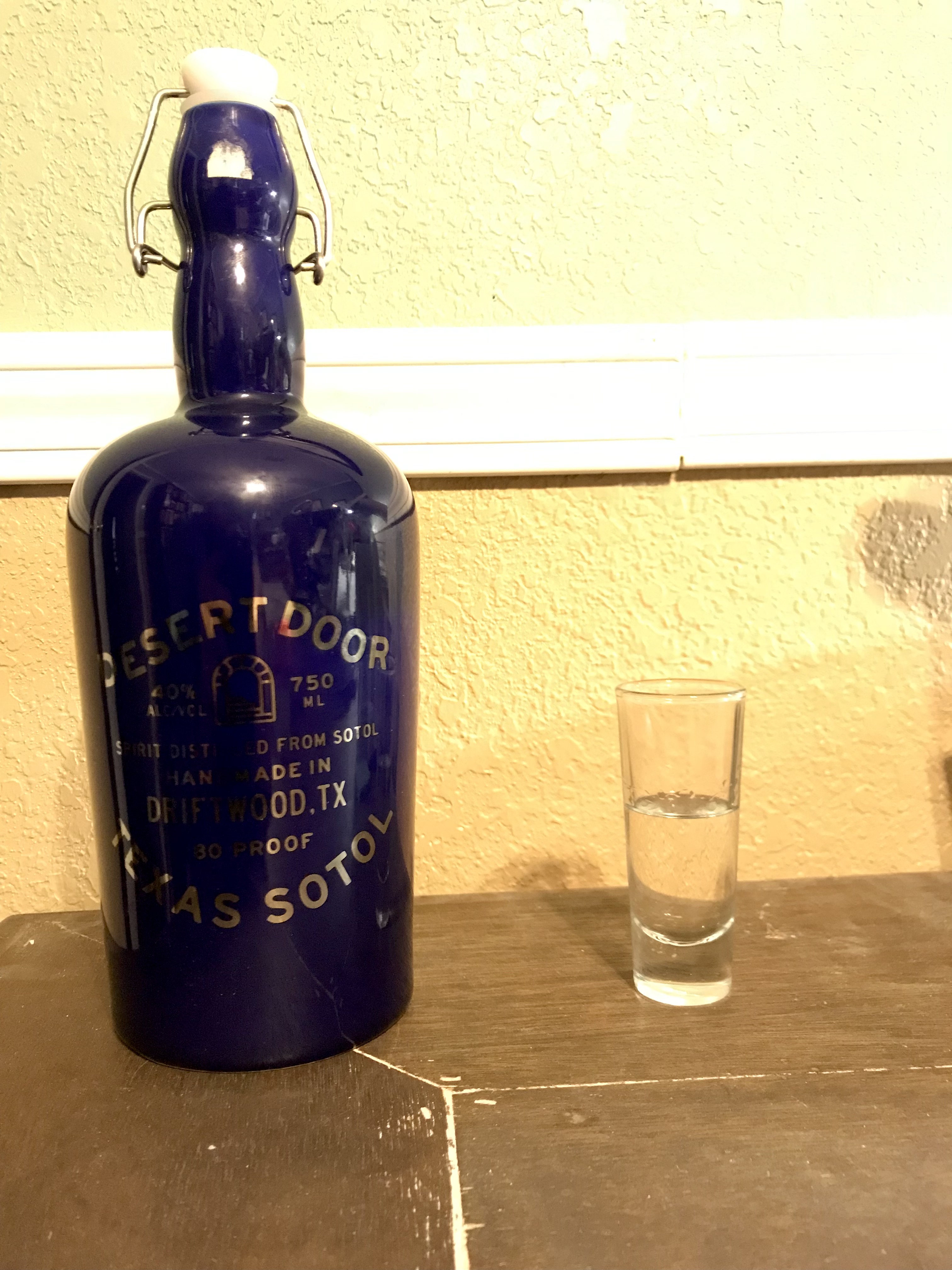|
Baker Cave
Baker Cave is a prehistoric archaeological site, located on a small canyon near Devils River (Texas), Devils River in Southwest Texas. Dating from ''circa'' 7,000–7,800 BCE, Baker Cave is a part of a system of rock shelters in the Lower Pecos Canyons region and was 120 feet long by 56 feet deep (37 m × 17 m). The ceiling varied from at the mouth to just a few inches in the back. These sites are common in the limestone formations in the Lower Pecos region. The site was perched well above the flood, preserving the materials that ancient peoples had left behind. A large cooking hearth was found inside it, dating to around 9,000 years ago, and containing small creatures such as snakes, rats, fish, and rabbits, and a wide variety of seeds and nuts, indicating a diversified diet."Lower Pecos Canyonland." ''Texa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mescal Bean
''Dermatophyllum'' is a genus of three or four species of shrubs and small trees in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family, Fabaceae. The genus is native to southwestern North America from western Texas to New Mexico and Arizona in the United States, and south through Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Nuevo León in northern Mexico. Members of the genus are commonly known as mescalbean, mescal bean, or ''frijolito''. One of the common names of ''Dermatophyllum secundiflorum'' is Texas mountain laurel, although the name mountain laurel also refers to the very dissimilar and unrelated genus ''Kalmia'' (family Ericaceae) and the name laurel refers generally to plants in the unrelated order Laurales. Although still commonly treated in the genus ''Sophora'', recent genetic evidence has shown that the mescalbeans are only distantly related to the other species of ''Sophora''. Species ''Dermatophyllum'' comprises the following species: * '' Dermatophyllum arizonicum'' (S.Watson) Vincent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age Sites
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Texas
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as '' speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Texas
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitetail Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black-tailed or mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') from that point west except for mixed deciduous riparian corridors, river valley bottomlands, and lower foothills of the northern Rocky Mountain region from Wyoming west to eastern Washington and eastern Oregon and north to northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lechuguilla
''Agave lechuguilla'' (common name in Chihuahua: ''lechuguilla'', meaning "small lettuce") is an ''Agave'' species found only in the Chihuahuan Desert. The plant flowers once in its life and then dies. Description The plant reproduces most often through underground offshoots, creating large colonies. It also can flower at any time after the plant has reached three to 21 years of age, producing a leafless stalk that can reach in height. The flower clusters are located at the top and are funnel-shaped in purples, reds, and yellows. The plant dies after flowering in May–July. The leaves are long, tough, and rigid, with very sharp, hard points that can easily penetrate clothing and even leather, giving the colloquial name "shin-daggers". Taxonomy Charles Wright first collected the plant in 1849 and it was described by John Torrey in 1859. Distribution and habitat It is an indicator species in the Chihuahuan Desert, the only place it is found. It typically grows on calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nolina
''Nolina'' is a genus of tropical xerophytic flowering plants, with the principal distribution being in Mexico and extending into the southern United States. They are large, dioecious plants. Some botanists have included the genus ''Beaucarnea'' in ''Nolina''. In the APG III classification system, it is placed in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Nolinoideae (formerly the family Ruscaceae). Former alternative placements include Nolinaceae and Agavaceae. The genus is named for 18th century French arboriculturist Abbé C. P. Nolin. Members of the genus are known as beargrasses, some of which are cultivated as ornamental plants. Species Accepted species: # ''Nolina arenicola'' Correll – Trans-Pecos beargrass - western Texas # ''Nolina atopocarpa'' Bartlett – Florida beargrass - Florida # ''Nolina azureogladiata'' D.Donati - Oaxaca # '' Nolina beldingi'' Brandegee - Baja California Sur # ''Nolina bigelovii'' (Torr.) S.Watson – Bigelow's nolina - Sonora, Ariz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotol
Sotol is a distilled spirit from the Chihuahuan desert northern Mexico, western Texas sourced from the family of Asparagaceae; the genus Dasylirion and several species, most commonly: ''Dasylirion wheeleri'', Dasylirion durangense, '' Dasylirion cedrosanum'', and ''Dasylirion leiophyllum'', less commonly with Dasylirion texanum and Dasylirion lucidum (commonly known as Desert Spoon or, in Spanish, ''sotol, sereque, cucharilla, or palmilla''), a plant that grows in the Chihuahua desert of northern Mexico, New Mexico, Arizona, and west and central Texas. Sotol liquor is a Mexican drink that is known as the state spirit of Chihuahua, Durango and Coahuila. Sotol has its own appellation of origin since 2002, and may be produced only in Chihuahua, Coahuila and Durango. There are dozens of commercial examples available. Production of sotol spirits exists outside the Sotol Denomination of Origin in several regions such as Sonora where it is known as Palmilla, Oaxaca (Cucharillo), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persimmon
The persimmon is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus ''Diospyros''. The most widely cultivated of these is the Oriental persimmon, '' Diospyros kaki'' ''Diospyros'' is in the family Ebenaceae, and a number of non-persimmon species of the genus are grown for ebony timber. In 2019, China produced 75% of the world total of persimmons. Description Like the tomato, persimmons are not commonly considered to be berries, but morphologically the fruit is in fact a berry. The tree '' Diospyros kaki'' is the most widely cultivated species of persimmon. Typically the tree reaches in height and is round-topped. It usually stands erect, but sometimes can be crooked or have a willowy appearance. The leaves are long, and are oblong in shape with brown-hairy petioles in length. They are leathery and glossy on the upper surface, brown and silky underneath. The leaves are deciduous and bluish-green in color. In autumn, they turn to yellow, orange, or red. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesquite
Mesquite is a common name for several plants in the genus '' Prosopis'', which contains over 40 species of small leguminous trees. They are native to dry areas in the Americas. They have extremely long roots to seek water from very far under ground. As a legume, mesquites are one of the few sources of fixed nitrogen in the desert habitat. These trees bloom from spring to summer. They often produce fruits known as "pods". ''Prosopis'' spp. are able to grow up to tall, depending on site and climate. They are deciduous and depending on location and rainfall have either deep or shallow roots. ''Prosopis'' is considered long-lived because of the low mortality rate after the dicotyledonous stage and juveniles are also able to survive in conditions with low light and drought. The Cahuilla indigenous people of western North America were known to eat the seeds of mesquite. History ''Prosopis'' spp. have been in North America since the Pliocene era and their wood has been dated to 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne in a cup-shaped cupule. Acorns are long and on the fat side. Acorns take between 5 and 24 months (depending on the species) to mature; see the list of ''Quercus'' species for details of oak classification, in which acorn morphology and phenology are important factors. Etymology The word ''acorn'' (earlier ''akerne'', and ''acharn'') is related to the Gothic name ''akran'', which had the sense of "fruit of the unenclosed land". The word was applied to the most important forest produce, that of the oak. Chaucer spoke of "achornes of okes" in the 14th century. By degrees, popular etymology connected the word both with "corn" and "oak-horn", and the spelling changed accordingly. The current spelling (emerged 15c.-16c.), derives from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)