|
Balancing Selection
Balancing selection refers to a number of selective processes by which multiple alleles (different versions of a gene) are actively maintained in the gene pool of a population at frequencies larger than expected from genetic drift alone. Balancing selection is rare compared to purifying selection. It can occur by various mechanisms, in particular, when the heterozygotes for the alleles under consideration have a higher fitness than the homozygote. In this way genetic polymorphism is conserved. Evidence for balancing selection can be found in the number of alleles in a population which are maintained above mutation rate frequencies. All modern research has shown that this significant genetic variation is ubiquitous in panmictic populations. There are several mechanisms (which are not exclusive within any given population) by which balancing selection works to maintain polymorphism. The two major and most studied are heterozygote advantage and frequency-dependent selection. Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation of traits, both Genotype, genotypic and phenotypic, exists within all populations of organisms. However, some traits are more likely to facilitate survival and reproductive success. Thus, these traits are passed the next generation. These traits can also become more Allele frequency, common within a population if the environment that favours these traits remains fixed. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in a specific Ecological niche, niche, microevolution occurs. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostatic Selection
Apostatic selection is a form of negative frequency-dependent selection. It describes the survival of individual prey animals that are different (through mutation) from their species in a way that makes it more likely for them to be ignored by their predators. It operates on polymorphic species, species which have different forms. In apostatic selection, the common forms of a species are preyed on more than the rarer forms, giving the rare forms a selective advantage in the population. It has also been discussed that apostatic selection acts to stabilize prey polymorphisms. The term "apostatic selection" was introduced in 1962 by Bryan Clarke in reference to predation on polymorphic grove snails and since then it has been used as a synonym for negative frequency-dependent selection. The behavioural basis of apostatic selection was initially neglected, but was eventually established by A.B Bond. Apostatic selection can also apply to the predator if the predator has various mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
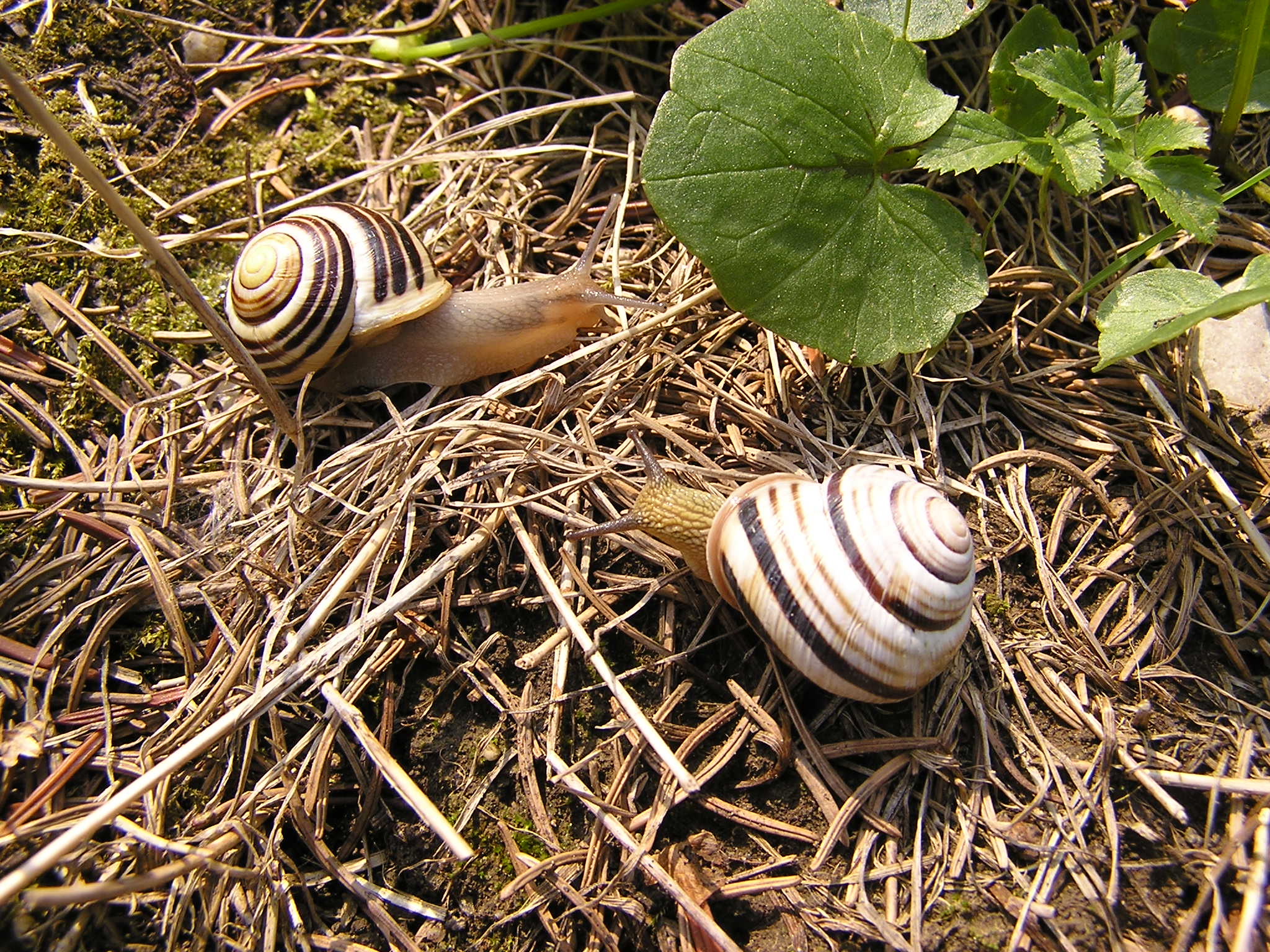
Cepaea Nemoralis Active Pair On Tree Trunk
''Cepaea'' is a genus of large air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs in the family Helicidae. The shells are often brightly coloured and patterned with brown stripes. The two living species in this genus, ''C. nemoralis'' and ''C. hortensis'', are widespread and common in Western and Central Europe. In North America, ''C. hortensis'' is native on the northeast coast, but both species have been introduced elsewhere, and they are also spreading further east in Europe. Both have been influential model species for ongoing studies of genetics and natural selection. Like many Helicidae, these snails use love darts during mating. Species For a long time, four living species were classified in the genus ''Cepaea''. However, molecular phylogenetic studies suggested that two of them should be placed in the genera '' Macularia'' and ''Caucasotachea'', which are not immediate relatives of either ''Cepaea'' or each other: * ''Cepaea hortensis'' (O. F. Müller, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
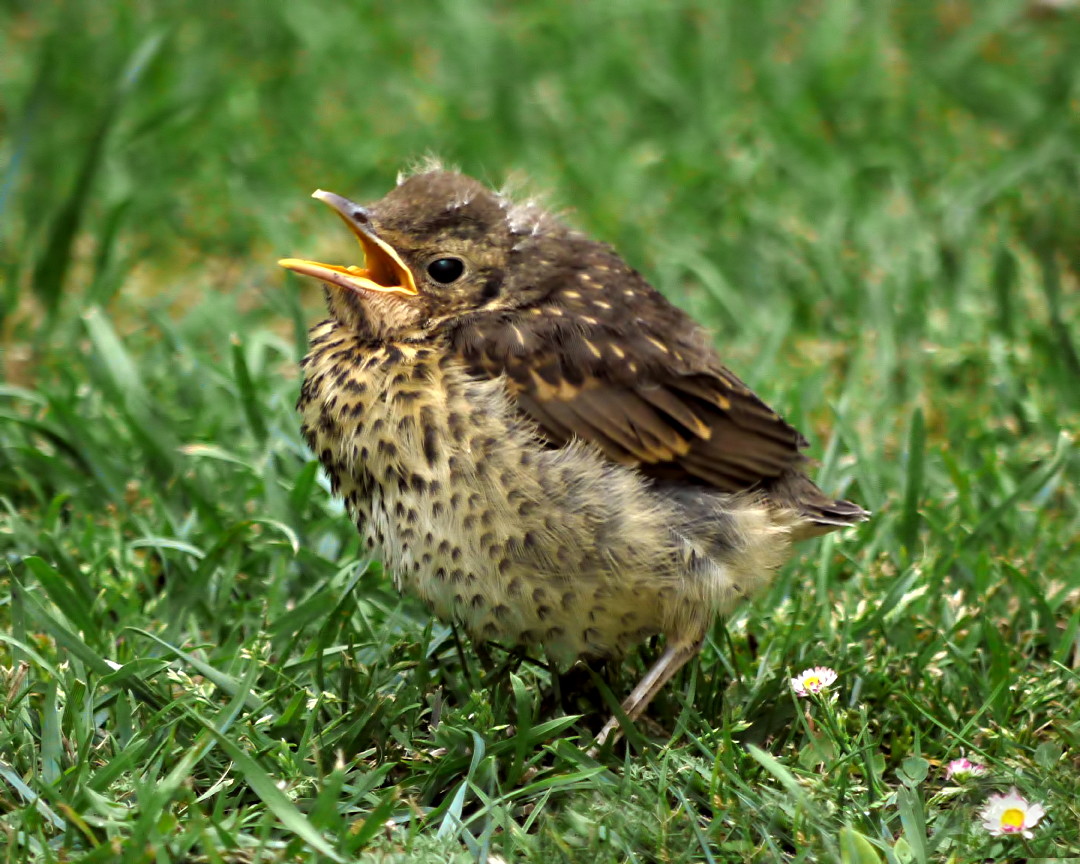
Song Thrush
The song thrush (''Turdus philomelos'') is a Thrush (bird), thrush that breeds across the West Palearctic. It has brown upper-parts and black-spotted cream or buff underparts and has four recognised subspecies. Its distinctive Birdsong, song, which has repeated musical phrases, has frequently been referred to in poetry. The song thrush breeds in forests, gardens and parks, and is partially bird migration, migratory with many birds wintering in southern Europe, North Africa and the Middle East; it has also been introduced into New Zealand and Australia. Although it is not threatened globally, there have been serious population declines in parts of Europe, possibly due to changes in farming practices. The song thrush builds a neat mud-lined bird nest#Cup, cup nest in a bush or tree and lays four to five dark-spotted blue bird egg, eggs. It is omnivorous and has the habit of using a favourite stone as an "anvil" on which to break open the shells of land snail, snails. Like other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
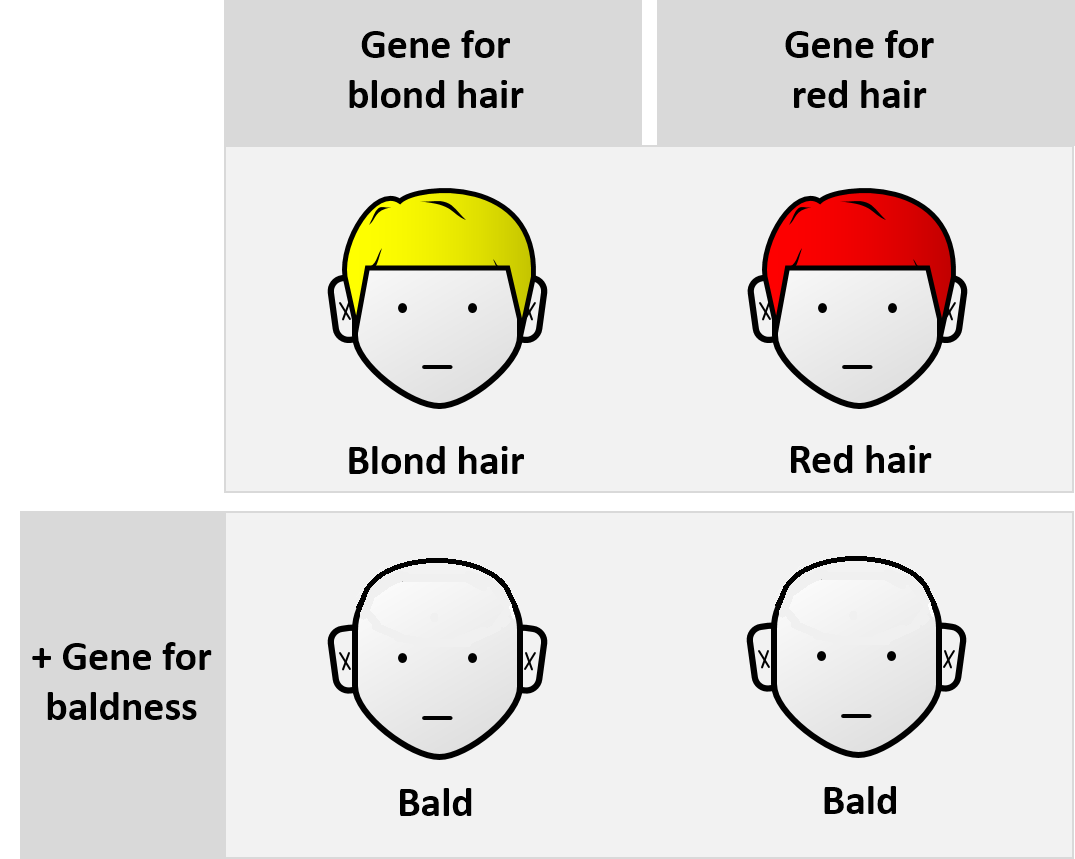
Epistasis
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics in which the effect of a gene mutation is dependent on the presence or absence of mutations in one or more other genes, respectively termed modifier genes. In other words, the effect of the mutation is dependent on the genetic background in which it appears. Epistatic mutations therefore have different effects on their own than when they occur together. Originally, the term ''epistasis'' specifically meant that the effect of a gene variant is masked by that of different gene. The concept of ''epistasis'' originated in genetics in 1907 but is now used in biochemistry, computational biology and evolutionary biology. The phenomenon arises due to interactions, either between genes (such as mutations also being needed in regulators of gene expression) or within them (multiple mutations being needed before the gene loses function), leading to non-linear effects. Epistasis has a great influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes, which leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Alleles
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or locus, on a DNA molecule. Alleles can differ at a single position through single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), but they can also have insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function or amount of the gene product(s) they code or regulate for. However, sometimes different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles. Nearly all multicellular organisms have two sets of chromosomes at some point in their biological life cycle; that is, they are diploid. For a given locus, if the two chromosomes contain the same allele, they, and the organism, are homozygous with respect to that allele. If the alleles are differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepaea Nemoralis
The grove snail, brown-lipped snail or lemon snail (''Cepaea nemoralis'') is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc. It is one of the most common large species of land snail in Europe, and has been introduced to North America. ;Subspecies: * ''Cepaea nemoralis etrusca'' (Rossmässler, 1835) * ''Cepaea nemoralis nemoralis'' (Linnaeus, 1758) ''Cepaea nemoralis'' is the type species of the genus ''Cepaea''. It is used as a model organism in ecological genetics, including in citizen science projects. Description ''Cepaea nemoralis'' is among the largest and, because of its bright colouration, one of the best-known snails in Western Europe. The colour of the gastropod shell, shell is highly variable; it ranges from brown, through pink, to yellow or even whitish, with or without one to five dark-brown bands. Names for many colour variants were coined in the nineteenth century but this system has been replaced by an inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a finite collection of positive real numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean of numbers is the Nth root, th root of their product (mathematics), product, i.e., for a collection of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as : \sqrt[n]. When the collection of numbers and their geometric mean are plotted in logarithmic scale, the geometric mean is transformed into an arithmetic mean, so the geometric mean can equivalently be calculated by taking the natural logarithm of each number, finding the arithmetic mean of the logarithms, and then returning the result to linear scale using the exponential function , :\sqrt[n] = \exp \left( \frac \right). The geometric mean of two numbers is the square root of their product, for example with numbers and the geometric mean is \textstyle \sqrt = The geometric mean o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prey Switching
Prey switching is frequency-dependent predation, where the predator preferentially consumes the most common type of prey. The phenomenon has also been described as apostatic selection, however the two terms are generally used to describe different parts of the same phenomenon. Apostatic selection has been used by authors looking at the differences between different genetic morphs. In comparison, prey switching has been used when describing the choice between different species. Definition The term ''switching'' was first coined by the ecologist Murdoch in 1969 to describe the situation where a predator eats disproportionately more of the most common type of prey. Eight years earlier in 1962 the geneticst B. C. Clarke described a similar phenomenon and called it " apostatic selection". Since then the term ''prey switching'' has mainly been used by ecologists, while ''apostatic selection'' has been used by geneticists, and because of this they have been used to describe different as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underdominance
In genetics, underdominance, also known as homozygote advantage, heterozygote disadvantage, or negative overdominance," is the opposite of overdominance. It is the selection against the heterozygote, causing disruptive selection and divergent genotypes. Underdominance exists in situations where the heterozygotic genotype is inferior in fitness to either the dominant or recessive homozygotic genotype. Compared to examples of overdominance in actual populations, underdominance is considered more unstable and may lead to the fixation of either allele. An example of stable underdominance may occur in individuals who are heterozygotic for polymorphisms that would make them better suited for one of two niches. Consider a situation in which a population is completely homozygotic for an "A" allele, allowing exploitation of a particular resource. Eventually, a polymorphic "a" allele may be introduced into the population, resulting in an individual who is capable of exploiting a differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |