|
Bcrypt
bcrypt is a password-hashing function designed by Niels Provos and David Mazières. It is based on the Blowfish (cipher), Blowfish cipher and presented at USENIX in 1999. Besides incorporating a salt (cryptography), salt to protect against rainbow table attacks, bcrypt is an adaptive function: over time, the iteration count can be increased to make it slower, so it remains resistant to brute-force search attacks even with increasing computation power. The bcrypt function is the default password hash algorithm for OpenBSD, and was the default for some Linux distributions such as SUSE Linux. There are implementations of bcrypt in C (programming language), C, C++, C Sharp (programming language), C#, Embarcadero Delphi, Elixir (programming language), Elixir, Go (programming language), Go, Java (programming language), Java, JavaScript, Perl, PHP, Ruby (programming language), Ruby, Python (programming language), Python, Rust (programming language), Rust,V (programming language), V ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypt (C)
crypt is a C POSIX librar, POSIX C library function. It is typically used to compute the cryptographic hash function, hash of user account passwords. The function outputs a text string which also code, encodes the salt (cryptography), salt (usually the first two characters are the salt itself and the rest is the hashed result), and identifies the hash algorithm used Detailing to the Traditional one explained be This output string forms a password which is usually stored in a text file. More formally, crypt provides cryptographic key derivation functions for password validation and storage on Unix systems. Relationship to Unix crypt utility There is an unrelated Crypt (Unix), crypt utility in Unix, which is often confused with the C library function. To distinguish between the two, writers often refer to the utility program as ''crypt(1)'', because it is documented in section 1 of the Unix Manual page (Unix), manual pages, and refer to the C library function as ''crypt(3)'', be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blowfish (cipher)
Blowfish is a Symmetric-key algorithm, symmetric-key block cipher, designed in 1993 by Bruce Schneier and included in many cipher suites and encryption products. Blowfish provides a good encryption rate in software, and no effective cryptanalysis of it has been found to date for smaller files. It is recommended Blowfish should not be used to encrypt files larger than 4GB in size, Twofish should be used instead. Blowfish has a 64-bit block size and therefore it could be vulnerable to Sweet32 birthday attacks. Schneier designed Blowfish as a general-purpose algorithm, intended as an alternative to the aging Data Encryption Standard, DES and free of the problems and constraints associated with other algorithms. At the time Blowfish was released, many other designs were proprietary, encumbered by patents, or were commercial or government secrets. Schneier has stated that "Blowfish is unpatented, and will remain so in all countries. The algorithm is hereby placed in the public domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base64
In computer programming, Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes that transforms binary data into a sequence of printable characters, limited to a set of 64 unique characters. More specifically, the source binary data is taken 6 bits at a time, then this group of 6 bits is mapped to one of 64 unique characters. As with all binary-to-text encoding schemes, Base64 is designed to carry data stored in binary formats across channels that only reliably support text content. Base64 is particularly prevalent on the World Wide Web where one of its uses is the ability to embed image files or other binary assets inside textual assets such as HTML and CSS files. Base64 is also widely used for sending e-mail attachments, because SMTP – in its original form – was designed to transport 7-bit ASCII characters only. Encoding an attachment as Base64 before sending, and then decoding when received, assures older SMTP servers will not interfere with the attachment. Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
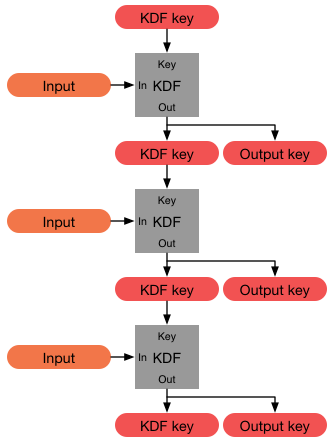
Password-hashing Function
In cryptography, a key derivation function (KDF) is a cryptographic algorithm that derives one or more secret keys from a secret value such as a master key, a password, or a passphrase using a pseudorandom function (which typically uses a cryptographic hash function or block cipher). KDFs can be used to stretch keys into longer keys or to obtain keys of a required format, such as converting a group element that is the result of a Diffie–Hellman key exchange into a symmetric key for use with AES. Keyed cryptographic hash functions are popular examples of pseudorandom functions used for key derivation. History The first deliberately slow (key stretching) password-based key derivation function was called "crypt" (or "crypt(3)" after its man page), and was invented by Robert Morris in 1978. It would encrypt a constant (zero), using the first 8 characters of the user's password as the key, by performing 25 iterations of a modified DES encryption algorithm (in which a 12-bit n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Derivation Function
In cryptography, a key derivation function (KDF) is a cryptographic algorithm that derives one or more secret keys from a secret value such as a master key, a password, or a passphrase using a pseudorandom function (which typically uses a cryptographic hash function or block cipher). KDFs can be used to stretch keys into longer keys or to obtain keys of a required format, such as converting a group element that is the result of a Diffie–Hellman key exchange into a symmetric key for use with AES. Keyed cryptographic hash functions are popular examples of pseudorandom functions used for key derivation. History The first deliberately slow (key stretching) password-based key derivation function was called "crypt" (or "crypt(3)" after its man page), and was invented by Robert Morris in 1978. It would encrypt a constant (zero), using the first 8 characters of the user's password as the key, by performing 25 iterations of a modified DES encryption algorithm (in which a 12-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Provos
Niels Provos is a German-American researcher in security engineering, malware, and cryptography. He received a PhD in computer science from the University of Michigan. From 2003 to 2018, he worked at Google as a Distinguished Engineer on security for Google. In 2018, he left Google to join Stripe as its new head of security. In 2022, Provos left Stripe and joined Lacework as head of Security Efficacy. For many years, Provos contributed to the OpenBSD operating system, where he developed the bcrypt adaptive cryptographic hash function. He is the author of numerous software packages, including the libevent event driven programming system, the Systrace access control system, the honeyd honeypot system, the StegDetect steganography detector, the Bcrypt password encryption technique, and many others. Provos has been an outspoken critic of the effect of the DMCA and similar laws on security researchers, arguing that they threaten to make criminals of people conducting legitimate sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Table
A rainbow table is a precomputed table for caching the outputs of a cryptographic hash function, usually for cracking password hashes. Passwords are typically stored not in plain text form, but as hash values. If such a database of hashed passwords falls into the hands of attackers, they can use a precomputed rainbow table to recover the plaintext passwords. A common defense against this attack is to compute the hashes using a key derivation function that adds a "salt" to each password before hashing it, with different passwords receiving different salts, which are stored in plain text along with the hash. Rainbow tables are a practical example of a space–time tradeoff: they use less computer processing time and more storage than a brute-force attack which calculates a hash on every attempt, but more processing time and less storage than a simple table that stores the hash of every possible password. Rainbow tables were invented by Philippe Oechslin as an application of an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pbkdf2
In cryptography, PBKDF1 and PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 1 and 2) are key derivation functions with a sliding computational cost, used to reduce vulnerability to brute-force attacks. PBKDF2 is part of RSA Laboratories' Public-Key Cryptography Standards (PKCS) series, specifically PKCS#5 v2.0, also published as Internet Engineering Task Force's RFC2898. It supersedes PBKDF1, which could only produce derived keys up to 160 bits long. RFC8018 (PKCS#5 v2.1), published in 2017, recommends PBKDF2 for password hashing. Purpose and operation PBKDF2 applies a pseudorandom function, such as hash-based message authentication code (HMAC), to the input password or passphrase along with a salt value and repeats the process many times to produce a ''derived key'', which can then be used as a cryptographic key in subsequent operations. The added computational work makes password cracking much more difficult, and is known as key stretching. When the standard was written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a security-focused operating system, security-focused, free software, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by fork (software development), forking NetBSD 1.0. The OpenBSD project emphasizes software portability, portability, software standard, standardization, software bug, correctness, proactive computer security, security, and integrated cryptography. The OpenBSD project maintains portable versions of many subsystems as package manager, packages for other operating systems. Because of the project's preferred BSD license, which allows binary redistributions without the source code, many components are reused in proprietary and corporate-sponsored software projects. The firewall (computing), firewall code in Apple Inc., Apple's macOS is based on OpenBSD's PF (firewall), PF firewall code, Android (operating system), Android's Bionic (software), Bionic C standard library is based on OpenBSD c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USENIX
USENIX is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit membership organization based in Berkeley, California and founded in 1975 that supports advanced computing systems, operating system (OS), and computer networking research. It organizes several conferences in these fields. History USENIX was established in 1975 under the name "Unix Users Group," focusing primarily on the study and development of the Unix OS family and similar systems. In June 1977, a lawyer from AT&T Corporation informed the group that they could not use the word "Unix" in their name as it was a trademark of Western Electric (the manufacturing arm of AT&T until 1995), which led to the change of name to USENIX. Since its founding, it has published a technical journal titled '' ;login:''. USENIX was started as a technical organization. As commercial interest grew, a number of separate groups started in parallel, most notably the Software Tools Users Group (STUG), a technical adjunct for Unix-like tools and interfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Schneier
Bruce Schneier (; born January 15, 1963) is an American cryptographer, computer security professional, privacy specialist, and writer. Schneier is an Adjunct Lecturer in Public Policy at the Harvard Kennedy School and a Fellow at the Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society as of November, 2013. He is a board member of the Electronic Frontier Foundation, Access Now, and The Tor Project; and an advisory board member of Electronic Privacy Information Center and VerifiedVoting.org. He is the author of several books on general security topics, computer security and cryptography and is a squid enthusiast. Early life and education Bruce Schneier is the son of Martin Schneier, a Brooklyn Supreme Court judge. He grew up in the Flatbush neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York, attending P.S. 139 and Hunter College High School. After receiving a physics bachelor's degree from the University of Rochester in 1984, he went to American University in Washington, D.C., and got his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |