|
Bight (geography)
In geography, a bight () is a concave bend or curvature in a coastline, river or other geographical feature, or it may refer to a very open bay formed by such a feature. Such bays are typically broad, open, shallow and only slightly recessed. Description The size of bights differs greatly, which may be as small as a bend in a river or large like a sound. Large bights are shallower than sounds. Traditionally, explorers defined a bight as a bay that could be sailed out of on a single tack in a square-rigged sailing vessel, regardless of the direction of the wind (typically meaning the apex of the bight is less than 25 degrees from the edges). According to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, an indentation with an area as large as (or larger than) that of the semi-circle whose diameter is a line drawn across the mouth of that indentation, can be regarded as a bay not merely a bight. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Australian Bight Marine Park
Great Australian Bight Marine Park is the name given to a group of marine protected areas which are located together within both Australian and South Australian jurisdictions in the Great Australian Bight and which has been in use as recently as 2005. The constituent protected areas are the Great Australian Bight Marine National Park and the Great Australian Bight Marine Park Whale Sanctuary within the coastal waters of South Australia, and the Great Australian Bight Commonwealth Marine Reserve in waters within the Australian Exclusive economic zone. It was listed on the now-defunct Register of the National Estate The Register of the National Estate was a heritage register that listed natural and cultural heritage places in Australia that was closed in 2007. Phasing out began in 2003, when the Australian National Heritage List and the Commonwealth Heri .... See also * Great Australian Bight Marine Park (Commonwealth waters) References External linksGreat Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bight Of Benin
The Bight of Benin, or Bay of Benin, is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin. Geography The Bight of Benin was named after the Kingdom of Benin. It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of the Niger River, Historical associations with the Atlantic slave trade led to the region becoming known as the Slave Coast. As in many other regions across Africa, powerful indigenous kingdoms along the Bight of Benin relied heavily on a long-established slave trade that expanded greatly after the arrival of European powers and became a global trade with the colonization of the Americas. Estimates from the 1640s suggest that Benin (Beneh) took in 1200 slaves a year. Restrictions made it hard for slave volume to grow until new states and different routes began to make an increase in slave trade possible. Cultural references The Bight of Benin has a long association with slaver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Taranaki Bight
The South Taranaki Bight is a large bay on the west coast of New Zealand, south of Taranaki, west of the Manawatu, north and west of the western entrance of Cook Strait and north of the South Island. The name is sometimes used for a much smaller bay in South Taranaki, between the mouth of the Kaupokonui Stream directly south of Mount Taranaki and the mouth of the Pātea River. Approximately 18,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum when sea levels were over lower than present day levels, the South Taranaki Bight was a coastal plain which connected the North and South Islands, featuring rivers which drained into the Cook Strait (then a harbour) to the south-east. Sea levels began to rise 7,000 years ago, eventually separating the islands and connecting the Cook Strait to the Tasman Sea. The bight was once a calving ground for southern right whales in winter and spring and early Europeans in New Zealand called it Mothering Bay after the large number of cow-calf pairs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Monica Bay
Santa Monica Bay is a bight of the Pacific Ocean in Southern California, United States. Its boundaries are slightly ambiguous, but it is generally considered to be the part of the Pacific within an imaginary line drawn between Point Dume, in Malibu, and the Palos Verdes Peninsula. Its eastern shore forms the western boundary of the Los Angeles Westside and South Bay regions. Although it was fed by the Los Angeles River until the river's catastrophic change of course in 1825, the only stream of any size now flowing into it is Ballona Creek. Smaller waterways draining into the bay include Malibu Creek, Topanga Creek, and Santa Monica Creek. The Santa Monica Bay is home to some of the most famous beaches in the world, including Malibu Lagoon State Beach (Surfrider), Will Rogers State Beach, Santa Monica State Beach, and Dockweiler State Beach. Several piers extend into the bay, including Malibu Pier, Santa Monica Pier, Venice Pier, Manhattan Beach Pier, Hermosa Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robson Bight
Robson Bight is a small Vancouver Island bay at the west end of Johnstone Strait across from West Cracroft Island in British Columbia, Canada that includes a protected killer whale habitat famous for its whale-rubbing beaches. The bight is adjacent to Lower Tsitika River Provincial Park. The nearest access point is Telegraph Cove on the east coast of Northern Vancouver Island. Ecological Reserve Robson Bight (Michael Bigg) Ecological Reserve was established in 1982 as a sanctuary for killer whales. The area, 10 km south east of Telegraph Cove and 40 km from Port McNeill, British Columbia, is restricted. Access by boat or land is prohibited. The Robson Bight Warden Program is operated by the Cetus Research and Conservation Society. This program educates visitors to the area about the Ecological Reserve and asks visitors to remain outside the Ecological Reserve boundaries. The Reserve extends 1 km offshore from markers at either end of the Reserve. The total a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Taranaki Bight
The North Taranaki Bight is a large bay that extends north and east from the north coast of Taranaki in New Zealand's North Island. The name is echoed by the South Taranaki Bight to the south of Cape Egmont. As with its southern counterpart, the size of the bight depends to a large extent on the source referring to it. Strict definitions refer to it stretching from the mouth of the Waitara River, 10 kilometres northeast of New Plymouth, to the mouth of the Mokau River. Looser descriptions refer to it extending as far north as Tirua Point, 50 kilometres southwest of Te Kūiti, or even to Albatross Point, close to the entrance to Kawhia Harbour. Some include New Plymouth in the bight. See also * South Taranaki Bight The South Taranaki Bight is a large bay on the west coast of New Zealand, south of Taranaki, west of the Manawatu, north and west of the western entrance of Cook Strait and north of the South Island. The name is sometimes used for a much smaller ... Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Bight
The New York/New Jersey Bight is the geological identification applied to a roughly triangular indentation, regarded as a bight, along the Atlantic coast of the United States that extends northeasterly from Cape May Inlet in New Jersey to Montauk Point on the eastern tip of Long Island. As the result of direct contact with the Gulf Stream along the coast of North America, the coastal climate of the bight area is temperate. Geography The bight is formed by the roughly right-angled intersection of the generally north-south Atlantic coast of New Jersey and the approximately east–west southern coast of Long Island at the mouth of the Hudson River. The New York Bight Apex is the area including and between the Hudson River estuary and the Raritan River estuary extending 6–7 km from the coast, and it includes both the Raritan Bay and the Lower Bay. Weather The geography of the bight has long been of major concern to meteorologists in the study of tropical storm pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
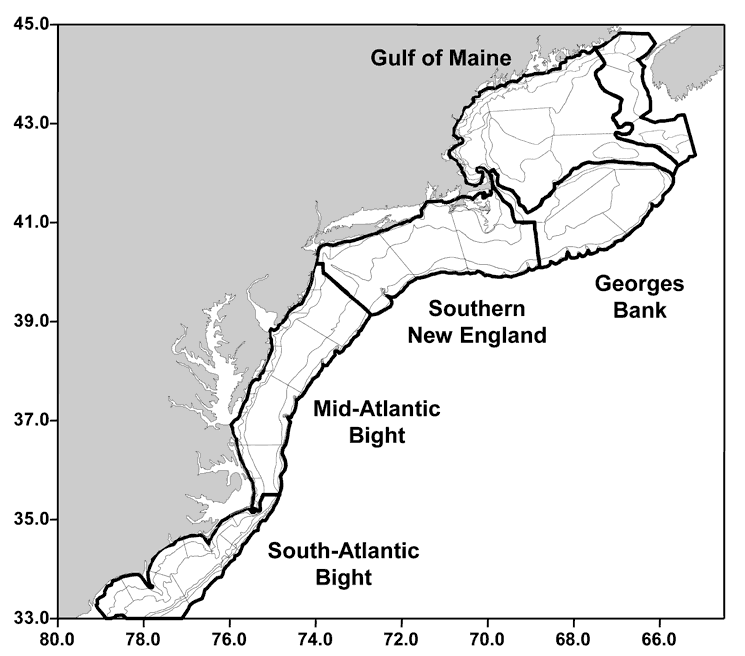
Mid-Atlantic Bight
The Mid-Atlantic Bight is a coastal region running from Massachusetts to North Carolina. It contains the New York Bight. It is separated from the South Atlantic Bight by Cape Hatteras to the south and the Gulf of Maine to the north by Cape Cod Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The .... References External linksThe Mid-Atlantic Bight (MAB) National Undersea Research Center Landforms of Massachusetts Landforms of New York (state) Landforms of New Jersey Landforms of North Carolina Landforms of the Atlantic Ocean Bights (geography) Landforms of Virginia {{Marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg Bight
The Bay of Mecklenburg ( or ''Mecklenburgische Bucht''; ), also known as the Mecklenburg Bay or Mecklenburg Bight, is a long narrow basin making up the southwestern finger-like arm of the Baltic Sea, between the shores of Germany to the south and the Danish islands of Lolland, Falster, and Møn to the north, the shores of Jutland to the west, and joining the largest part of the Baltic to the east. The Bay of Mecklenburg, which includes the Bay of Wismar and the Bay of Lübeck, connects to the Bay of Kiel in the northwest. Notable ports in the bay are Lübeck, Rostock and Wismar. The Blinkerwall In 2024, a long wall was discovered on the seabed at a depth of , off the coast. Named "the Blinkerwall" by its discoverers, the wall is around high. Its direction changes when it meets a series of larger boulders. In total, the wall's stones weigh more than 142 tonnes. It is thought to be Europe's oldest megastructure (around 10,000 years old) and may have been used by hunter-gath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McKenzie Bight
McKenzie Bight is a feature on the southeast side of Saanich Inlet in British Columbia, Canada. This bight is located in Gowlland Tod Provincial Park directly adjacent to the rural community of Willis Point. McKenzie Bight can be accessed by trail from the Mount Work parking area and trailhead on Ross-Durrance road, or via a short hike from the southern end of Mark Lane in Willis Point. Nearby is a reef which is a popular shore-dive location for scuba diving Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub .... Occasionally river otters can be seen in the area. References External linksBC Parks Gowlland Tod Website*https://www.crd.bc.ca/parks-recreation-culture/parks-trails/find-park-trail/mount-work Strait of Georgia Bays of British Columbia Saanich Peninsula Bights (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
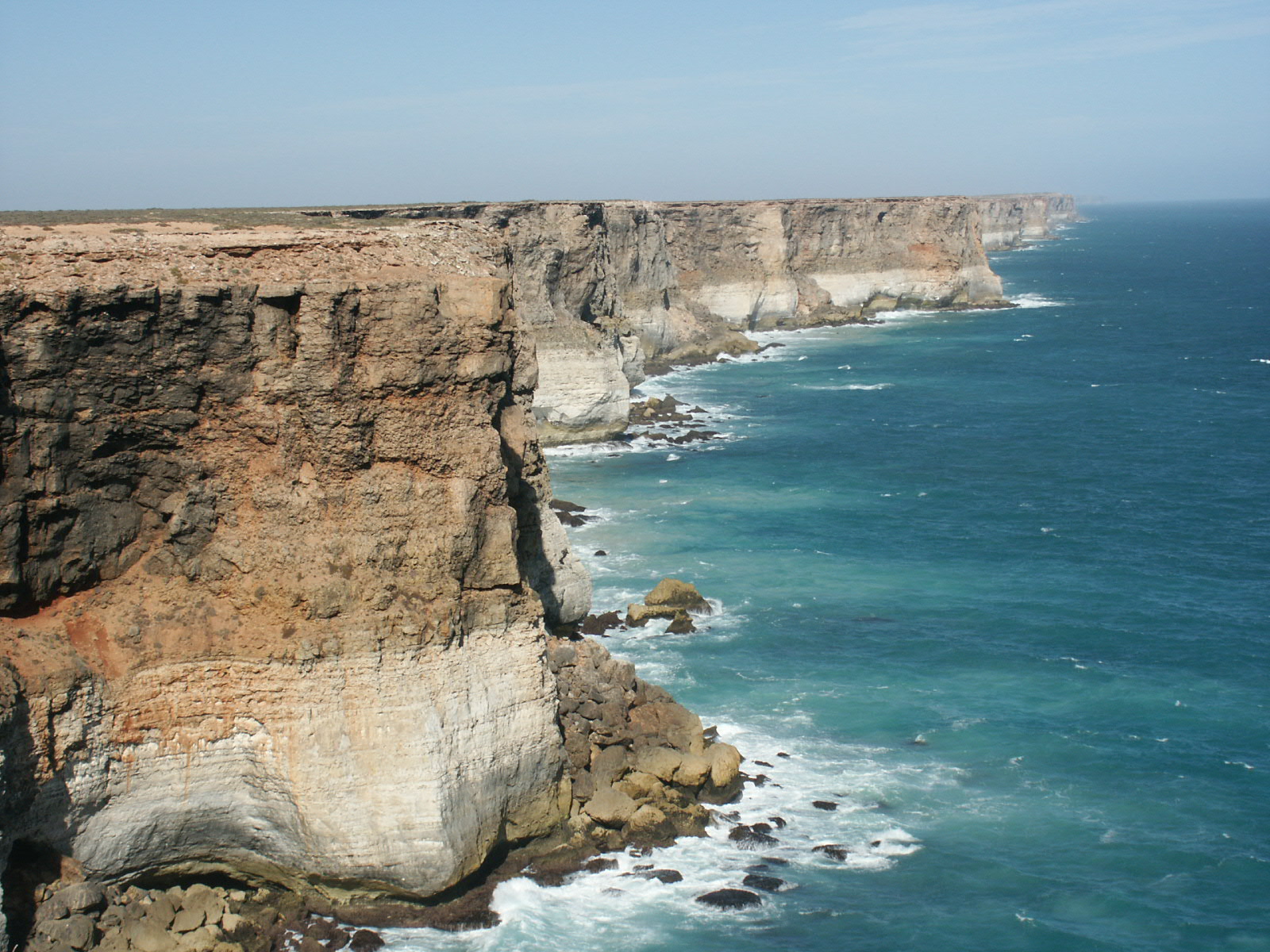
Great Australian Bight
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight (geography), bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern Coast, coastline of mainland Australia. There are two definitions for its extent—one by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and another by the Australian Hydrographic Service (AHS). The bight is generally considered part of the Indian Ocean, although the AHS classifies it as part of the Southern Ocean. Its coastline is characterized by cliff faces and rocky capes, making it an ideal location for whale-watching. This oceanic feature was first encountered by European explorers in 1627, and was accurately charted by English navigator Matthew Flinders in 1802. The Great Australian Bight came into existence about 50 million years ago when the supercontinent Gondwana broke apart, separating Antarctica from Australia. The Bight's waters are highly Biodiversity, biodiverse, especially in zooplankton, due to specific ocean currents. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heligoland Bight
The Heligoland Bight, also known as Helgoland Bight, (, ) is a bay which forms the southern part of the German Bight, itself a bay of the North Sea, located at the mouth of the Elbe river. The Heligoland Bight extends from the mouth of the Elbe to the islands of Heligoland and lies between the East Frisian island of Wangerooge and the North Frisian peninsula of Eiderstedt. The bight is named after Heligoland. It was the location of World War I naval battles in 1914 and 1917. In 1939 it also had a World War II aerial battle named after it. In the Heligoland Basin (''Helgoländer Becken''), a basin lying directly southwest of Heligoland, the bight is up to deep. One of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, from Hamburg and the mouth of the Elbe to the Straits of Dover and the English Channel, runs through the Heligoland Bight. The area also includes nature reserves such as the ''Heligoland Felssockel'' and the protected Wadden Sea, in which the Wadden Sea National P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |