|
Binary Cyclic Group
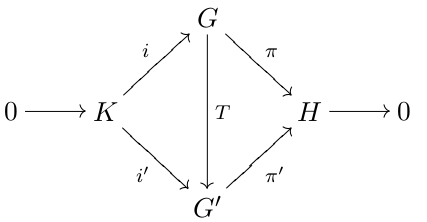
In mathematics, the binary cyclic group of the ''n''-gon is the cyclic group of order 2''n'', C_, thought of as an extension of the cyclic group C_n by a cyclic group of order 2. Coxeter writes the ''binary cyclic group'' with angle-brackets, ⟨''n''⟩, and the index 2 subgroup as (''n'') or 'n''sup>+. It is the binary polyhedral group corresponding to the cyclic group.. In terms of binary polyhedral groups, the binary cyclic group is the preimage of the cyclic group of rotations (C_n < \operatorname(3)) under the 2:1 covering homomorphism : of the by the |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Extension
In mathematics, a group extension is a general means of describing a group in terms of a particular normal subgroup and quotient group. If Q and N are two groups, then G is an extension of Q by N if there is a short exact sequence :1\to N\;\overset\;G\;\overset\;Q \to 1. If G is an extension of Q by N, then G is a group, \iota(N) is a normal subgroup of G and the quotient group G/\iota(N) is isomorphic to the group Q. Group extensions arise in the context of the extension problem, where the groups Q and N are known and the properties of G are to be determined. Note that the phrasing "G is an extension of N by Q" is also used by some. Since any finite group G possesses a maximal normal subgroup N with simple factor group G/N, all finite groups may be constructed as a series of extensions with finite simple groups. This fact was a motivation for completing the classification of finite simple groups. An extension is called a central extension if the subgroup N lies in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Group
In group theory, a branch of abstract algebra in pure mathematics, a cyclic group or monogenous group is a group, denoted C''n'', that is generated by a single element. That is, it is a set of invertible elements with a single associative binary operation, and it contains an element ''g'' such that every other element of the group may be obtained by repeatedly applying the group operation to ''g'' or its inverse. Each element can be written as an integer power of ''g'' in multiplicative notation, or as an integer multiple of ''g'' in additive notation. This element ''g'' is called a '' generator'' of the group. Every infinite cyclic group is isomorphic to the additive group of Z, the integers. Every finite cyclic group of order ''n'' is isomorphic to the additive group of Z/''n''Z, the integers modulo ''n''. Every cyclic group is an abelian group (meaning that its group operation is commutative), and every finitely generated abelian gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Polyhedral Group
In geometry, a point group in three dimensions is an isometry group in three dimensions that leaves the origin fixed, or correspondingly, an isometry group of a sphere. It is a subgroup of the orthogonal group O(3), the group of all isometries that leave the origin fixed, or correspondingly, the group of orthogonal matrices. O(3) itself is a subgroup of the Euclidean group E(3) of all isometries. Symmetry groups of geometric objects are isometry groups. Accordingly, analysis of isometry groups is analysis of possible symmetries. All isometries of a bounded (finite) 3D object have one or more common fixed points. We follow the usual convention by choosing the origin as one of them. The symmetry group of an object is sometimes also called its full symmetry group, as opposed to its proper symmetry group, the intersection of its full symmetry group with E+(3), which consists of all ''direct isometries'', i.e., isometries preserving orientation. For a bounded object, the proper symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covering Homomorphism
In mathematics, a covering group of a topological group ''H'' is a covering space ''G'' of ''H'' such that ''G'' is a topological group and the covering map is a continuous group homomorphism. The map ''p'' is called the covering homomorphism. A frequently occurring case is a double covering group, a topological double cover in which ''H'' has index 2 in ''G''; examples include the spin groups, pin groups, and metaplectic groups. Roughly explained, saying that for example the metaplectic group Mp2''n'' is a ''double cover'' of the symplectic group Sp2''n'' means that there are always two elements in the metaplectic group representing one element in the symplectic group. Properties Let ''G'' be a covering group of ''H''. The kernel ''K'' of the covering homomorphism is just the fiber over the identity in ''H'' and is a discrete normal subgroup of ''G''. The kernel ''K'' is closed in ''G'' if and only if ''G'' is Hausdorff (and if and only if ''H'' is Hausdorff). Going in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Orthogonal Group
In mathematics, the orthogonal group in dimension , denoted , is the group of distance-preserving transformations of a Euclidean space of dimension that preserve a fixed point, where the group operation is given by composing transformations. The orthogonal group is sometimes called the general orthogonal group, by analogy with the general linear group. Equivalently, it is the group of orthogonal matrices, where the group operation is given by matrix multiplication (an orthogonal matrix is a real matrix whose inverse equals its transpose). The orthogonal group is an algebraic group and a Lie group. It is compact. The orthogonal group in dimension has two connected components. The one that contains the identity element is a normal subgroup, called the special orthogonal group, and denoted . It consists of all orthogonal matrices of determinant . This group is also called the rotation group, generalizing the fact that in dimensions 2 and 3, its elements are the usual rotati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Group
In mathematics the spin group Spin(''n'') page 15 is the double cover of the special orthogonal group , such that there exists a short exact sequence of Lie groups (when ) :1 \to \mathrm_2 \to \operatorname(n) \to \operatorname(n) \to 1. As a Lie group, Spin(''n'') therefore shares its dimension, , and its Lie algebra with the special orthogonal group. For , Spin(''n'') is simply connected and so coincides with the universal cover of SO(''n''). The non-trivial element of the kernel is denoted −1, which should not be confused with the orthogonal transform of reflection through the origin, generally denoted −. Spin(''n'') can be constructed as a subgroup of the invertible elements in the Clifford algebra Cl(''n''). A distinct article discusses the spin representations. Motivation and physical interpretation The spin group is used in physics to describe the symmetries of (electrically neutral, uncharged) fermions. Its complexification, Spinc, is used to describe ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. Hamilton defined a quaternion as the quotient of two '' directed lines'' in a three-dimensional space, or, equivalently, as the quotient of two vectors. Multiplication of quaternions is noncommutative. Quaternions are generally represented in the form :a + b\ \mathbf i + c\ \mathbf j +d\ \mathbf k where , and are real numbers; and , and are the ''basic quaternions''. Quaternions are used in pure mathematics, but also have practical uses in applied mathematics, particularly for calculations involving three-dimensional rotations, such as in three-dimensional computer graphics, computer vision, and crystallographic texture analysis. They can be used alongside other methods of rotation, such as Euler angles and rotation matrices, or as an alternative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sp(1)
In mathematics, the name symplectic group can refer to two different, but closely related, collections of mathematical groups, denoted and for positive integer ''n'' and field F (usually C or R). The latter is called the compact symplectic group and is also denoted by \mathrm(n). Many authors prefer slightly different notations, usually differing by factors of . The notation used here is consistent with the size of the most common matrices which represent the groups. In Cartan's classification of the simple Lie algebras, the Lie algebra of the complex group is denoted , and is the compact real form of . Note that when we refer to ''the'' (compact) symplectic group it is implied that we are talking about the collection of (compact) symplectic groups, indexed by their dimension . The name "symplectic group" is due to Hermann Weyl as a replacement for the previous confusing names (line) complex group and Abelian linear group, and is the Greek analog of "complex". The metaplect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternions And Spatial Rotation
unit vector, Unit quaternions, known as versor, ''versors'', provide a convenient mathematics, mathematical notation for representing spatial Orientation (geometry), orientations and rotations of elements in three dimensional space. Specifically, they encode information about an Axis–angle representation, axis-angle rotation about an arbitrary axis. Rotation and orientation quaternions have applications in computer graphics, Presented at SIGGRAPH '85. computer vision, robotics, navigation, molecular dynamics, flight dynamics, orbital mechanics of satellites, and Texture (crystalline), crystallographic texture analysis. When used to represent rotation, unit quaternions are also called rotation quaternions as they represent the 3D rotation group. When used to represent an Orientation (geometry), orientation (rotation relative to a reference coordinate system), they are called orientation quaternions or attitude quaternions. A spatial rotation around a fixed point of \theta radians ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Dihedral Group
In group theory, a dicyclic group (notation Dic''n'' or Q4''n'', Coxeter&Moser: Generators and Relations for discrete groups: : Rl = Sm = Tn = RST) is a particular kind of non-abelian group of order 4''n'' (''n'' > 1). It is an extension of the cyclic group of order 2 by a cyclic group of order 2''n'', giving the name ''di-cyclic''. In the notation of exact sequences of groups, this extension can be expressed as: :1 \to C_ \to \mbox_n \to C_2 \to 1. \, More generally, given any finite abelian group with an order-2 element, one can define a dicyclic group. Definition For each integer ''n'' > 1, the dicyclic group Dic''n'' can be defined as the subgroup of the unit quaternions generated by :\begin a & = e^\frac = \cos\frac + i\sin\frac \\ x & = j \end More abstractly, one can define the dicyclic group Dic''n'' as the group with the following presentation :\operatorname_n = \left\langle a, x \mid a^ = 1,\ x^2 = a^n,\ x^ax = a^\right\rangle.\,\! Some things to note which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Tetrahedral Group
In mathematics, the binary tetrahedral group, denoted 2T or , Coxeter&Moser: Generators and Relations for discrete groups: : Rl = Sm = Tn = RST is a certain nonabelian group of order 24. It is an extension of the tetrahedral group T or (2,3,3) of order 12 by a cyclic group of order 2, and is the preimage of the tetrahedral group under the 2:1 covering homomorphism Spin(3) → SO(3) of the special orthogonal group by the spin group. It follows that the binary tetrahedral group is a discrete subgroup of Spin(3) of order 24. The complex reflection group named 3(24)3 by G.C. Shephard or 3 and by Coxeter, is isomorphic to the binary tetrahedral group. The binary tetrahedral group is most easily described concretely as a discrete subgroup of the unit quaternions, under the isomorphism , where Sp(1) is the multiplicative group of unit quaternions. (For a description of this homomorphism see the article on quaternions and spatial rotations.) Elements Expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |