|
Biridiya
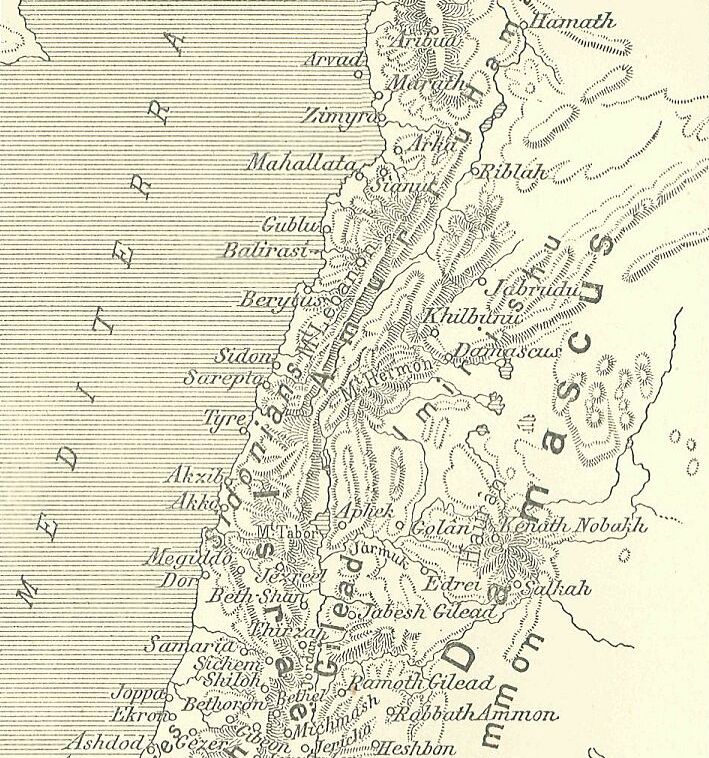
Biridiya was the ruler of Megiddo, northern part of the southern Levant, in the 14th century BC. At the time Megiddo was a city-state submitting to the Egyptian Empire. He is part of the intrigues surrounding the rebel Labaya of Shechem. History Biridiya was the ruler of Magidda (Megiddo). At the time, Labaya of Shechem tried to expand his territory and power. Labaya attacked Megiddo (EA 244) forcing the people to flee inside the city walls and making it impossible to harvest fields. Both Biridiya and Yashdata (EA 248/EA 245) attacked Labaya, apparently with the support of Suruata of Akko. At one point Suruata took Labaya away from Megiddo to send him by boat to the Pharaoh, but he received a ransom and released Labaya (EA 245). Amarna Archive In Egypt, the Amarna Archive (c. 1350 BC) contained letters authored by Biridya. The archive covers diplomatic correspondence from the time of Amenhotep III, Akhenaten Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 245
Amarna letter EA 245, titled: ''"Assignment of Guilt,"'' is a medium length clay tablet Amarna letter from Biridiya the governor-'mayor' of Magidda. It is letter number four of five from Biridiya. The letter is in pristine condition except for a missing flake (lower-right, obverse) causing a lacuna at the end of a few lines. The cuneiform characters are finely inscribed, with some photos that can even show the individual strokes of the cuneiform characters (the stroke sequence). The letter is 47-lines long, and about 5-in tall. Letter EA 245 (see here-(Obverse), is numbered BM 29855, at the British Museum. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1350 BC and 20–25 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters were found at Akhenaten's city Akhetaten, in the floor of the Bureau of Correspondence of Pharaoh; others were later found, adding to the body of letters. The letter EA 245: ''"Assignment of Guilt"'' EA 245, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labaya
Labaya (Labayu or Lib'ayu) was the ruler of Shechem and warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan during the Amarna Period (c. 1350 BC). He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters (abbreviated "EA", for 'el Amarna'). He is the author of letters Amarna letter EA 252, EA 252–Amarna letter EA 254, 54. Labaya was active over the whole length of Samaria and slightly beyond, as he gave land to Habiru in the vicinity of Šakmu (Shechem) and he and his sons threatened such powerful towns as Jerusalem and Gazru (Gezer) to the south, and Megiddo (place), Megiddo to the north. Career The Amarna letters give an incomplete look at Labaya's career. In the first of Labaya's letters thus far discovered (EA 252), he defends himself to the Pharaoh against complaints of other city rulers about him, for example, the complaint that he has hired mercenaries from among the Habiru. Labaya further admitted to having invaded Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannathon
Hannathon or Hinnatuna was a city-state in Canaan during the Late Bronze Age. It is most likely identical with the archaeological site Tel Hanaton. History In the Late Bronze, Hinnatuna was a city-state in Canaan. It was located near Akko and Megiddo. It is attested in the Amarna Archive around 1350 BC as "Hinnatuna". It associated with the Biblical city/city-state of Hannathon, (meaning: ''"the Gift of Grace"''). While the city has not been identified with certainty, the ancient settlement of Tel Hanaton in Lower Galilee has been suggested as a candidate. Amarna Archive In Egypt, the Amarna Archive mentions "Hinnatuna" first in Amarna Letters EA 245 and later in Amarna Letter EA 8. We learn that Surata of Akka was the father of Satatna of Akka, thus the events in EA 245 comes prior to the events in EA 8. Amarna Letter EA 245 Letter EA 245, to pharaoh, letter no. 4 of 7 by Biridiya, concerns the rebel, and mayor of Shechem-(Amarna Šakmu), Labayu, and his cohort and protector: S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megiddo (place)
Tel Megiddo (from ) is the site of the ancient city of Megiddo (; ), the remains of which form a tell or archaeological mound, situated in northern Israel at the western edge of the Jezreel Valley about southeast of Haifa near the depopulated Palestinian town of Lajjun and subsequently Kibbutz Megiddo. Megiddo is known for its historical, geographical, and theological importance, especially under its Greek name Armageddon. During the Bronze Age, Megiddo was an important Canaanite city-state. During the Iron Age, it was a royal city in the Kingdom of Israel. Megiddo's strategic location at the northern end of the defile of the Wadi Ara, which acts as a pass through the Carmel Ridge, and its position overlooking the rich Jezreel Valley from the west gave it much of its importance. Excavations have unearthed 20 strata of ruins since the Neolithic phase, indicating a long settlement period. The site is protected as Megiddo National Park and is a World Heritage Site. Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( , ; "Amun is satisfied"), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great and Hellenization, Hellenized as Amenophis III, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors following the "Low Chronology", he ruled New Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya. His reign was a period of unprecedented prosperity and splendour, when Egypt reached the peak of its artistic and international power, and as such he is considered one of ancient Egypt's greatest pharaohs. He is also one of the few pharaohs who was one of the few pharoahs who was List of pharaohs deified during lifetime, worshipped as a deity during his lifetime. When he died in the 38th or 39th year of his reign he was succeeded by his son Amenhotep IV, who later changed his name to Akhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV (, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning traditional ancient Egyptian religion of polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheism, monotheistic, or whether it was monolatristic, religious syncretism, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name Damnatio memoriae, excluded from regnal list, lists of rulers compiled by lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of ancient Egyptian religion, undoing a previous shift to the religion known as Atenism. Tutankhamun's reign is considered one of the greatest restoration periods in ancient Egyptian history. His endowments and restorations of cults were recorded on what is today known as the Restoration Stela. The cult of the god Amun at Thebes, Egypt, Thebes was restored to prominence, and the royal couple changed their names to "Tutankhamun" and "Ankhesenamun", replacing the -aten suffix. He also moved the royal court from Akhenaten's capital, Amarna, back to Memphis, Egypt, Memphis almost immediately on his accession to the kingship. He reestablished diplomatic relations with the Mitanni and carried out military campaigns in Nubia and the Near East. Tutankh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamid Al Lawz
Kamid el-Loz, also spelled Kamid al-Lawz, is located in West Bekaa, Lebanon. The settlement has a population numbering several thousand, mostly Sunni, people and is also a site of archaeological excavations. History In 1838, Eli Smith noted ''Kamid el-Lauz'' as a Sunni Muslim village in the Beqaa Valley. The ancient name of the site is thought to be Kumidi.Jens KamlahThe Significance of the Bronze Age Temples at Kamid el-Loz (Lebanon) for the Research on Phoenician Temple Cult Rivista di studi fenici XL, 2, 2012 Archaeology Kamid el-Loz was the site of major German archaeological excavations between 1963 and 1981. One of the most important sites in Lebanon where archaeologists found and recorded many spectacular buildings, which are very important to the history of the region. Paleolithic material was found alongside Heavy Neolithic on through to the late Neolithic period, becoming a human settlement during the Bronze Age and continuing until the Byzantine era, a German te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EA (el Amarna)
Amarna (; ) is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the ruins of Akhetaten, the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era. Name The name ''Amarna'' comes from the Beni Amran tribe that lived in the region and founded a few settlements. The ancient Egyptian name means " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |