|
Build System (software Development)
A build system or build automation tool is a tool or set of tools that automate the compilation and linking of source code into an executable program or library. It streamlines the software development process by managing dependencies, resolving conflicts, and ensuring consistent builds across different environments. When software projects grow complex, their build steps may involve multiple programming languages or compilation units, making manual build processes increasingly cumbersome. Dependencies between code components necessitate careful ordering and potentially different tools for each piece. Managing these dependencies manually can quickly lead to version conflicts, stale binaries, and difficulty tracking updates, making solutions such as shell scripts too difficult to maintain. While individual developers might compile code directly, a robust build system is foundational to efficient software development in large organizations and teams, where automated builds b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Tool
A programming tool or software development tool is a computer program that is used to develop another computer program, usually by helping the developer manage computer files. For example, a programmer may use a tool called a source code editor to edit source code files, and then a compiler to convert the source code into machine code files. They may also use build tools that automatically package executable program and data files into shareable packages or install kits. A set of tools that are run one after another, with each tool feeding its output to the next one, is called a toolchain. An integrated development environment (IDE) integrates the function of several tools into a single program. Usually, an IDE provides a source code editor as well as other built-in or plug-in tools that help with compiling, debugging, and testing. Whether a program is considered a development tool can be subjective. Some programs, such as the GNU compiler collection The GNU Compiler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bazel (software)
Bazel () is a free and open-source software tool used for the automation of building and testing software. Similar to build tools like Make, Apache Ant, and Apache Maven, Bazel builds software applications from source code using rules. Rules and macros are created in the Starlark language, a dialect of Python. There are built-in rules for building software written in Java, Kotlin, Scala, C, C++, Go, Python, Rust, JavaScript, Objective-C, and bash scripts. Bazel can produce software application packages suitable for deployment for the Android and iOS operating systems. History In 2006, Google started the development of a build tool called ''Blaze''. The motivation was to have a build system that provides both speed and correctness in a large monorepo. Bazel was created as an open-source port of Blaze, using its anagram as a name. Bazel was first released in March 2015 and entered beta by September 2015. Version 1.0 was released in October 2019. Rationale Bazel has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
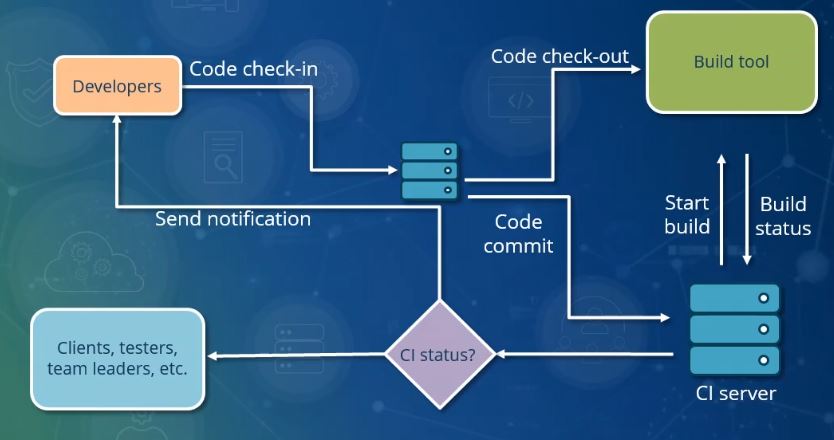
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Build Automation
Build automation is the practice of building software systems in a relatively unattended fashion. The build is configured to run with minimized or no software developer interaction and without using a developer's personal computer. Build automation encompasses the act of configuring the build system as well the resulting system itself. Build automation encompasses both sequencing build operations via non-interactive interface tools and running builds on a shared server. Tools Build automation tools allow for sequencing the tasks of building software via a non-interactive interface. Existing tools such as Make can be used via custom configuration file or using the command-line. Custom tools such as shell scripts can also be used, although they become increasingly cumbersome as the codebase grows more complex. Some tools, such as shell scripts, are task-oriented declarative programming. They encode sequences of commands to perform with usually minimal conditional logic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in (computing)
In computing, a plug-in (also spelled plugin) or add-in (also addin, add-on, or addon) is a software component that extends the functionality of an existing software system without requiring the system to be software build, re-built. A plug-in software feature, feature is one way that a system can be customizable. Applications support plug-ins for a variety of reasons including: * Enable third-party developers to extend an application * Support easily adding new features * Reduce the size of an application by not loading unused features * Separate source code from an application because of incompatible software licenses Examples Examples of plug-in use for various categories of applications: * Digital audio workstations and audio editing software use audio plug-ins to generate, process or analyze sound. Ardour (software), Ardour, Audacity (audio editor), Audacity, Cubase, FL Studio, Logic Pro, Logic Pro X and Pro Tools are examples of such systems. * Email clients use plug-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computing, computation in which many calculations or Process (computing), processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: Bit-level parallelism, bit-level, Instruction-level parallelism, instruction-level, Data parallelism, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of Desktop computer, desktop and laptop computers, it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS and SteamOS. , the most recent release of macOS is MacOS Sequoia, macOS 15 Sequoia, the 21st major version of macOS. Mac OS X succeeded classic Mac OS, the primary Mac operating systems, Macintosh operating system from 1984 to 2001. Its underlying architecture came from NeXT's NeXTSTEP, as a result of NeXT#1997–2006: Acquisition by Apple, Apple's acquisition of NeXT, which also brought Steve Jobs back to Apple. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released on March 24, 2001. Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incremental Build (build System)
An incremental build is a process within a build system where build tools use an incremental compiler to recompile only the parts of a software project that have changed since the last build, rather than rebuilding everything from scratch. This optimization reduces build time by leveraging dependency tracking, caching, and selective compilation. Incremental builds are especially valuable in large-scale software projects, where recompiling the entire codebase can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By identifying and compiling only the modified components—such as source files, libraries, or modules—the build system ensures faster iteration cycles, enabling developers to test and debug changes more efficiently. The process relies on a dependency graph, which maps relationships between files, modules, or components in the project. When a change is detected, the build system traverses this graph to determine which parts of the project are affected and need to be recompi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language, low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different Central processing unit, CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
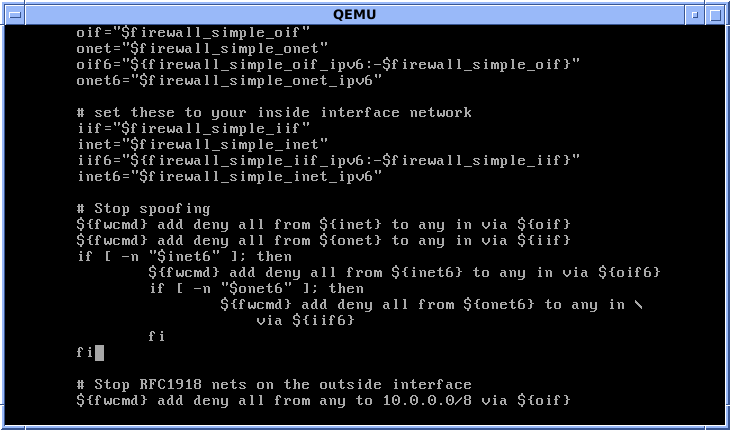
Shell Script
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be command languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing text. A script which sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup or logging, is called a wrapper. The term is also used more generally to mean the automated mode of running an operating system shell; each operating system uses a particular name for these functions including batch files (MSDos-Win95 stream, OS/2), command procedures (VMS), and shell scripts (Windows NT stream and third-party derivatives like 4NT—article is at cmd.exe), and mainframe operating systems are associated with a number of terms. Shells commonly present in Unix and Unix-like systems include the Korn shell, the Bourne shell, and GNU Bash. While a Unix operating system may have a different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |