|
Bruce E. Cain
Bruce E. Cain (born November 28, 1948) is a professor of political science at Stanford University and director of the Bill Lane Center for the American West. Cain's fields of interest include American politics, political regulation, democratic theory, and state and local government. He has written extensively on elections, legislative representation, California politics, redistricting, and political regulation. In addition to his academic work, Cain frequently is quoted in national and international media, and regularly appears as a political expert for KGO-TV in the San Francisco Bay Area. He is a member of the American Political Science Association, and serves on the editorial boards of ''Election Law Journal'' and ''American Politics Research''. Cain has been a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences since 2000. During AY 2012–13, Cain will serve as a Straus Fellow at New York University's Straus Institute for the Advanced Study of Law and Justice. Education Cain g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. Specialists in the field are political scientists. History Origin Political science is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political institutions, political thought and behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. As a social science, contemporary political science started to take shape in the latter half of the 19th century and began to separate itself from political philosophy and history. Into the late 19th century, it was still uncommon for political science to be considered a distinct field from history. The term "political science" was not always distinguished from political philosophy, and the modern dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland, California, Oakland and Emeryville, California, Emeryville to the south and the city of Albany, California, Albany and the Unincorporated area, unincorporated community of Kensington, California, Kensington to the north. Its eastern border with Contra Costa County, California, Contra Costa County generally follows the ridge of the Berkeley Hills. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census recorded a population of 124,321. Berkeley is home to the oldest campus in the University of California, the University of California, Berkeley, and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, which is managed and operated by the university. It also has the Graduate Theological Union, one of the largest religious studies institutions in the world. Berkeley is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairbanks, Alaska
Fairbanks is a Municipal home rule, home rule city and the county seat, borough seat of the Fairbanks North Star Borough, Alaska, United States. Fairbanks is the largest city in the Interior Alaska, interior region of Alaska and the second largest in the state. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census put the population of the city proper at 32,515 and the population of the Fairbanks North Star Borough at 95,655, making it the second most populous metropolitan area in Alaska, after Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage. The Metropolitan Statistical Area encompasses all of the Fairbanks North Star Borough and is the northernmost metropolitan statistical area in the United States, located by road ( by air) south of the Arctic Circle. In August 1901, E. T. Barnette founded a trading post on the south bank of the Chena River. A gold discovery near the trading post sparked the Fairbanks Gold Rush, and many miners moved to the area. There was a boom in construction, and in November 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Sigma Alpha
Pi Sigma Alpha ( or PSA), the National Political Science Honor Society, is the only honor society for college and university students of political and social sciences in the United States. Its purpose is to recognize and promote high academic achievement in the field of political science. It is a member of the Association of College Honor Societies. Chapters The first chapter of Pi Sigma Alpha was founded in 1920 at the University of Texas at Austin, and the society has grown over the years to nearly 850 campuses (as of 2020). A local chapter may be established at any college or university granting the baccalaureate or higher degrees, which is accredited by a regional or national accrediting association, and which offers a major sequence of courses in political science through an appropriate administrative department, school, or division of the institution, and which conforms to other requirements established by the Executive Council of the society. Chapters are guided by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Service
A public service or service of general (economic) interest is any service intended to address the needs of aggregate members of a community, whether provided directly by a public sector agency, via public financing available to private businesses or voluntary organisations, or by private businesses subject to government regulation. Some public services are provided on behalf of a government's residents or in the interest of its citizens. The term is associated with a social consensus (usually expressed through democratic elections) that certain services should be available to all, regardless of income, physical ability or mental acuity. Examples of such services include the fire services, police, air force, paramedics and public service broadcasting. Even where public services are neither publicly provided nor publicly financed, they are usually subject to regulation beyond that applying to most economic sectors for social and political reasons. Public policy, when made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Legislature (United States)
In the United States, the state legislature is the legislative branch in each of the 50 U.S. states. A legislature generally performs state duties for a state in the same way that the United States Congress performs national duties at the national level. Generally, the same system of checks and balances that exists at the federal level also exists between the state legislature, the state executive officer (governor) and the state judiciary. In 27 states, the legislature is called the ''legislature'' or the ''state legislature'', while in 19 states the legislature is called the ''general assembly''. In Massachusetts and New Hampshire, the legislature is called the ''general court'', while North Dakota and Oregon designate the legislature the ''legislative assembly''. Legislature overview Responsibilities The responsibilities of a state legislature vary from state to state, depending on state's constitution. The primary function of any legislature is to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partisan (political)
A partisan is a committed member or supporter of a political party or political movement. In multi-party systems, the term is used for persons who strongly support their party's policies and are reluctant to compromise with political opponents. United States The term's meaning has changed dramatically over the last 60 years in the United States. Before the American National Election Study (described in Angus Campbell et al., in '' The American Voter'') began in 1952, an individual's partisan tendencies were typically determined by their voting behaviour. Since then, "partisan" has come to refer to an individual with a psychological identification with one or the other of the major parties. Depending on their political beliefs, candidates may join a party. As they build the framework for career advancement, parties are more often than not the preferred choice for candidates. There are many parties in a system, and candidates often join them instead of standing as an Independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without legislator, elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy model which occurs in the majority of established democracies. The theory and practice of direct democracy and participation as its common characteristic constituted the core of the work of many theorists, philosophers, politicians, and social critics, among whom the most important are Jean-Jacques Rousseau, John Stuart Mill, and G. D. H. Cole, G.D.H. Cole. Overview In direct democracy the people decide on policies without any intermediary or representative, whereas in a representative democracy people vote for representatives who then enact policy initiatives. Depending on the particular system in use, direct democracy might entail passing executive decisions, the use of sortition, making laws, directly electing or dismissing officials, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
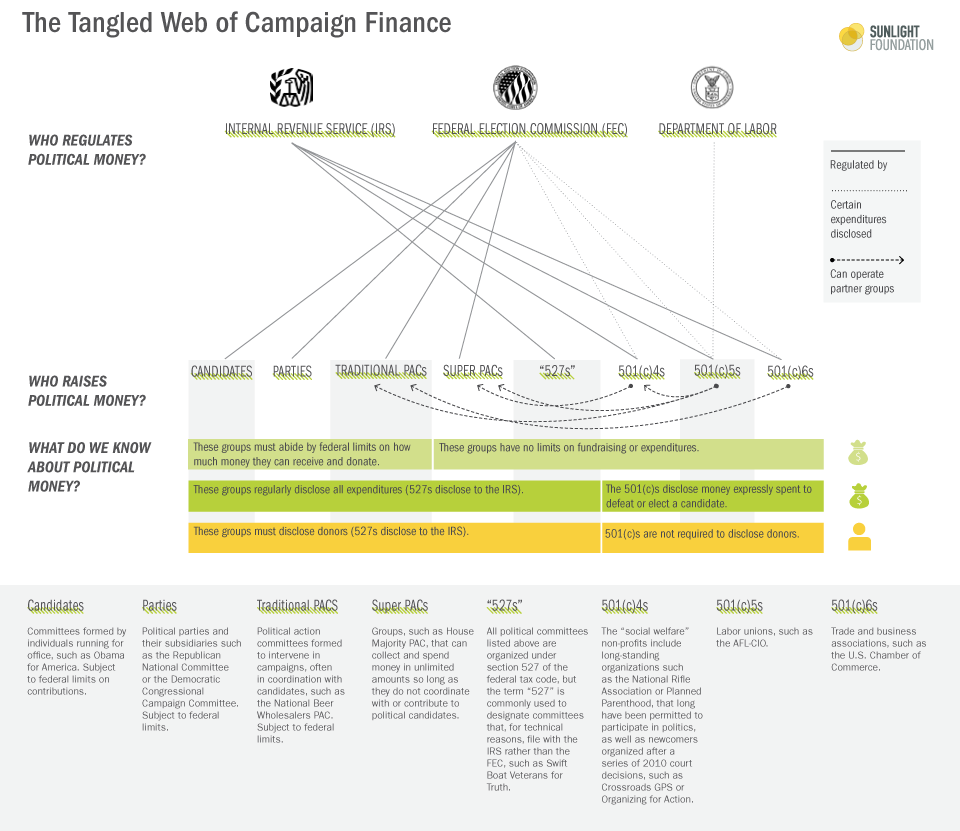
Campaign Finance
Campaign financealso called election finance, political donations, or political financerefers to the funds raised to promote candidates, political parties, or policy initiatives and referendums. Donors and recipients include individuals, corporations, political parties, and charitable organizations. Political campaigns usually involve considerable costs, travel, staff, political consulting, and advertising. Campaign spending depends on the region. For instance, in the United States, television advertising time must be purchased by campaigns, whereas in other countries, it is provided for free. The need to raise money to maintain expensive political campaigns diminishes ties to a representative democracy because of the influence large contributors have over politicians. Although the political science literature indicates that most contributors give to support parties or candidates with whom they are already in agreement, there is wide public perception that donors expect gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Term Limit
A term limit is a legal restriction on the number of terms a person may serve in a particular elected office. When term limits are found in presidential and semi-presidential systems they act as a method of curbing the potential for monopoly, where a leader effectively becomes " president for life". Term limits may be a lifetime limit on the number of terms an officeholder may serve, or a limit on the number of consecutive terms. According to a 2020 analysis, nearly one in four incumbents who face term limits seek to circumvent the term limits through various strategies, including constitutional amendments, working with the judiciary to reinterpret the term limits, let a placeholder govern for the incumbent, and cancelling or delaying elections. History Europe Term limits date back to Ancient Greece and the Roman Republic, as well as the Republic of Venice. In ancient Athenian democracy, many officeholders were limited to a single term. Council members were allowed a maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election Law
Election law is a branch of public law that relates to the democratic processes, election of representatives and office holders, and referendums, through the regulation of the electoral system, voting rights, ballot access, election management bodies, election campaign, the division of the territory into electoral zones, the procedures for the registration of voters and candidacies, its financing and propaganda, voting, counting of votes, scrutiny, electoral disputes, electoral observation and all contentious matters derived from them. It is a discipline falling at the juncture of constitutional law and political science, and involves "the politics of law and the law of politics". History and the field After the legally-contested 2000 United States presidential election between George W. Bush and Al Gore, the importance of election law has grown in the United States. According to the National Law Journal, election law "grew from a niche to multi million-dollar draw." The UC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminar
A seminar is a form of academic instruction, either at an academic institution or offered by a commercial or professional organization. It has the function of bringing together small groups for recurring meetings, focusing each time on some particular subject, in which everyone present is requested to participate. This is often accomplished through an ongoing Socratic method, Socratic dialogue with a seminar leader or instructor, or through a more formal presentation of research. It is essentially a place where assigned readings are discussed, questions can be raised and debates can be conducted. Etymology The word ''seminar'' was borrowed from German (in which it is capitalized as ), and is ultimately derived from the Latin word , meaning 'seed plot' (an old-fashioned term for 'seedbed'). Its Root (linguistics), root word is (Latin for 'seed'). Overview In some European universities, a ''seminar'' may be a large lecture course, especially when conducted by a renowned thinker ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |