|
Bank1
Bank1 (B-cell scaffold protein with ankyrin repeats 1) is a protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ... encoded in humans by the ''BANK1'' gene. This gene is located at region 2, band 4 (see chromosome nomenclature) on the long, i.e., "q", arm of chromosome 4. This gene location is abbreviated as 4q24. Adaptor protein that binds the proteins of the family SCR with Calcium channels in the LB.. References Genes on human chromosome 4 {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
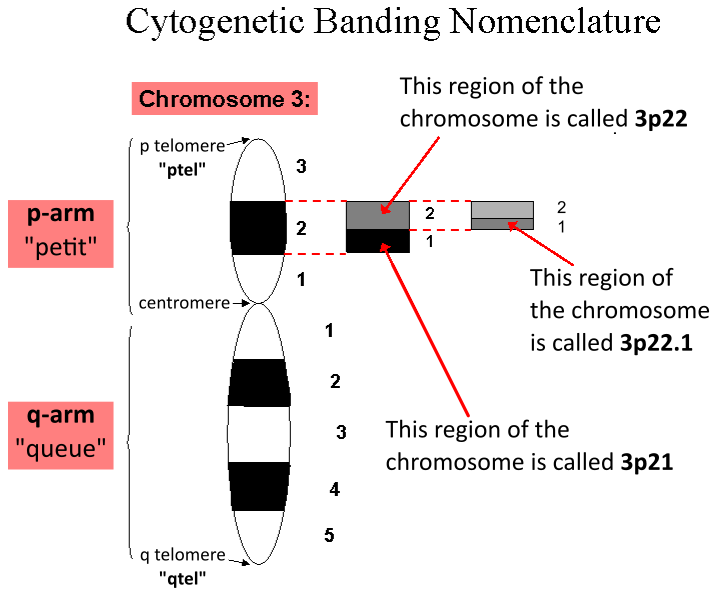
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (: loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of Human genome#Coding sequences (protein-coding genes), protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygote, homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygote, heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 4
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 190 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genomics The chromosome is ~193 megabases in length. In a 2012 paper, 775 protein-encoding genes were identified on this chromosome.Chen LC, Liu MY, Hsiao YC, Choong WK, Wu HY, Hsu WL, Liao PC, Sung TY, Tsai SF, Yu JS, Chen YJ (2012) Decoding the disease-associated proteins encoded in the human chromosome 4. J Proteome Res 211 (27.9%) of these coding sequences did not have any experimental evidence at the protein level, in 2012. 271 appear to be membrane proteins. 54 have been classified as cancer-associated proteins. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 4. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transducing Adaptor Protein
Signal transducing adaptor proteins (STAPs) are proteins that are accessory to main proteins in a signal transduction pathway. Adaptor proteins contain a variety of protein-binding modules that link protein-binding partners together and facilitate the creation of larger signaling complexes. These proteins tend to lack any intrinsic enzymatic activity themselves, instead mediating specific protein–protein interactions that drive the formation of Multiprotein complex, protein complexes. Examples of adaptor proteins include MYD88, Grb2 and SHC1. Signaling components Much of the specificity of signal transduction depends on the recruitment of several signalling components such as protein kinases and G-protein GTPases into short-lived active complexes in response to an activating signal such as a growth factor binding to its receptor (biochemistry), receptor. Domains Adaptor proteins usually contain several domains within their structure (e.g., SH2 domain, Src homology 2 (SH2) and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |