|
BOR-4
The BOR-4 (''БОР-4'' russian: Беспилотный Орбитальный Ракетоплан 4, , "Unpiloted Orbital Rocketplane 4") flight vehicle is a scaled (1:2) prototype of the Soviet Spiral VTHL (vertical takeoff, horizontal landing) spaceplane. An uncrewed, subscale spacecraft, its purpose was to test the heatshield tiles and reinforced carbon-carbon for the Buran space shuttle, then under development. Several of them were built and flown between 1982 and 1984 from the Kapustin Yar launch site at speeds of up to Mach 25. After reentry, they were designed to parachute to an ocean splashdown for recovery by the Soviet Navy. The testing was nearly identical to that carried out by the US Air Force ASSET program in the 1960s, which tested the heatshield design for the X-20 Dyna-Soar. On 16 March 1983 a Royal Australian Air Force P-3 Orion reconnaissance aircraft captured the first Western images of the craft as it was recovered by a Soviet ship near the Cocos Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HL-20 Personnel Launch System
The HL-20 Personnel Launch System is a NASA spaceplane concept for crewed orbital missions studied by NASA's Langley Research Center around 1990. It was envisaged as a lifting body re-entry vehicle similar to the Soviet BOR-4 spaceplane design. Its stated goals were to achieve low operational costs, improved flight safety, and a possibility of landing on conventional runways. No flight hardware was built. PLS concept With increasing national interest in obtaining routine access to space, a number of Earth-to-orbit transportation systems were studied in the mid-1980s. One, referred to as a ''Personnel Launch System'' (PLS), could utilize the HL-20 and an expendable launch system to provide crewed access complementing the Space Shuttle. A full-size engineering research model of the HL-20 was constructed in 1990 by the students and faculty of North Carolina State University and North Carolina A & T University for studying crew seating arrangements, habitability, equipment layout an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASSET (spaceplane)
ASSET, or Aerothermodynamic Elastic Structural Systems Environmental Tests was an experimental US space project involving the testing of an uncrewed sub-scale reentry vehicle. Development and testing Begun in 1960, ASSET was originally designed to verify the superalloy heat shield of the X-20 Dyna-Soar prior to full-scale crewed flights. The vehicle's biconic shape and low delta wing were intended to represent Dyna-Soar's forward nose section, where the aerodynamic heating would be the most intense; in excess of an estimated 2200 °C (4000 °F) at the nose cap. Following the X-20 program's cancellation in December 1963, completed ASSET vehicles were used in reentry heating and structural investigations with hopes that data gathered would be useful for the development of future space vehicles, such as the Space Shuttle. Built by McDonnell, each vehicle was launched on a suborbital trajectory from Cape Canaveral's Pad 17B at speeds of up to 6000 m/s before mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dream Chaser
Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane being developed by Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) Space Systems. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the cargo variant, Dream Chaser Cargo System, is operational. The crewed variant is planned to carry up to seven people and cargo to and from low Earth orbit. The cargo Dream Chaser is designed to resupply the International Space Station with both pressurized and unpressurized cargo. It is intended to launch vertically on the Vulcan Centaur rocket and autonomously land horizontally on conventional runways. A proposed version to be operated by ESA would launch on an Arianespace vehicle. Spacecraft The Dream Chaser design is derived from NASA's HL-20 Personnel Launch System spaceplane concept, which in turn is descended from a series of test vehicles, including the X-20 Dyna-Soar, Northrop M2-F2, Northrop M2-F3, Northrop HL-10, Martin X-24A and X-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Spaceplane
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-105, part of the Spiral program, was a crewed test vehicle to explore low-speed handling and landing. It was a visible result of a Soviet project to create an orbital spaceplane. The MiG 105 was nicknamed "Lapot" (russian: лапоть, or bast shoe (the word is also used as a slang for "shoe")), for the shape of its nose. Development The program was also known as the Experimental Passenger Orbital Aircraft (EPOS). Work on this project began in 1965, with the project being halted in 1969, only to be restarted in 1974 in response to the U.S. Space Shuttle Program. The test vehicle made its first subsonic free-flight test in 1976, taking off under its own power from an old airstrip near Moscow. Flight tests, totaling eight in all, continued sporadically until 1978. The actual space plane project was cancelled when the decision was made to instead proceed with the Buran project. The MiG test vehicle itself still exists and is currently on display at the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
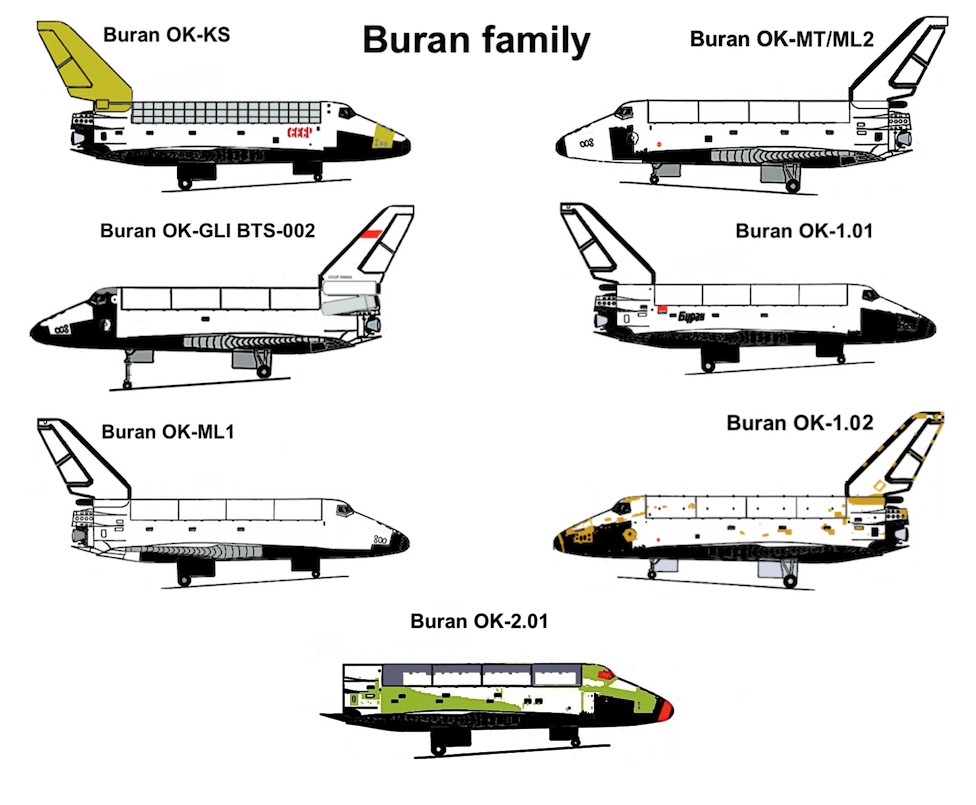
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-20 Dyna-Soar
The Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar ("Dynamic Soarer") was a United States Air Force (USAF) program to develop a spaceplane that could be used for a variety of military missions, including aerial reconnaissance, bombing, space rescue, satellite maintenance, and as a space interceptor to sabotage enemy satellites. The program ran from October 24, 1957, to December 10, 1963, cost US$660 million ($ in current dollars), and was cancelled just after spacecraft construction had begun. Other spacecraft under development at the time, such as Mercury or Vostok, were space capsules with ballistic re-entry profiles that ended in a landing under a parachute. Dyna-Soar was more like an aircraft. It could travel to distant targets at the speed of an intercontinental ballistic missile, was designed to glide to Earth like an aircraft under control of a pilot, and could land at an airfield. Dyna-Soar could also reach Earth orbit, like conventional, manned space capsules. These characteristics ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered but then landed as unpowered gliders. Four types of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese CSSHQ. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2019 all past, current, and planned orbital vehicles launch vertically on a separate rocket. Orbital spaceflight takes place at high velocities, with orbital kinetic energies typically at least 50 times greater than suborbital trajectories. Consequently, heavy heat shielding is requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buran Program
The ''Buran'' program (russian: Буран, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter program" (russian: ВКК «Воздушно-Космический Корабль», lit=Air and Space Ship), was a Soviet and later Russian reusable spacecraft project that began in 1974 at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute in Moscow and was formally suspended in 1993. In addition to being the designation for the whole Soviet/Russian reusable spacecraft project, ''Buran'' was also the name given to Orbiter K1, which completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988 and was the only Soviet reusable spacecraft to be launched into space. The ''Buran''-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket as a launch vehicle. Unlike the Space Shuttle, Buran had a capability of flying uncrewed missions, as well as performing fully automated landings. The Buran program was started by the Soviet Union as a response to the United States Space Shuttle program. The project was the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhukovsky, Moscow Oblast
Zhukovsky (russian: link=no, Жуковский, ) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Moskva River, southeast of Moscow. Population: History The urban-type settlement of Stakhanovo was founded in 1935 from the dacha settlement Otdykh (literally, "Relaxation"). It was named after Alexey Stakhanov, a famous Soviet miner. On April 23, 1947, the settlement was granted town status and renamed Zhukovsky, in honor of scientist Nikolay Zhukovsky. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Zhukovsky City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts.Law #11/2013-OZ As a municipal division, Zhukovsky City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Zhukovsky Urban Okrug.Law #171/2004-OZ Research and economy Zhukovsky is a home to the M. M. Gromov Flight Research Institute and N. Ye. Zhukovsky Central Aerohydrodynamic Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocos Islands
) , anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''" , song_type = , song = , image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands , map_caption = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands (circled in red) , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Annexed by the United Kingdom , established_date = 1857 , established_title2 = Transferred from Singaporeto Australia , established_date2 = 23 November 1955 , official_languages = None , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = , capital = West Island , coordinates = , largest_settlement_type = village , largest_settlement = Bantam , demonym = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , government_type = Directly administered dependency , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor-General , leader_name2 = David Hurley , leader_title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-3 Orion
The Lockheed P-3 Orion is a four-engined, turboprop Anti-submarine warfare, anti-submarine and maritime patrol aircraft, maritime surveillance aircraft developed for the United States Navy and introduced in the 1960s. Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed based it on the Lockheed L-188 Electra, L-188 Electra commercial airliner. The aircraft is easily distinguished from the Electra by its distinctive tail stinger or "MAD" boom, used for the Magnetic anomaly detector, magnetic anomaly detection (MAD) of submarines. Over the years, the aircraft has seen numerous design developments, most notably in its electronics packages. Numerous navies and air forces around the world continue to use the P-3 Orion, primarily for maritime patrol, reconn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |