|
Ban (medieval)
In the Middle Ages, the ban (Latin ''bannus'' or ''bannum'', German ''Bann'') or banality (French ''banalité'') was originally the power to command men in war and evolved into the general authority to order and to punish. As such, it was the basis for the raising of armies and the exercise of justice.Mathieu Arnoux, "Ban, Banality", in André Vauchez (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of the Middle Age'' (James Clarke and Co., 2002 xford Reference Online, 2005. The word is of Germanic origin and first appears in fifth-century law codes. Under the Franks it was a royal prerogative, but could be delegated and, from the tenth century, was frequently usurped by lesser nobles.Theodore Evergates, "Ban, Banalité", in Joseph R. Strayer (ed.), ''Dictionary of the Middle Ages'' (New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1983), vol. 2, p. 69. The adjective "banal" or "bannal" describes things pertaining to the ban. Its modern sense of "commonplace" (even "trite") derives from the fact that tenants were frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
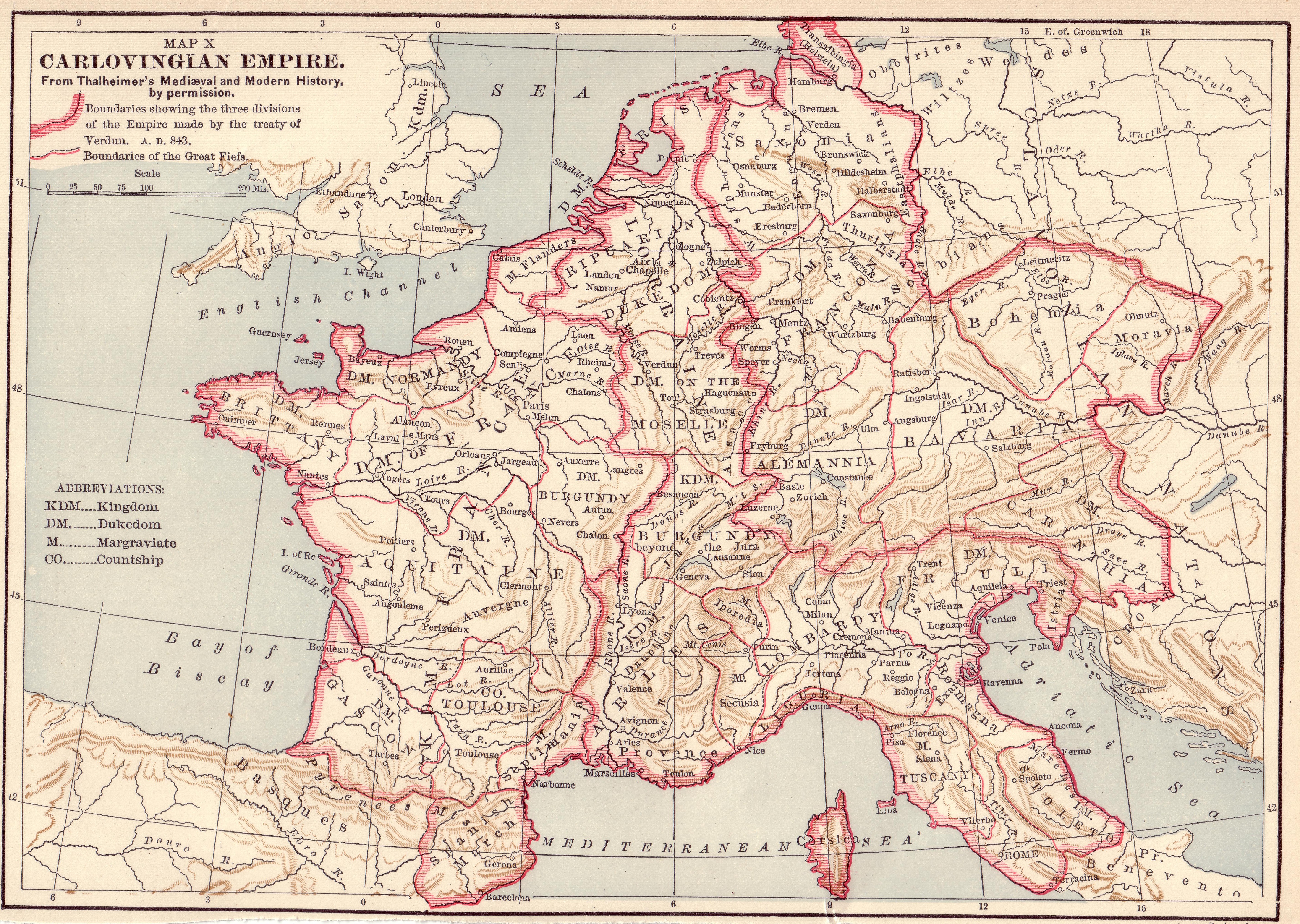
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first polity in French history. West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of Burgundy (the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Königsbann
{{Short description, Exercise of royal jurisdiction ''Königsbann'', literally king's ban ( lat, bannus, more rarely ''bannum'', from the OHG: ''ban''), was the exercise of royal jurisdiction in the Holy Roman Empire. A specific ban (German: ''Bann'') identified: * the actual order or prohibition * the penalties for contravening the ban * the region to which the ban applied The king's ban in the legal history of the Holy Roman Empire was divided into several distinct types depending on their function: * ''Heerbann'', the right to raise an army, * ''Blutbann'' (''blood courts''; high jurisdiction which included capital punishment), * ''Friedensbann'' (special royal protection of people and property), * ''Verordnungsbann'' (the authority to decide legal standards) and * ''Verwaltungsbann'' (the force to be used). The king used a so-called '' Bannleihe'' ("ban investiture") to transfer (invest) the ban, especially the ''Blutbann'', to counts or advocates to exercise. See also * I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heerbann
The ''Heerbann'' (also formerly ''Heermannie'', MHG ''herban'', OHG: ''heriban'', Mid. Latin: ''Heribannus''), in the Imperial Military Constitution (''Reichsheeresverfassung'') of the Holy Roman Empire, was the call to all free landowners capable of bearing arms to participate in a military campaign, i.e. in an imperial war ('' Reichskrieg''). According to the original meaning of the word (OHG: ''bannan'' = to 'demand' or 'prohibit', actually 'to speak'), the ''Heerbann'' was a 'call of the king or duke to military service;c.f''Heerbann''at Duden online see also king's ban. However, as the feudal system in the Holy Roman Empire developed in the Early Middle Ages, the ''Heerbann'' became superfluous as a means of raising armies and increasingly fell into disuse after the death of Charlemagne. The ''Heerbann'' was particularly onerous for poorer landowners, several of whom had to equip a knight for war (one for every 3 hides), so they would attempt to withdraw themselves fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrière-ban
In medieval and early modern France, the arrière-ban (Latin ''retrobannum'') was a general proclamation whereby the king (or duke) summoned to war all the vassals of his vassals.. The term is a folk-etymological correction of Old French ''herban'' (attested 1101), from Germanic ''here'' (army) and ''ban'' (proclamation); compare German '' Heerbann''. Although in theory, the arrière-ban depended on feudal relations, in practice it amounted to a general levy on all able-bodied males in the kingdom. In theory, this included all men between the ages of 18 and 60 years, in practice such a wide-ranging levy was never carried out for fear of conjuring an ill-suited mob. Most arrière-ban's were in fact local in nature. Conscription could be commuted by a money payment, which became an important source of revenue for the crown. The Duke of Normandy retained the right of arrière-ban and used it routinely down to 1204. The distinction between the public obligation of freemen and the feu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement In France Before The French Revolution
Unit may refer to: Arts and entertainment * UNIT, a fictional military organization in the science fiction television series ''Doctor Who'' * Unit of action, a discrete piece of action (or beat) in a theatrical presentation Music * ''Unit'' (album), 1997 album by the Australian band Regurgitator * The Units, a synthpunk band Television * ''The Unit'', an American television series * '' The Unit: Idol Rebooting Project'', South Korean reality TV survival show Business * Stock keeping unit, a discrete inventory management construct * Strategic business unit, a profit center which focuses on product offering and market segment * Unit of account, a monetary unit of measurement * Unit coin, a small coin or medallion (usually military), bearing an organization's insignia or emblem * Work unit, the name given to a place of employment in the People's Republic of China Science and technology Science and medicine * Unit, a vessel or section of a chemical plant * Blood unit, a measurem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banlieue
In France, the term banlieue (; ) refers to a suburb of a large city. Banlieues are divided into autonomous administrative entities and do not constitute part of the city proper. For instance, 80% of the inhabitants of the Paris Metropolitan Area live outside the city of Paris. Nevertheless, beginning in the 1970s, the term ''banlieue'' has taken on a particular connotation, becoming a popular word for economically-deprived suburbs featuring low-income housing projects (HLMs) that are home to large immigrant populations. People of foreign descent reside in what are often called poverty traps. History In France, since the establishment of the Third Republic at the beginning of the 1870s, communities beyond the city centre essentially stopped spreading their own boundaries, as a result of the extension of the larger Paris urban agglomeration. The city – which in France corresponds to the concept of the "urban unit" – does not necessarily have a correspondence with a single a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Fee
In feudal Anglo-Norman England and Ireland, a knight's fee was a unit measure of land deemed sufficient to support a knight. Of necessity, it would not only provide sustenance for himself, his family, and servants, but also the means to furnish himself and his retinue with horses and armour to fight for his overlord in battle. It was effectively the size of a fee (or "fief" which is synonymous with "fee") sufficient to support one knight in the ongoing performance of his feudal duties (knight-service). A knight's fee cannot be stated as a standard number of acres as the required acreage to produce a given crop or revenue would vary depending on many factors, including its location, the richness of its soil and the local climate, as well as the presence of other exploitable resources such as fish-weirs, quarries of rock or mines of minerals. If a knight's fee is deemed co-terminous with a manor, an average size would be between 1,000 and 5,000 acres, of which much in early times w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potestas
''Potestas'' is a Latin word meaning power or faculty. It is an important concept in Roman Law. Origin of the concept The idea of ''potestas'' originally referred to the power, through coercion, of a Roman magistrate to promulgate edicts, give action to litigants, etc. This power, in Roman political and legal theory, is considered analogous in kind though lesser in degree to military power. The most important magistrates (such as consuls and praetors) are said to have ''imperium'', which is the ultimate form of ''potestas,'' and refers indeed to military power. ''Potestas'' strongly contrasts with the power of the Senate and the ''prudentes'', a common way to refer to Roman jurists. While the magistrates had ''potestas'', the ''prudentes'' exercised '' auctoritas''. It is said that ''auctoritas'' is a manifestation of socially recognized knowledge, while ''potestas'' is a manifestation of socially recognized power. In Roman political theory, both were necessary to guide the '' res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. The concept originated in the Kingdom of France and found its way to foreign lands influenced by it or its fiefdoms. In England, Wales and Northern Ireland, royal demesne is the land held by the Crown, and ancient demesne is the legal term for the land held by the king at the time of the Domesday Book. Etymology The word derives from Old French , ultimately from Latin , "lord, master of a household" – ''demesne'' is a variant of ''domaine''. The word ''barton'', which is historically synonymous to ''demesne'' and is an element found in many place-names, can refer to a demesne farm: it derives from Old English ''bere'' (barley) and ''ton'' (enclosure). Development The system of manorial land tenure, broadly termed feudalism, was conceived in Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid, forced labour, that is intermittent in nature lasting for limited periods of time: typically for only a certain number of days' work each year. Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state for the purposes of public works. As such it represents a form of levy (taxation). Unlike other forms of levy, such as a tithe, a corvée does not require the population to have land, crops or cash. The obligation for tenant farmers to perform corvée work for landlords on private landed estates was widespread throughout history before the Industrial Revolution. The term is most typically used in reference to medieval and early modern Europe, where work was often expected by a feudal landowner (of their vassals), or by a monarch of their subjects. The application of the term is not limited to that time or place; the corvée has existed in modern and ancient Egypt, ancient Sumer, ancient Rome, China, Japan, everywhere in continental Europe, the Incan civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |