|
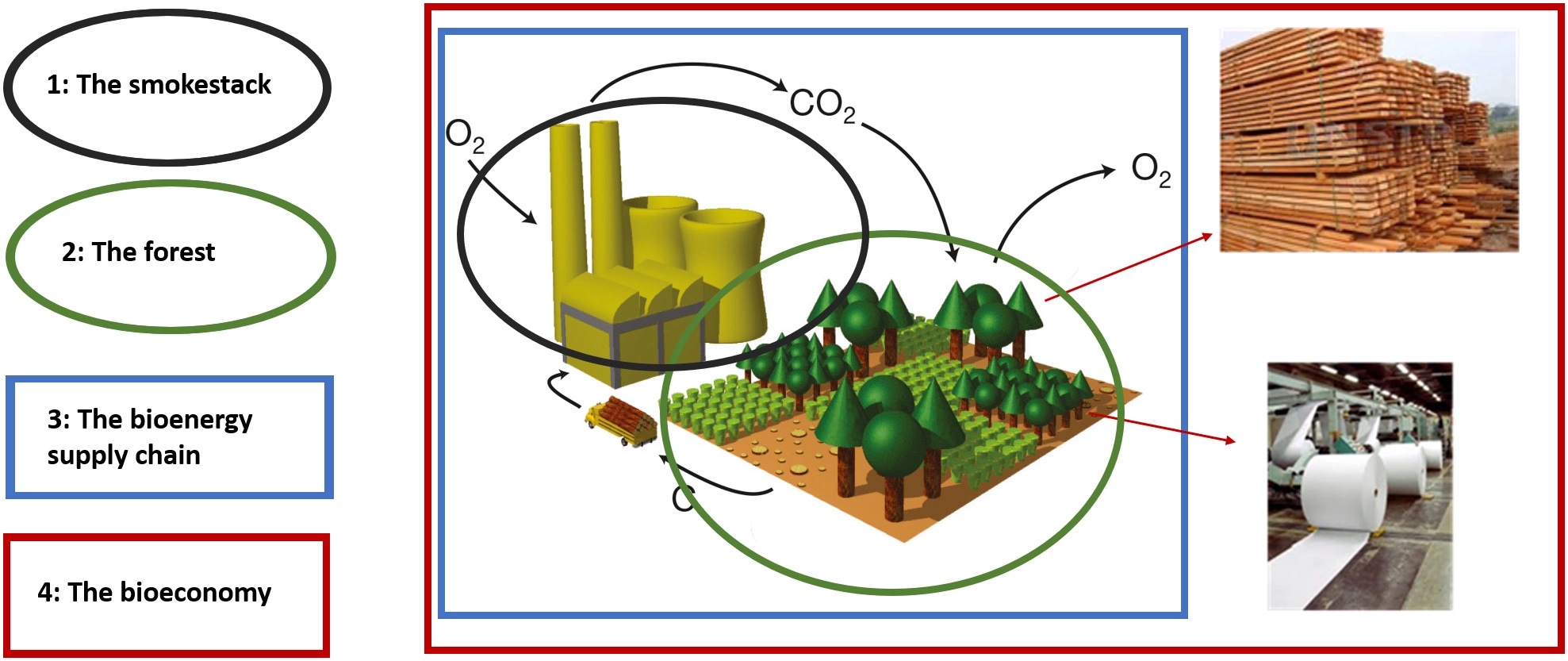
BECCS
Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is the process of extracting bioenergy from Biomass (energy), biomass and capturing and storing the carbon dioxide (CO2) that is produced. Greenhouse gas emissions from bioenergy can be low because when vegetation is harvested for bioenergy, new vegetation can grow that will absorb CO2 from the air through photosynthesis. After the biomass is harvested, energy ("bioenergy") is extracted in useful forms (electricity, heat, biofuels, etc.) as the biomass is utilized through combustion, fermentation, pyrolysis or other conversion methods. Using bioenergy releases CO2. In BECCS, some of the CO2 is captured before it enters the atmosphere, and stored underground using carbon capture and storage technology. Under some conditions, BECCS can Carbon dioxide removal, remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The potential range of negative emissions from BECCS was estimated to be zero to 22 gigatonnes per year. As of 2024, there are large-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that is derived from plants and animal waste. The Biomass (energy), biomass that is used as input materials consists of recently living (but now dead) organisms, mainly plants. Thus, Fossil fuel, fossil fuels are not regarded as biomass under this definition. Types of biomass commonly used for bioenergy include wood, food crops such as corn, energy crops and waste from forests, yards, or farms. Bioenergy can help with climate change mitigation but in some cases the required biomass production can increase greenhouse gas emissions or lead to local biodiversity loss. The environmental impacts of biomass production can be problematic, depending on how the biomass is produced and harvested. But it still produces CO2; so long as the energy is derived from breaking chemical bonds. The International Energy Agency, IEA's Net Zero by 2050 scenario calls for traditional bioenergy to be phased out by 2030, with modern bioenergy's share increasing fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is a process in which carbon dioxide () is removed from the atmosphere by deliberate human activities and durably stored in geological, terrestrial, or ocean reservoirs, or in products.IPCC, 2021:Annex VII: Glossary. Matthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.). InClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2215–2256, This process is also known as carbon removal, greenhouse gas removal or negative emissions. CDR is more and more often in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Capture And Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process by which carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial installations is separated before it is released into the atmosphere, then transported to a long-term storage location.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary atthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.) IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2215–2256, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.022. The CO2 is captured from a large point source pollution, point source, such as a natural gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass (energy)
In the context of energy production, biomass is matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms which is used for bioenergy production. Examples include wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues including straw, and Biodegradable waste, organic waste from industry and households. Wood and wood residues is the largest biomass energy source today. Wood can be used as a fuel directly or processed into pellet fuel or other forms of fuels. Other plants can also be used as fuel, for instance maize, switchgrass, miscanthus and bamboo. The main Waste energy, waste feedstocks are wood waste, agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, and manufacturing waste. Upgrading raw biomass to higher grade fuels can be achieved by different methods, broadly classified as thermal, chemical, or biochemical. The Greenhouse gas emissions, climate impact of bioenergy varies considerably depending on where biomass feedstocks come from and how they are grown. For example, wood fuel, bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle
integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) is a technology using a high pressure gasifier to turn coal and other carbon based fuels into pressurized synthesis gas. This enables removal of impurities from the fuel prior to generating electricity, reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide, particulates, mercury, and in some cases carbon dioxide. Some of these impurities, such as sulfur, can be turned into re-usable byproducts through the Claus process. With additional process equipment, carbon monoxide can be converted to carbon dioxide via water-gas shift reaction, enabling it to be sequestered and increasing gasification efficiency. Excess heat from the primary combustion and syngas fired generation is then passed to a steam cycle, producing additional electricity. This process results in improved thermodynamic efficiency, compared to conventional pulverized coal combustion. Significance Coal can be found in abundance in the USA and many other countries and its price has rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxy-fuel Combustion Process
Oxy-fuel combustion is the process of burning a fuel using pure oxygen, or a mixture of oxygen and recirculated flue gas, instead of air. Since the nitrogen component of air is not heated, fuel consumption is reduced, and higher flame temperatures are possible. Historically, the primary use of oxy-fuel combustion has been in welding and cutting of metals, especially steel, since oxy-fuel allows for higher flame temperatures than can be achieved with an air-fuel flame. It has also received a lot of attention in recent decades as a potential carbon capture and storage technology. There is currently research being done in firing fossil fuel power plants with an oxygen-enriched gas mix instead of air. Almost all of the nitrogen is removed from input air, yielding a stream that is approximately 95% oxygen. Firing with pure oxygen would result in too high a flame temperature, so the mixture is diluted by mixing with recycled flue gas, or staged combustion. The recycled flue gas can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husky Energy
Husky Energy Inc. was a Canadian company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration, headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. It operated in Western and Atlantic Canada, the United States and the Asia Pacific region, with upstream and downstream business segments. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Husky Energy was ranked as the 1443rd-largest public company in the world. In January 2021, Husky was acquired by Cenovus Energy. Its retail operations were sold to Federated Co-operatives and Parkland Corporation later that year. History Husky Energy was founded in 1938 in Cody, Wyoming as the Husky Refining Company, with the acquisition by Glenn Nielsen of assets of the 4-year-old Park Refining Company from founder Valentine Monroe Kirk. The first refinery was in Cody, with a second constructed later in Riverton, Wyoming. In 1946, the Company relocated to Canada, with the Riverton refinery moved to Lloydminster, Alberta to take advantage of the expanding asphalt and heavy oil opport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio of the net work output to the heat input; in the case of a heat pump, thermal efficiency (known as the '' coefficient of performance'' or COP) is the ratio of net heat output (for heating), or the net heat removed (for cooling) to the energy input (external work). The efficiency of a heat engine is fractional as the output is always less than the input while the COP of a heat pump is more than 1. These values are further restricted by the Carnot theorem. Overview In general, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of a device and the input, in energy terms. For thermal efficiency, the input, Q_, to the device is heat, or the heat-content of a fuel that is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |