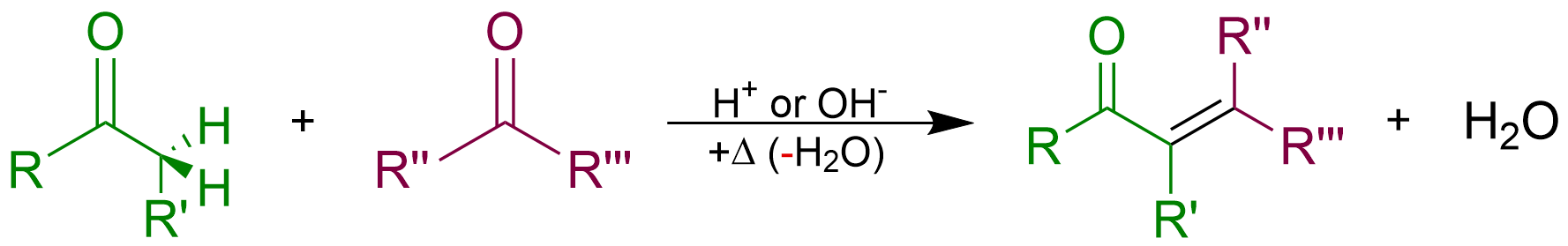|
Befunolol
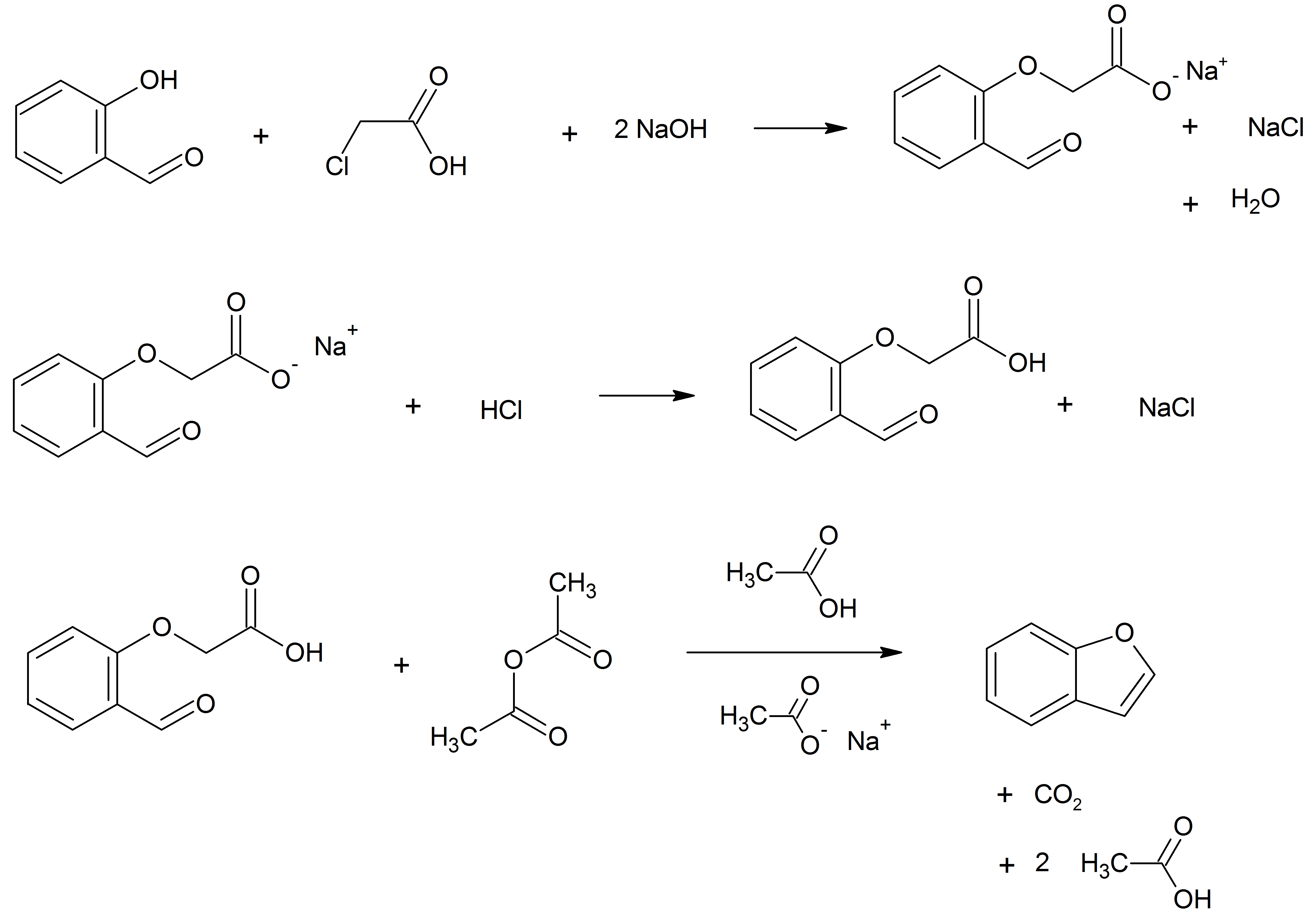
Befunolol (International Nonproprietary Name, INN) is a beta blocker with beta blocker#Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity, intrinsic sympathomimetic activity used in the management of glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma. It also acts as a Beta-adrenergic agonist, β adrenoreceptor partial agonist. Befunolol was introduced in Japan in 1983 by Kakenyaku Kako Co. under the trade name Bentos. Synthesis : The first reported synthesis of befunolol in 1974 used a benzofuran derivative (4) with epichlorohydrin and then isopropylamine to add the sidechain which was known to produce beta blockers, by analogy with drugs discovered by Imperial Chemical Industries, such as Discovery_and_development_of_beta-blockers#Synthesis, propanolol. The requisite intermediate was synthesized from ortho-vanillin (1) by a condensation reaction with chloroacetone (2) in the presence of potassium hydroxide, giving 2-acetyl-7-methoxybenzofuran (3), which was demethylated using hydrobromic acid. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-adrenergic Agonist
Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers: beta-adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the actions of both epinephrine- and norepinephrine- signaling, in the heart and lungs, and in smooth muscle tissue; epinephrine expresses the higher affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue. Function Activation of β1 receptors induces positive inotropic, chronotropic output of the cardiac muscle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroacetone
Chloroacetone is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . At Standard temperature and pressure, STP it is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. On exposure to light, it turns to a dark yellow-amber color. It was used as a lachrymatory agent, tear gas in World War I. Synthesis Chloroacetone may be synthesized from the reaction between chlorine and diketene, or by the chlorination of acetone. Applications Chloroacetone is used to make dye couplers for colour photography, and is an intermediate in chemical manufacturing. It is also used in the Feist-Benary synthesis of furans. : *Reaction of phenoxide with chloroacetone gives phenoxyacetone, which is used to make a wide variety of different pharmaceuticals. A catalytic amount of potassium iodide is also necessary to facilitate a Finkelstein reaction. Purification Chloroacetone purchased from commercial suppliers contains 5% impurities including mesityl oxide, which is not removed by distillation. Mesityl oxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechol Ethers
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables. Isolation and synthesis Catechol was first isolated in 1839 by Edgar Hugo Emil Reinsch (1809–1884) by distilling it from the solid tannic preparation catechin, which is the residuum of catechu, the boiled or concentrated juice of ''Mimosa catechu'' ('' Acacia catechu''). Upon heating catechin above its decomposition point, a substance that Reinsch first named ''Brenz-Katechusäure'' (burned catechu acid) sublimated as a white efflore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most people. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Beta-adrenergic receptors are found on cells of the heart muscles, smooth muscles, airways, arteries, kidneys, and other tissues that are part of the sympathetic nervous system and lead to stress responses, especially when they are stimulated by epinephrine (adrenaline). Beta blockers interfere with the binding to the receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzofuran Ethers At The Benzene Ring
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus (parent compound) of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. *Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : *Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : * Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols: : Related compounds * Substituted benzofurans * Dibenzofuran, an analog with a second fused b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobromic Acid
Hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution of hydrogen bromide. It is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known. Uses Hydrobromic acid is mainly used for the production of inorganic bromides, especially the bromides of zinc, calcium, and sodium. It is a useful reagent for generating organobromine compounds. Certain ethers are cleaved with HBr. It also catalyzes alkylation reactions and the extraction of certain ores. Industrially significant organic compounds prepared from hydrobromic acid include allyl bromide, tetrabromobis(phenol), and bromoacetic acid. HBr participates in anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes in the presence of peroxides. The resulting 1-bromoalkanes are versatile alkylating agents, giving rise to fatty amines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demethylated
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms. The counterpart of demethylation is methylation. In biochemistry : Demethylation is relevant to epigenetics. Demethylation of DNA is catalyst, catalyzed by demethylases. These enzymes oxidize N-methyl groups, which occur in histones, in lysine derivatives, and in some forms of DNA. :R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O One family of such oxidative enzymes is the cytochrome P450. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are also active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar stoichiometry. These reactions, which proceed via hydroxylation, exploit the slightly weakened Carbon–hydrogen bond, C-H bonds of methylamines and methyl ethers. Demethylation of some sterols are steps in the biosynthesis of testosterone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utilize its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |