|
Bag Of Words Assumption
The bag-of-words (BoW) model is a model of text which uses an unordered collection (a "bag") of words. It is used in natural language processing and information retrieval (IR). It disregards word order (and thus most of syntax or grammar) but captures multiplicity. The bag-of-words model is commonly used in methods of document classification where, for example, the (frequency of) occurrence of each word is used as a feature for training a classifier. It has also been used for computer vision. An early reference to "bag of words" in a linguistic context can be found in Zellig Harris's 1954 article on ''Distributional Structure''. Definition The following models a text document using bag-of-words. Here are two simple text documents: (1) John likes to watch movies. Mary likes movies too. (2) Mary also likes to watch football games. Based on these two text documents, a list is constructed as follows for each document: "John","likes","to","watch","movies","Mary","likes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiset
In mathematics, a multiset (or bag, or mset) is a modification of the concept of a set that, unlike a set, allows for multiple instances for each of its elements. The number of instances given for each element is called the ''multiplicity'' of that element in the multiset. As a consequence, an infinite number of multisets exist that contain only elements and , but vary in the multiplicities of their elements: * The set contains only elements and , each having multiplicity 1 when is seen as a multiset. * In the multiset , the element has multiplicity 2, and has multiplicity 1. * In the multiset , and both have multiplicity 3. These objects are all different when viewed as multisets, although they are the same set, since they all consist of the same elements. As with sets, and in contrast to ''tuples'', the order in which elements are listed does not matter in discriminating multisets, so and denote the same multiset. To distinguish between sets and multisets, a notat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
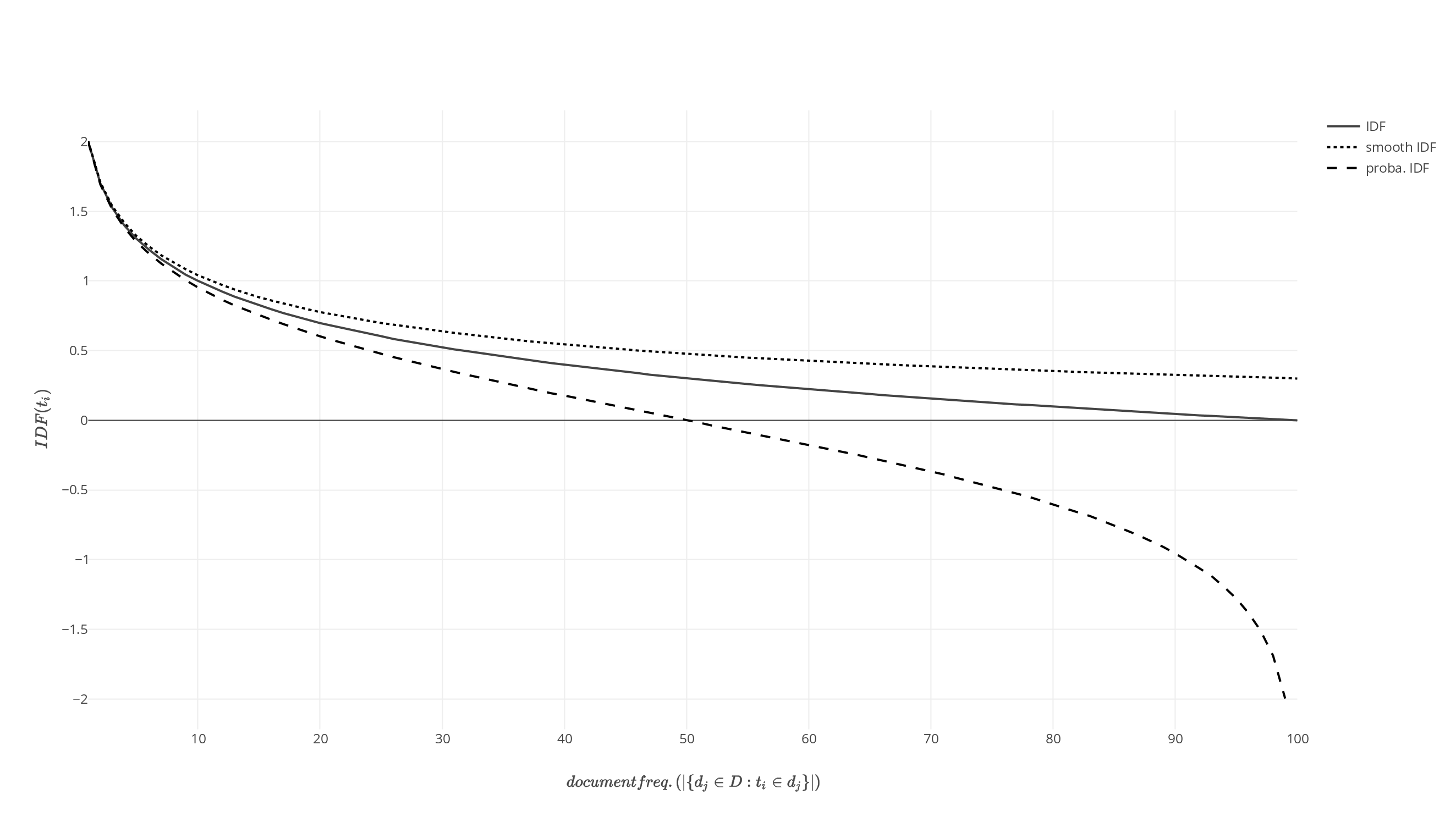
Tf–idf
In information retrieval, tf–idf (term frequency–inverse document frequency, TF*IDF, TFIDF, TF–IDF, or Tf–idf) is a measure of importance of a word to a document in a collection or Text corpus, corpus, adjusted for the fact that some words appear more frequently in general. Like the bag-of-words model, it models a document as a multiset of words, without word order. It is a refinement over the simple bag-of-words model, by allowing the weight of words to depend on the rest of the corpus. It was often used as a weighting factor in searches of information retrieval, text mining, and user modeling. A survey conducted in 2015 showed that 83% of text-based recommender systems in digital libraries used tf–idf. Variations of the tf–idf weighting scheme were often used by search engines as a central tool in scoring and ranking a document's Relevance (information retrieval), relevance given a user Information retrieval, query. One of the simplest ranking functions is computed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W-shingling
In natural language processing a ''w''-shingling is a set of ''unique'' ''shingles'' (therefore ''n-grams'') each of which is composed of contiguous subsequences of tokens within a document, which can then be used to ascertain the similarity between documents. The symbol ''w'' denotes the quantity of tokens in each shingle selected, or solved for. The document, "a rose is a rose is a rose" can therefore be maximally tokenized as follows: :(a,rose,is,a,rose,is,a,rose) The set of all contiguous ''sequences of 4 tokens'' (Thus 4=''n'', thus 4-''grams'') is : Which can then be reduced, or maximally shingled in this particular instance to :. Resemblance For a given shingle size, the degree to which two documents ''A'' and ''B'' resemble each other can be expressed as the ratio of the magnitudes of their shinglings' intersection In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (or more generally, items) as vector space, vectors such that the distance between vectors represents the relevance between the documents. It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, index (search engine), indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions In this section we consider a particular vector space model based on the Bag-of-words model, bag-of-words representation. Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each Dimension (vector space), dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MinHash
In computer science and data mining, MinHash (or the min-wise independent permutations locality sensitive hashing scheme) is a technique for quickly estimating how similar two sets are. The scheme was published by Andrei Broder in a 1997 conference, and initially used in the AltaVista search engine to detect duplicate web pages and eliminate them from search results.. It has also been applied in large-scale clustering problems, such as clustering documents by the similarity of their sets of words.. Jaccard similarity and minimum hash values The Jaccard similarity coefficient is a commonly used indicator of the similarity between two sets. Let be a set and and be subsets of , then the Jaccard index is defined to be the ratio of the number of elements of their intersection and the number of elements of their union: : J(A,B) = . This value is 0 when the two sets are disjoint, 1 when they are equal, and strictly between 0 and 1 otherwise. Two sets are more similar (i.e. have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature Extraction
Feature may refer to: Computing * Feature recognition, could be a hole, pocket, or notch * Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob * Feature (machine learning), in statistics: individual measurable properties of the phenomena being observed * Software feature, a distinguishing characteristic of a software program Science and analysis * Feature data, in geographic information systems, comprise information about an entity with a geographic location * Features, in audio signal processing, an aim to capture specific aspects of audio signals in a numeric way * Feature (archaeology), any dug, built, or dumped evidence of human activity Media * Feature film, a film with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole film to fill a program ** Feature length, the standardized length of such films * Feature story, a piece of non-fiction writing about news * Radio documentary (feature), a radio program devoted to covering a particular topic in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Smoothing
In statistics, additive smoothing, also called Laplace smoothing or Lidstone smoothing, is a technique used to smooth count data, eliminating issues caused by certain values having 0 occurrences. Given a set of observation counts \mathbf = \langle x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_d \rangle from a d-dimensional multinomial distribution with N trials, a "smoothed" version of the counts gives the estimator : \hat\theta_i = \frac \qquad (i = 1, \ldots, d), where the smoothed count \hat x_i = N \hat\theta_i, and the "pseudocount" ''α'' > 0 is a smoothing parameter, with ''α'' = 0 corresponding to no smoothing (this parameter is explained in below). Additive smoothing is a type of shrinkage estimator, as the resulting estimate will be between the empirical probability ( relative frequency) x_i/N and the uniform probability 1/d. Common choices for ''α'' are 0 (no smoothing), (the Jeffreys prior), or 1 (Laplace's rule of succession), but the parameter may also be set empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashing Trick
In machine learning, feature hashing, also known as the hashing trick (by analogy to the kernel trick), is a fast and space-efficient way of vectorizing features, i.e. turning arbitrary features into indices in a vector or matrix. It works by applying a hash function to the features and using their hash values as indices directly (after a modulo operation), rather than looking the indices up in an associative array. In addition to its use for encoding non-numeric values, feature hashing can also be used for dimensionality reduction. This trick is often attributed to Weinberger et al. (2009), but there exists a much earlier description of this method published by John Moody in 1989. Motivation Motivating example In a typical document classification task, the input to the machine learning algorithm (both during learning and classification) is free text. From this, a bag of words (BOW) representation is constructed: the individual tokens are extracted and counted, and each disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weka (machine Learning)
The weka, also known as the Māori hen or woodhen (''Gallirallus australis'') is a flightless bird species of the rail family. It is endemic to New Zealand. Some authorities consider it as the only extant member of the genus '' Gallirallus''. Four subspecies are recognized but only two (northern/southern) are supported by genetic evidence. The weka are sturdy brown birds about the size of a chicken. As omnivores, they feed mainly on invertebrates and fruit. Weka usually lay eggs between August and January; both sexes help to incubate. Description Weka are large rails. They are predominantly rich brown mottled with black and grey; the brown shade varies from pale to dark depending on subspecies. The male is the larger sex at in length and in weight. Females measure in length and weigh . The reduced wingspan ranges from . The relatively large, reddish-brown beak is about long, stout and tapered, and used as a weapon. The pointed tail is near-constantly being flicked, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, reporting nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science (informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Interest Group On Information Retrieval
SIGIR is the Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Information Retrieval. The scope of the group's specialty is the theory and application of computers to the acquisition, organization, storage, retrieval and distribution of information; emphasis is placed on working with non-numeric information, ranging from natural language to highly structured data bases. Conferences The annual international SIGIR conference, which began in 1978, is considered the most important in the field of information retrieval. SIGIR also sponsors the annual Joint Conference on Digital Libraries (JCDL) in association with SIGWEB, the Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), and the International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM) in association with SIGKDD, SIGMOD, and SIGWEB. SIGIR conference locations Awards The group gives out several awards to contributions to the field of information retrieval. The most important award is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |