|
Bestiarii
Among Ancient Romans, ''bestiarii'' (singular ''bestiarius'') were those who went into combat with beasts, or were exposed to them. It is conventionalEntry on Bestiarii at Chambers, Ephraim, '' Cyclopaedia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences'', c. 1680-1740 to distinguish two categories of ''bestiarii'': the first were those condemned to death via the beasts (see '' damnatio ad bestias'') and the second were those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damnatio Ad Bestias
''Damnatio ad bestias'' (Latin for "condemnation to beasts") was a form of Roman capital punishment where the condemned person was killed by wild animals, usually Lion, lions or other Big cat, big cats. This form of execution, which first appeared during the Roman Republic around the 2nd century BC, had been part of a wider class of blood sports called ''Bestiarii''. The act of ''damnatio ad bestias'' was considered a common form of entertainment for the lower class citizens of Rome (plebeians). Killing by wild animals, such as Barbary lions, formed part of the inaugural games of the Flavian Amphitheatre in AD 80. Between the 1st and 3rd centuries AD, this penalty was also applied to the worst of criminals, runaway slaves, and Early Christianity, Christians. History The exact purpose of the early ''damnatio ad bestias'' is not known and might have been a religious sacrifice rather than a legal punishment, especially in the regions where lions existed naturally and were revered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladiator
A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death. Irrespective of their origin, gladiators offered spectators an example of Rome's martial ethics and, in fighting or dying well, they could inspire admiration and popular acclaim. They were celebrated in high and low art, and their value as entertainers was commemorated in precious and commonplace objects throughout the Roman world. The origin of gladiatorial combat is open to debate. There is evidence of it in funeral rites during the Punic Wars of the 3rd century BC, and thereafter it rapidly became an essential feature of politics and social life in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Gladiator Types
There were many different types of gladiators in ancient Rome. Some of the first gladiators had been prisoner of war, prisoners-of-war, and so some of the earliest types of gladiators were experienced fighters; Gauls, Samnites, and ''Thraeces'' (Thracians) used their native weapons and armor. Different gladiator types specialized in specific weapons and fighting techniques. Combatants were usually pitted against opponents with different, but more or less equivalent equipment, for the sake of a fair and balanced contest. Most gladiators only fought others from within the same school or ''ludus'', but sometimes specific gladiators could be requested to fight one from another ''ludus''. Elite gladiators wore high-quality decorative armour for the pre-game parade ''(pompa)''. Julius Caesar's gladiators wore silver armour, Domitian's wore golden armour, and Nero's armour decorated with carved amber. Peacock feathers were used for plumes while tunics and loincloths had patterns in gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venatio
Venatio (, "hunting", plural ''venationes'') was a type of entertainment in Roman amphitheaters involving the hunting and killing of wild animals. History Venatio was first introduced by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, who celebrated his Greek campaign by hosting games where gladiators would fight lions and panthers. Exotic wild beasts from the far reaches of the Roman Empire were brought to Rome and hunts were held in the morning prior to the afternoon main event of gladiatorial duels. The hunts were held in the Roman Forum, the Saepta, and in the Circus Maximus, though none of these venues offered protection to the crowd from the wild animals on display. Special precautions were taken to prevent the animals from escaping these venues, such as the erection of barriers and the digging of ditches. Very few animals survived these hunts though they did sometimes defeat the " bestiarius", or hunter of wild beast. Thousands of wild animals would be slaughtered in one day. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures. The Romans adapted the Greek hero's iconography and myths for their literature and art under the name ''Hercules''. In later Western art and literature and in popular culture, ''Hercules'' is more commonly used than ''Heracles'' as the name of the hero. Hercules is a multifaceted figure with contradictory characteristics, which enabled later artists and writers to pick and choose how to represent him. This article provides an introduction to representations of Hercules in the later tradition. Mythology Birth and early life In Roman mythology, although Hercules was seen as the champion of the weak and a great protector, his personal problems started at birth. Juno sent two witches to prevent the birth, but they were tricked by one of Alcmene's servants and se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
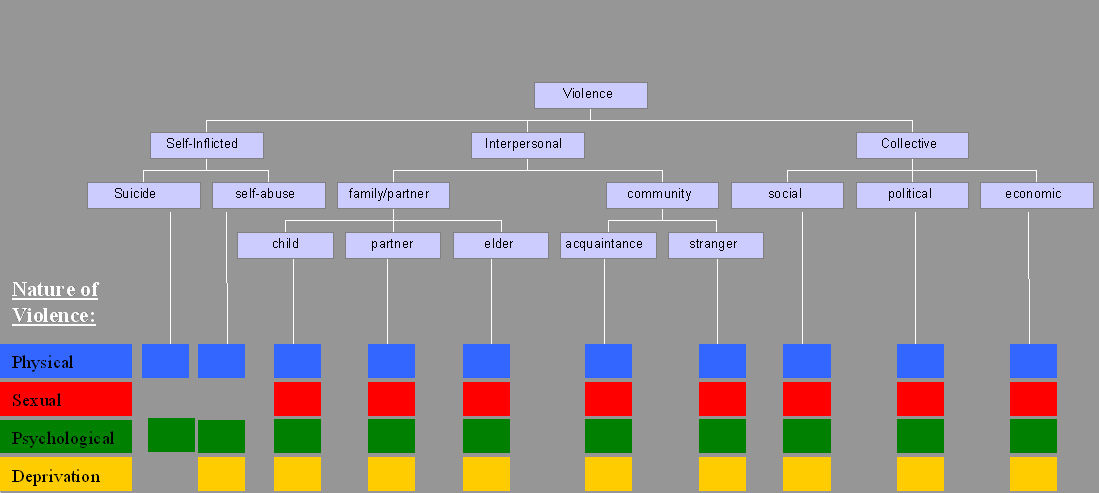
Violence In Sports
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Occupations
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Execution Methods
This is a list of methods of capital punishment, also known as execution. Current methods These methods of capital punishment are currently legal in at least one country. Former methods Many historically recorded methods of execution include torture Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ..., often intending to make a spectacle of pain and suffering with overtones of sadism, cruelty, intimidation, and dehumanisation, at times aimed at attempting to deter the commission of offences. Some of these methods may still be in practice by terrorist groups. See also * Capital punishment in Judaism References External linksDeath Penalty Worldwide: Academic research database on the laws, practice, and statistics of capital punishment for every death penalty country in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apologeticus
''Apologeticus'' ( or ''Apologeticus'') is a text attributed to Tertullian according to Christian tradition, consisting of apologetic and polemic. In this work Tertullian defends Christianity, demanding legal toleration and that Christians be treated like all other sects of the Roman Empire. It is in this treatise that one finds the sentence "Plures efficimur, quotiens metimur a vobis: semen est sanguis Christianorum," which has been liberally and apocryphally translated as "the blood of the martyrs is the seed of the Church" (''Apologeticus'', L.13). Alexander Souter translated this phrase as "We spring up in greater numbers the more we are mown down by you: the blood of the Christians is the seed of a new life," but even this takes liberties with the original text. "We multiply when you reap us. The blood of Christians is seed," is perhaps a more faithful, if less poetic, rendering. There is a similarity of content, if not of purpose, between this work and Tertullian's '' Ad na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |