|
Bánk Bár-Kalán
Bánk of the Bár-Kalán clan ( hu, Bárkalán nembéli Bánk; died after 1222) was an influential nobleman in the Kingdom of Hungary in the first decades of the 13th century. He was Palatine of Hungary between 1212 and 1213, Judge royal from 1221 till 1222, and Ban of Slavonia between 1208 and 1209 and in 1217. He was also ''ispán'' of at least eight counties in the first decades of the 13th century. According to later tradition, Queen Gertrude of Merania's brother raped Bánk's wife, which caused her assassination in 1213. He is the subject of the play ''Bánk bán'' by József Katona, and of the opera of the same name by Ferenc Erkel. Family According to the 14th-century ''Illuminated Chronicle'' and Henry of Mügeln's ''Ungarnchronik'', Bánk (''Banc'' or ''Banco'') was born into the ''gens'' (clan) Bár-Kalán. His parentage is unknown. The Bár-Kaláns belonged to the ancient Hungarian clans. They considered Ond, one of the seven chieftains, who led the Hungarians into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Of Hungary
The Palatine of Hungary ( hu, nádor or , german: Landespalatin, la, palatinus regni Hungariae) was the highest-ranking office in the Kingdom of Hungary from the beginning of the 11th century to 1848. Initially, Palatines were representatives of the monarchs, later (from 1723) the vice-regent (viceroy). In the early centuries of the kingdom, they were appointed by the king, and later (from 1608) were elected by the Diet of the Kingdom of Hungary. A Palatine's jurisdiction included only Hungary proper, in the Kingdom of Croatia until 1918 the ban held similar function as the highest office in the Kingdom (after the king himself), monarch's representative, commander of the royal army and viceroy (after the union of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia with Hungary in 1102). Title The earliest recorded Medieval Latin form of the title was ''comes palatii'' ("count of the palace"); it was preserved in the deed of foundation of the Tihany Abbey, issued in 1055. A new varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Of Mügeln
Henry may refer to: People * Henry (given name) * Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany ** Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen V Of Hungary
Stephen V ( hu, V. István, hr, Stjepan V., sk, Štefan V; before 18 October 1239 – 6 August 1272, Csepel Island) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of Béla IV of Hungary, King Béla IV and Maria Laskarina. King Béla had his son coronation of the Hungarian monarch, crowned king at the age of six and appointed him Duke of Slavonia. Still a child, Stephen married Elizabeth the Cuman, Elizabeth, a daughter of a chieftain of the Cumans whom his father settled in the Great Hungarian Plain. King Béla appointed Stephen Duke of Transylvania in 1257 and Duke of Styria in 1258. The local noblemen in Duchy of Styria, Styria, which had been annexed four years before, opposed his rule. Assisted by King Ottokar II of Bohemia, they rebelled and expelled Stephen's troops from most parts of Styria. After Ottokar II routed the united army of Stephen and his father in the Battle of Kressenbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Kacsics
Simon from the kindred Kacsics ( hu, Kacsics nembeli Simon, hr, Šimun Kačić; died after 1228) was a Hungarian distinguished nobleman from the ''gens'' Kacsics (Kačić). He was one of the leading instigators of Queen Gertrude's assassination in September 1213. Origin His only known brother was Michael Kacsics, Voivode of Transylvania (1209–1212) and Ban of Slavonia in 1212. As Michael and Simon suddenly appeared in Hungarian contemporary sources without genealogical antecedents, several scholars, including Croatian historian Ivan Majnarić considered their kindred may have been descendants of the Omiš Kačić family, one of the Croatian "twelve noble tribes" described in the '' Pacta conventa'' and Supetar Cartulary. The brothers were first mentioned in the early 13th century, they possessed villages in Nógrád County, for instance Salgó and Hollókő. Majnarić argued the Kacsics brothers may have belonged to supporters of Duke Andrew in his rebellion against th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew II Of Hungary
Andrew II ( hu, II. András, hr, Andrija II., sk, Ondrej II., uk, Андрій II; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and 1210. He was the younger son of Béla III of Hungary, who entrusted him with the administration of the newly conquered Principality of Halych in 1188. Andrew's rule was unpopular, and the boyars (or noblemen) expelled him. Béla III willed property and money to Andrew, obliging him to lead a crusade to the Holy Land. Instead, Andrew forced his elder brother, King Emeric of Hungary, to cede Croatia and Dalmatia as an appanage to him in 1197. The following year, Andrew occupied Hum. Despite the fact that Andrew did not stop conspiring against Emeric, the dying king made Andrew guardian of his son, Ladislaus III, in 1204. After the premature death of Ladislaus, Andrew ascended the thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gömör County
Gömör (, , , Latin: ''Gömörinum'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the 19th century, and in the beginning of the 20th century, it was united with the Kis-Hont County to form Gömör-Kishont County. Its territory is located in southern Slovakia and northern Hungary. Today names Gömör/Gemer are only an informal designation of the corresponding territory without administrative role. Geography Gemer region is situated in Slovenské rudohorie approximately between the present-day Slovak-Hungarian border, the towns Poltár and Rožňava and the Low Tatras (Nízke Tatry). It borders traditional regions Spiš to the North, Abov to the East, Borsod to the South, Heves to the South-West, Novohrad to the west, and Zvolen and Liptov regions at North-West. The river Slaná (Sajó) flows through Gemer from North to the South. Gömör és Kishont County was covering area of 4,289 km² in 1910. Capitals The capital of Gömör region was orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bereg County
Bereg ( rue, Береґ; ) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now mostly in western Ukraine and a smaller part in northeastern Hungary. The capital of the county was Beregszász ("Berehove" in Ukrainian, ''Berehovo'' in Rusyn, ''Bergsaß'' in German, ''Beregovo'' in Russian, ''Bereg'' in Romanian). Geography Bereg county shared borders with the Austrian crownland Galicia (now in Poland and Ukraine) and the Hungarian counties Máramaros, Ugocsa, Szatmár, Szabolcs and Ung. It was situated between the Carpathian Mountains in the north and the river Tisza in the south. Its area was 3788 km² around 1910. History Bereg is one of the oldest counties in Hungary. In 1920 the Treaty of Trianon assigned most of the territory to Czechoslovakia. The southwestern part remained in Hungary and the county of Szatmár-Ugocsa-Bereg was created in 1923. Following the First Vienna Award Szatmár County was recreated, thus Bereg-Ugocsa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szabolcs County
Szabolcs was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now part of Hungary, except for three villages which are in the Zakarpattia Oblast of Ukraine. The capital of the county was Nyíregyháza. Geography Szabolcs county shared borders with the counties of Borsod, Zemplén, Ung, Bereg, Szatmár, Bihar and Hajdú. It was situated mostly south of the river Tisza. Its area was 4,637 km² around 1910. History Szabolcs is one of the oldest counties of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the 17th century, the towns of Hajdú separated from the county, creating the Hajdú district. The capital of Szabolcs County was initially Szabolcs (now a village), later Nagykálló took over this role (1747-1867), and since 1867 the capital was moved to Nyíregyháza. After World War I, it was merged with a very small part of the former Ung County to form Szabolcs-Ung county, with Nyíregyháza as the capital. However, the villages of Eszeny (present-day Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Csongrád County (former)
Csongrád ( Hungarian: ''Csongrád'', Serbian: ''Čongrad'' or ''Чонград'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was smaller than that of present-day Csongrád-Csanád County, is now part of Hungary, except a very small area which belongs to Serbia. The capital of the county was Szentes. Name The name Csongrád/Čongrad is Slavic by origin. In Slavic languages, this name means "a black city" (čon/čorni = black, grad = city/town). Indeed, the county was named after a town of Csongrád. Geography Csongrád county shared borders with the Hungarian counties Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok, Békés, Csanád, Torontál and Bács-Bodrog. The river Tisza flowed through the county. Its area was 3,544 km2 around 1910. History Csongrád county arose in the 11th century as one of the first counties of the Kingdom of Hungary. It was taken by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century, and reconquered by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
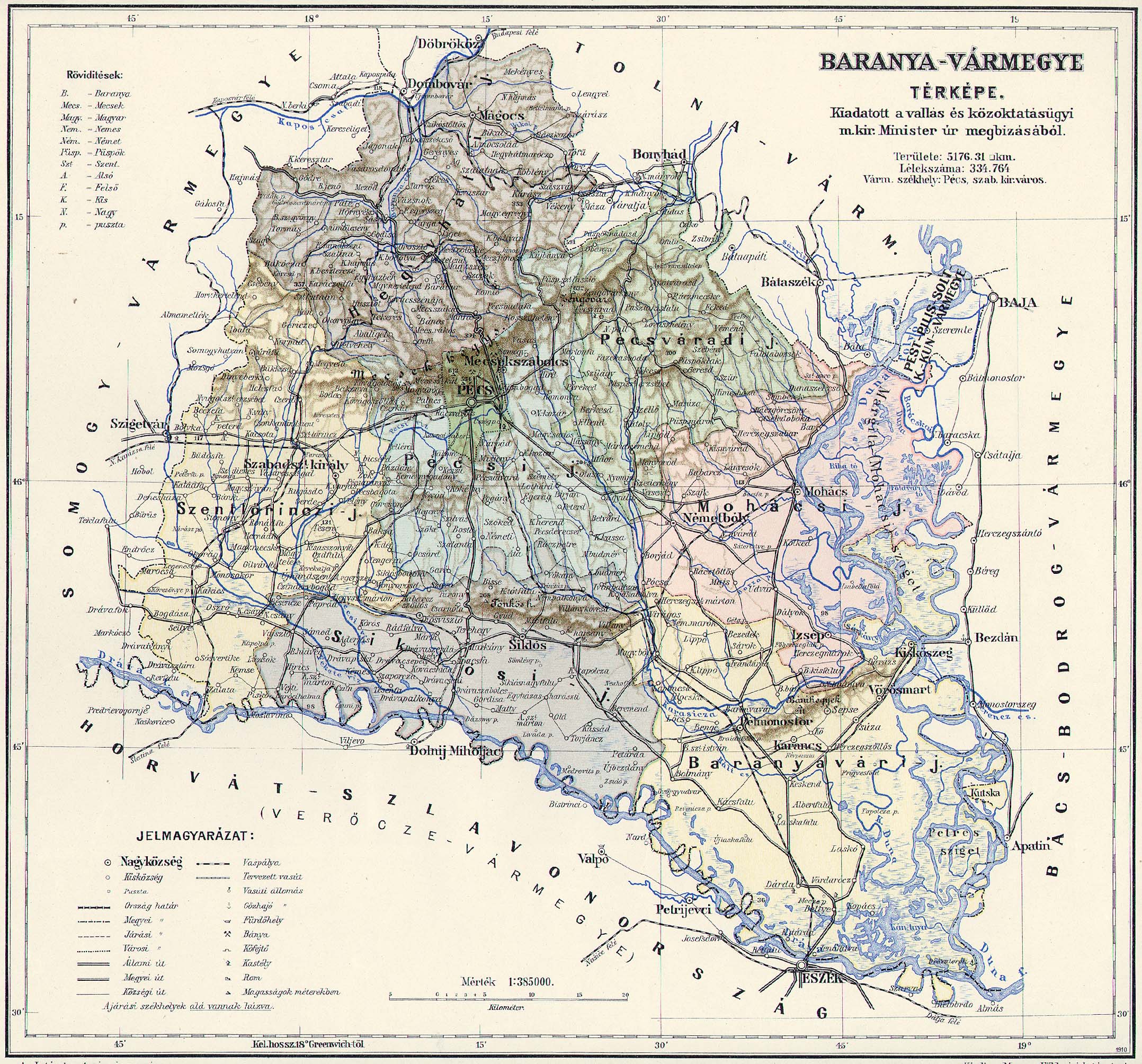
Baranya County (former)
Baranya ( hu, Baranya, hr, Baranja, sr, Барања / ''Baranja'', ger, Branau) was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between present-day Baranya County of Hungary and Osijek-Baranja County of Croatia. The capital of the county was Pécs. Geography Baranya county was located in Baranya region. It shared borders with the Hungarian counties Somogy, Tolna, Bács-Bodrog and Verőce (the latter county was part of Croatia-Slavonia). The county stretched along the rivers Drava (north bank) and Danube (west bank), up to their confluence. Its area was 5,176 km2 around 1910. Historical background Baranya county arose as one of the first counties of the Kingdom of Hungary, in the 11th century. Stephen I of Hungary founded an episcopal seat here. In the 15th century, Janus Pannonius was the Bishop of Pécs. In the 16th century, the Ottoman Empire conquered Baranya, and included it into the sanjak of Mohács, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the lowlands, the plain that remained when the Pliocene Epoch ''Pannonian Sea'' dried out. It is a geomorphological subsystem of the Alps-Himalaya system, specifically a sediment-filled back-arc basin which spread apart during the Miocene. The plain or basin is diagonally bisected by the Transdanubian Mountains, separating the larger Great Hungarian Plain (including the Eastern Slovak Lowland) from the Little Hungarian Plain. It forms a topographically discrete unit set in the European landscape, surrounded by imposing geographic boundaries—the Carpathian Mountains and the Alps. The Rivers Danube and Tisza divide the basin roughly in half. It extends roughly between Vienna in the northwest, Košice in the northeast, Zagreb in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)