|
Bose–Einstein Condensates
Bose–Einstein may refer to: * Bose–Einstein condensate, a phase of matter in quantum mechanics ** Bose–Einstein condensation (network theory), the application of this model in network theory ** Bose–Einstein condensation of polaritons ** Bose–Einstein condensation of quasiparticles * Bose–Einstein correlations * Bose–Einstein integral * Bose–Einstein statistics, in particle statistics See also *Bose (other) *Einstein (other) *Boson (other) *Satyendra Nath Bose Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was an Indian theoretical physicist and mathematician. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for Bose–Einstein statist ..., Indian physicist * Albert Einstein (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensate
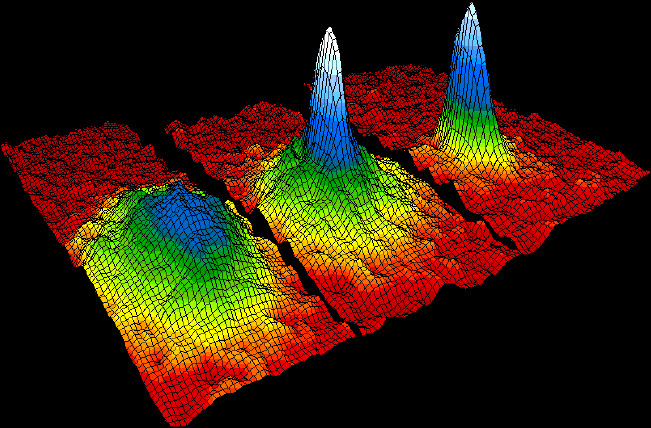
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einstein condensate, absolute zero, i.e. . Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which microscopic Quantum mechanics, quantum-mechanical phenomena, particularly wave interference#Quantum interference, wavefunction interference, become apparent Macroscopic quantum phenomena, macroscopically. More generally, condensation refers to the appearance of macroscopic occupation of one or several states: for example, in BCS theory, a superconductor is a condensate of Cooper pairs. As such, condensation can be associated with phase transition, and the macroscopic occupation of the state is the order parameter. Bose–Einstein condensate was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein, credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensation (network Theory)
Bose–Einstein may refer to: * Bose–Einstein condensate, a phase of matter in quantum mechanics ** Bose–Einstein condensation (network theory), the application of this model in network theory ** Bose–Einstein condensation of polaritons ** Bose–Einstein condensation of quasiparticles * Bose–Einstein correlations * Bose–Einstein integral * Bose–Einstein statistics, in particle statistics See also * Bose (other) * Einstein (other) * Boson (other) *Satyendra Nath Bose Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was an Indian theoretical physicist and mathematician. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for Bose–Einstein statist ..., Indian physicist * Albert Einstein (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensation Of Polaritons
Bose–Einstein condensation of polaritons is a growing field in semiconductor optics research, which exhibits spontaneous coherence similar to a laser, but through a different mechanism. A continuous transition from polariton condensation to lasing can be made similar to that of the crossover from a Bose–Einstein condensate to a BCS state in the context of Fermi gases. Polariton condensation is sometimes called “lasing without inversion”. Overview Polaritons are bosonic quasiparticles which can be thought of as dressed photons. In an optical cavity, photons have an effective mass, and when the optical resonance in a cavity is brought near in energy to an electronic resonance (typically an exciton) in a medium inside the cavity, the photons become strongly interacting, and repel each other. They therefore act like atoms which can approach equilibrium due to their collisions with each other, and can undergo Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) at high density or low temperatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensation Of Quasiparticles
Bose–Einstein condensation can occur in quasiparticles, particles that are effective descriptions of collective excitations in materials. Some have integer spins and can be expected to obey Bose–Einstein statistics like traditional particles. Conditions for condensation of various quasiparticles have been predicted and observed. The topic continues to be an active field of study. Properties BECs form when low temperatures cause nearly all particles to occupy the lowest quantum state. Condensation of quasiparticles occurs in ultracold gases and materials. The lower masses of material quasiparticles relative to atoms lead to higher BEC temperatures. An ideal Bose gas has a phase transitions when inter-particle spacing approaches the thermal De-Broglie wavelength: k_B T =~ \hbar^2 n^/M. The critical concentration is then N \propto (T/2 \pi)^3 u^ P / v \hbar^3, leading to a critical temperature: T_c < 32\pi^3 \hbar^6 V^2u_0P^2. The particles obey the Bose–Einstein dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Correlations
In astronomy, optics and particle physics, the Bose–Einstein correlations refer to correlations between identical bosons (like the photon, the quanta of light). Description The interference between two (or more) waves establishes a correlation between these waves. In optics, two beams of light are said to interfere coherently, when the phase difference between their waves is constant; if this phase difference is random or changing the beams are incoherent. In quantum mechanics, where to each particle there is associated a wave function, we encounter thus interference and correlations between two (or more) particles, described mathematically by second or higher order correlation functions.The correlation function of order ''n'' defines the transition amplitudes between states containing ''n'' particles. These correlations have quite specific properties for identical particles. We then distinguish Bose–Einstein correlations for bosons and Fermi–Dirac correlations fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Integral
In mathematics, the polylogarithm (also known as Jonquière's function, for Alfred Jonquière) is a special function of order and argument . Only for special values of does the polylogarithm reduce to an elementary function such as the natural logarithm or a rational function. In quantum statistics, the polylogarithm function appears as the closed form of integrals of the Fermi–Dirac distribution and the Bose–Einstein distribution, and is also known as the Fermi–Dirac integral or the Bose–Einstein integral. In quantum electrodynamics, polylogarithms of positive integer order arise in the calculation of processes represented by higher-order Feynman diagrams. The polylogarithm function is equivalent to the Hurwitz zeta function — either function can be expressed in terms of the other — and both functions are special cases of the Lerch transcendent. Polylogarithms should not be confused with polylogarithmic functions, nor with the offset logarithmic integral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Statistics
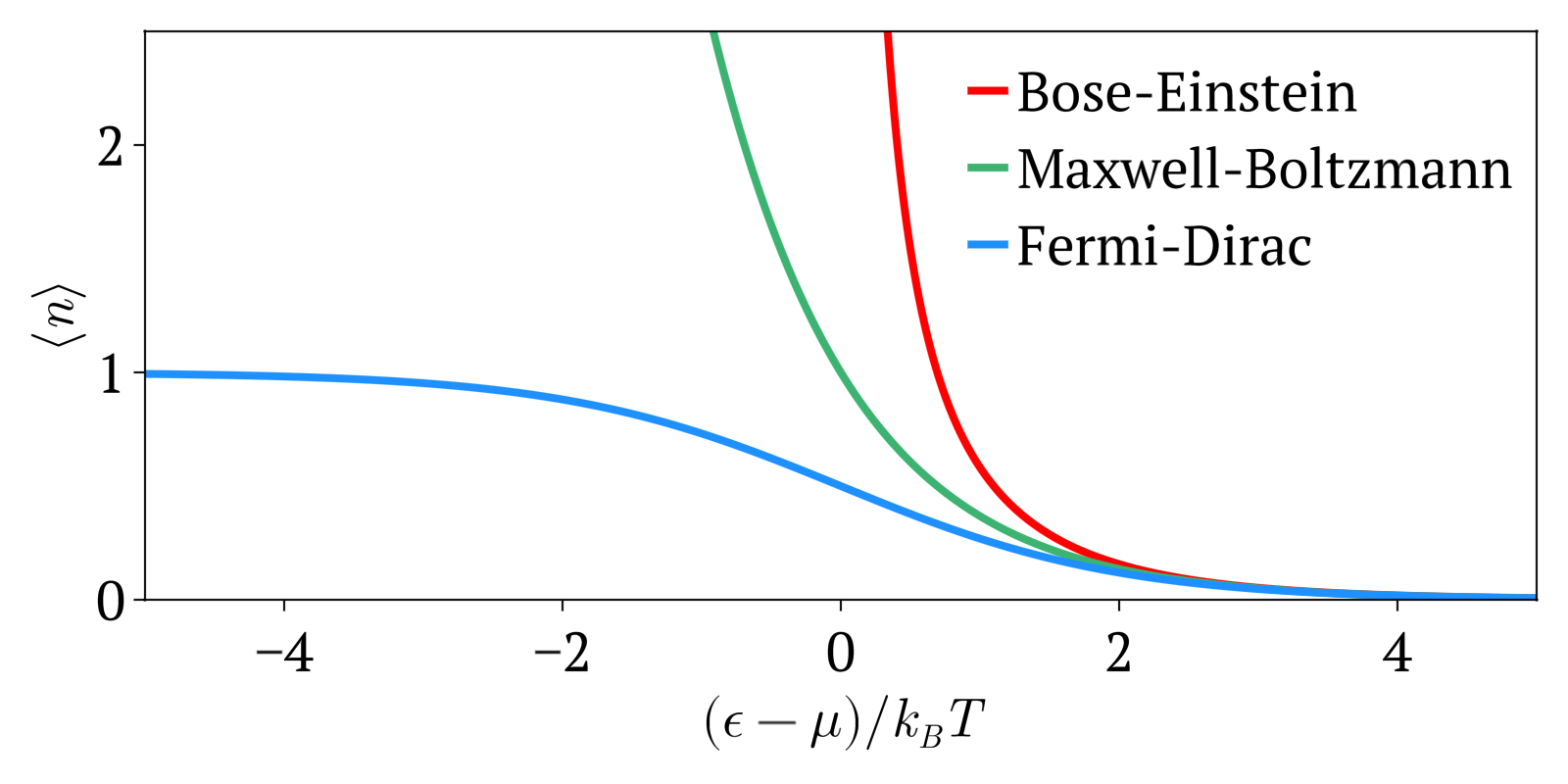
In quantum statistics, Bose–Einstein statistics (B–E statistics) describes one of two possible ways in which a collection of non-interacting identical particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states at thermodynamic equilibrium. The aggregation of particles in the same state, which is a characteristic of particles obeying Bose–Einstein statistics, accounts for the cohesive streaming of laser light and the frictionless creeping of superfluid helium. The theory of this behaviour was developed (1924–25) by Satyendra Nath Bose, who recognized that a collection of identical and indistinguishable particles could be distributed in this way. The idea was later adopted and extended by Albert Einstein in collaboration with Bose. Bose–Einstein statistics apply only to particles that do not follow the Pauli exclusion principle restrictions. Particles that follow Bose-Einstein statistics are called bosons, which have integer values of spin. In contrast, particles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose (other)
Bose may refer to: * Bose (crater), a lunar crater. * ''Bose'' (film), a 2004 Indian Tamil film starring Srikanth and Sneha * Bose (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name) * Bose (given name), a given name * Bose, Italy, a ''frazione'' in Magnano, Province of Biella ** Bose Monastic Community, a monastic community in the village * Bose, Poland * Bose Corporation, an audio company * Bose Ogulu, Nigerian manager of Burna Boy * Baise, or Bose, a prefecture-level city in Guangxi, China * '' Bose: The Forgotten Hero'', a 2004 Indian film about Subhas Chandra Bose * '' Bose: Dead/Alive'', a web series about Subhas Chandra Bose See also * * Boise (other) * Bos (other) * Bose–Einstein (other), articles relating to Bose–Einstein statistics In quantum statistics, Bose–Einstein statistics (B–E statistics) describes one of two possible ways in which a collection of non-interacting identical particles may occupy a set of availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein (other)
Albert Einstein (1879–1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist. Einstein may also refer to: * Einstein (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Science and technology * Einstein Observatory, the first fully imaging X-ray telescope put into orbit * Einstein Probe, Chinese X-ray telescope * Einstein (US-CERT program), an intrusion detection program used by the United States Department of Homeland Security * Einstein Telescope, a gravitational wave detector under design * Einstein Tower, an astrophysical observatory in Potsdam, Germany * Einstein (unit), a physical unit defined primarily as the energy in one mole of photons and sometimes as one mole of photons * Tatung Einstein, a personal computer produced by Taiwanese corporation Tatung Places * 2001 Einstein, a main belt asteroid * Einstein (crater), a large lunar crater * Mount Einstein in Alaska * Mount Einstein in the Paparoa Range in New Zealand * Einstein metro station, a station in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson (other)
A boson is a particle that has integer spin. Boson may also refer to: * John Boson, woodworker * John Boson (writer) (1655–1730), writer in the Cornish language * Nicholas Boson (1624–1708), writer in Cornish * Nicholas Bozon (''fl''. c. 1320), Anglo-Norman writer * Thomas Boson (1635–1719), writer in Cornish * Boso of Provence (Boson, c. 841–887), Frankish nobleman See also * Satyendra Nath Bose, Indian physicist, namesake of the particle * Bose (other) * Boatswain A boatswain ( , ), bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun, also known as a deck boss, or a qualified member of the deck department, or the third hand on a fishing vessel, is the most senior Naval rating, rate of the deck department and is responsible for the ..., bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun * The Bosonid dynasty, a dynasty of Franks * Bosön * Barbara Bosson (1939–2023), American actress * Bosson (born 1969), Swedish singer-songwriter {{disambiguation, surname Cornish-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satyendra Nath Bose
Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was an Indian theoretical physicist and mathematician. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for Bose–Einstein statistics, and the theory of the Bose–Einstein condensate. A Royal Society#Fellows, Fellow of the Royal Society, he was awarded India's second highest civilian award, the Padma Vibhushan, in 1954 by the Government of India. The class of particles that obey Bose statistics, bosons, was named after Bose by Paul Dirac. A polymath, he had a wide range of interests in varied fields, including physics, mathematics, chemistry, biology, mineralogy, philosophy, The arts, arts, literature, and music. He served on many research and development committees in India, after independence. Early life Bose was born in Calcutta (now Kolkata), the eldest of seven children in a Bengali Kayastha family. He was the only son, with six sisters after him. His ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |