|
Barbadian English
Barbadian English or Bajan () English is a dialect of the English language as used by Barbadians (Bajans) and by Barbadian diasporas. It should not be confused with Bajan Creole, which is an English-based creole language. Schneider, E.W., and Kortmann, B. " A Handbook of Varieties of English: Morphology and syntax ". Mouton de Gruyter, 2004. In '' Pronunciation Barbadian English is fully rhoticity in English, rhotic and full of glottal stops. One example of Barbadian English would be the pronunciation of ''departments'', which is . It is also notable, in comparison with standard American or British English, for the first vowel in ''price'' or ''prize''. Schneider, E.W., and Kortmann, B. " A Handbook of Varieties of English: Morphology and syntax ". Mouton de Gruyter, 2004. In '' Michelle Straw, Peter L. Patrick. " Dialect acquisition of glottal variation in /t/: Barbadians in Ipswich ". Language Sciences 29 (2007) 385–407. In '' * The realization of the vowel in Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Caribbean
The Commonwealth Caribbean is the region of the Caribbean with English-speaking countries and territories, which once constituted the Caribbean portion of the British Empire and are now part of the Commonwealth of Nations. The term includes many independent island nations, British Overseas Territories and some mainland nations. It is also known as the English-speaking Caribbean, Anglophone Caribbean or Anglo-Caribbean. The term is now used in preference over the older term ''British West Indies'', which was used to describe the British colonies in the West Indies during decolonisation and following independence from the United Kingdom. ''Anglo-Caribbean'' and ''British Commonwealth Caribbean'' also became preferred replacement terms to ''British West Indies''. Countries and territories The Commonwealth Caribbean consists of countries and territories, which include Caribbean islands or parts of mainland North and South America surrounding the Caribbean Sea. Independent islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Alphabet
The alphabet for Modern English is a Latin-script alphabet consisting of 26 letters, each having an upper- and lower-case form. The word ''alphabet'' is a compound of the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, ''alpha'' and '' beta''. The alphabet originated around the 7th century CE to write Old English from Latin script. Since then, letters have been added or removed to give the current letters: The exact shape of printed letters varies depending on the typeface (and font), and the standard printed form may differ significantly from the shape of handwritten letters (which varies between individuals), especially cursive. English Vowels and English Consonants. The English alphabet has 6 vowels and 20 consonants. Written English has a large number of digraphs (e.g., ''would'', ''beak'', ''moat''); it stands out (almost uniquely) as a European language without diacritics in native words. The only exceptions are: * a diaeresis (e.g., "coöperation") may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialects Of English
Dialects are linguistic varieties that may differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, spelling and grammar. For the classification of varieties of English only in terms of pronunciation, see regional accents of English. Overview Dialects can be defined as "sub-forms of languages which are, in general, mutually comprehensible." English speakers from different countries and regions use a variety of different accents (systems of pronunciation) as well as various localized words and grammatical constructions; many different dialects can be identified based on these factors. Dialects can be classified at broader or narrower levels: within a broad national or regional dialect, various more localised sub-dialects can be identified, and so on. The combination of differences in pronunciation and use of local words may make some English dialects almost unintelligible to speakers from other regions without any prior exposure. The major native dialects of English are often divided by linguists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Amerindians, Spanish navigators took possession of Barbados in the late 15th century, claiming it for the Crown of Castile. It first appeared on a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese Empire claimed the island between 1532 and 1536, but abandoned it in 1620 with their only remnants being an introduction of wild boars for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the ''Olive Blossom'', arrived in Barbados on 14 May 1625; its men took possession of the island in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and Barbados became an English and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
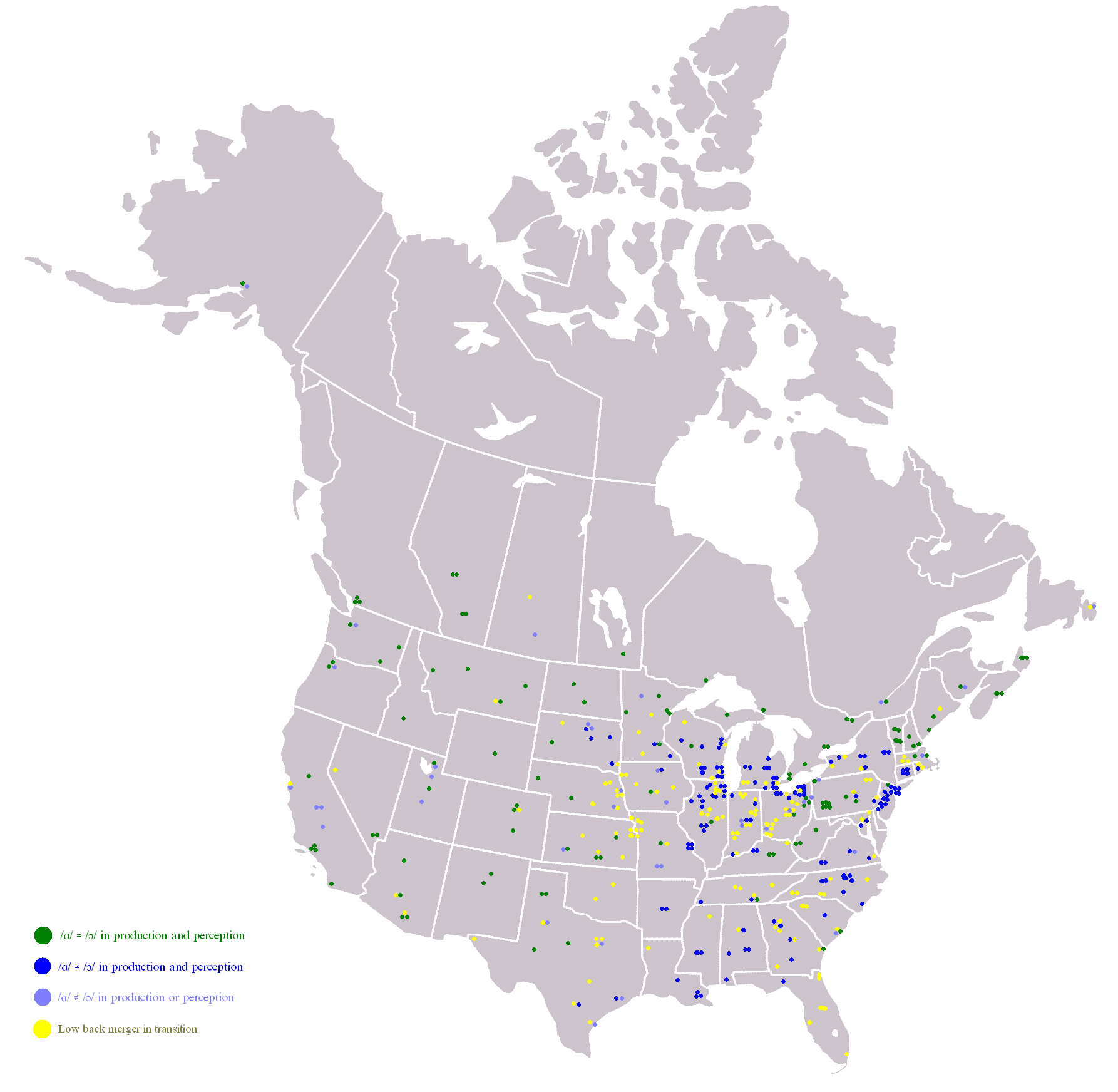
Cot–caught Merger
The ''cot''–''caught'' merger or merger, formally known in linguistics as the low back merger, is a sound change present in some dialects of English where speakers do not distinguish the vowel phonemes in "cot" and "caught". "Cot" and "caught" (along with "bot" and "bought", "pond" and "pawned", etc.) is an example of a minimal pair that is lost as a result of this sound change. The phonemes involved in the cot–caught merger, the low back vowels, are typically represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet as and , respectively (in the U.S., co-occurring with the father–bother merger, as and ). The merger is typical of most Canadian and Scottish English dialects as well as some Irish and U.S. English dialects. An additional vowel merger, the father–bother merger, which spread through North America in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, has resulted today in a three-way merger in which most Canadian and some U.S. accents have no vowel difference in words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-square Merger
In English, many vowel shifts affect only vowels followed by in rhotic dialects, or vowels that were historically followed by that has been elided in non-rhotic dialects. Most of them involve the merging of vowel distinctions and so fewer vowel phonemes occur before than in other positions of a word. Overview In rhotic dialects, is pronounced in most cases. In General American English (GA), is pronounced as an approximant or in most positions, but after some vowels, it is pronounced as ''r''-coloring. In Scottish English, is traditionally pronounced as a flap or trill , and there are no ''r''-colored vowels. In non-rhotic dialects like Received Pronunciation (RP), historic is elided at the end of a syllable, and if the preceding vowel is stressed, it undergoes compensatory lengthening or breaking (diphthongization). Thus, words that historically had often have long vowels or centering diphthongs ending in a schwa , or a diphthong followed by a schwa. * ''ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Stop
The glottal plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . As a result of the obstruction of the airflow in the glottis, the glottal vibration either stops or becomes irregular with a low rate and sudden drop in intensity. Features Features of the glottal stop: * It has no phonation, as there is no airflow through the glottis. It is voiceless, however, in the sense that it is produced without vibration of the vocal cords. Writing In the traditional Romanization of many languages, such as Arabic, the glottal stop is transcribed with the apostrophe or the symbol ʾ, which is the source of the IPA character . In many Polynesian languages that use the Latin alphabet, however, the glottal stop is written with a rotated apostrophe, (called '' ‘okina'' in Hawaiian and Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhoticity In English
Rhoticity in English is the pronunciation of the historical rhotic consonant by English speakers. The presence or absence of rhoticity is one of the most prominent distinctions by which varieties of English can be classified. In rhotic varieties, the historical English sound is preserved in all pronunciation contexts. In non-rhotic varieties, speakers no longer pronounce in postvocalic environments—that is, when it is immediately after a vowel and not followed by another vowel. For example, in isolation, a rhotic English speaker pronounces the words ''hard'' and ''butter'' as and , whereas a non-rhotic speaker "drops" or "deletes" the sound, pronouncing them as and . When an ''r'' is at the end of a word but the next word begins with a vowel, as in the phrase "bette''r a''pples", most non-rhotic speakers will pronounce the in that position (the linking R), since it is followed by a vowel in this case. The rhotic varieties of English include the dialects of South We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-based Creole Language
An English-based creole language (often shortened to English creole) is a creole language for which English was the '' lexifier'', meaning that at the time of its formation the vocabulary of English served as the basis for the majority of the creole's lexicon. Most English creoles were formed in British colonies, following the great expansion of British naval military power and trade in the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. The main categories of English-based creoles are Atlantic (the Americas and Africa) and Pacific (Asia and Oceania). Over 76.5 million people estimated globally speak some form of English-based creole. Sierra Leone, Malaysia, Nigeria, Ghana, Jamaica, and Singapore have the largest concentrations of creole speakers. Origin It is disputed to what extent the various English-based creoles of the world share a common origin. The '' monogenesis hypothesis'' posits that a single language, commonly called ''proto–Pidgin English'', spoken along the West African coast in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajan Creole
Bajan , or Bajan Dialect, is an English-based creole language with African and British influences spoken on the Caribbean island of Barbados. Bajan is primarily a spoken language, meaning that in general, standard English is used in print, in the media, in the judicial system, in government, and in day-to-day business, while Bajan is reserved for less formal situations, in music, or in social commentary. Ethnologue reports that, as of 2018, 30,000 Barbadians were native English speakers, while 260,000 natively spoke Bajan. Languages Bajan is the Caribbean creole with grammar that most resembles Standard English. There is academic debate on whether its creole features are due to an earlier pidgin state or to some other reason, such as contact with neighbouring English-based creole languages. Due to emigration to the Province of Carolina, Bajan has influenced American English and the Gullah language spoken in the Carolinas. Regionally, Bajan has ties to Belizean and Guyanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbadians
Barbadians or Bajans (pronounced ) are people who are identified with the country of Barbados, by being citizens or their descendants in the Barbadian diaspora. The connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Barbadians, several (or all) of those connections exist and are collectively the source of their identity. Barbadians are a multi-ethnic and multicultural society of various ethnic, religious and national origins; therefore Barbadians do not necessarily equate their ethnicity with their Barbadian nationality. Ethnic groups Most Barbadians are of African or mixed-race descent. They are descendants of slaves brought from West Africa. White Barbadians are mainly of British and Irish descent. There is also a small population of Syrians, Lebanese, Jewish, Indian and Chinese people in the country. Diaspora Many Barbadians now live overseas and outside of Barbados; the majority have migrated to Anglophone countries, including around 65,000 in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)