referred to by many authors as ''the Anglo-allied army'' or ''Wellington's army''). The other was composed of three corps of the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian army under the command of Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, von Blücher (the fourth corps of this army fought at the Battle of Wavre on the same day). The battle marked the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was contemporaneously known as the Battle of Mont Saint-J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Copy.jpg)