|
BINAP 3D
BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This Optical isomerism, chiral diphosphines, diphosphine ligand is widely used in chiral synthesis, asymmetric synthesis. It consists of a pair of 2-diphenylphosphinonaphthalene, naphthyl groups linked at the 1 and 1′ positions. This C2-Symmetric ligands, C2-symmetric framework lacks a stereocenter, stereogenic atom, but has axial chirality due to restricted rotation (atropisomerism). The barrier to racemization is high due to steric hindrance, which limits rotation about the bond linking the naphthyl rings. The dihedral angle between the naphthyl groups is approximately 90°. The natural bite angle is 93°. Use as ligand in asymmetric catalysis BINAP is used in organic synthesis for enantioselective transformations catalyzed by its complex (chemistry), complexes of ruthenium, rhodium, and palladium. As pioneered by Ryōji Noyori and his co-workers, rhodium complexes of BINAP are usefu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex (chemistry)
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEGPHOS
SEGPHOS is a chiral ligand developed by Takasago International Corporation that is used in asymmetric synthesis. It was developed after BINAP BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This Optical isomerism, chiral diphosphines, diphosphine ligand is widely used in chiral synthesis, asymmetric synthesis. It consists of a pair of 2-diphe ... and was investigated since it has a narrower dihedral angle between the aromatic faces. This was predicted and then confirmed to increase the enantioselectivity and activity of metal complexes of SEGPHOS. After its commercialization, SEGPHOS and its substituted derivatives have been found to constitute a privileged ligand class for a variety of transition metal catalysts and chemical transformations beyond its original application in ruthenium-catalyzed enantioselective hydrogenation. In addition to the parent ligand bearing phenyl groups on the phosphorus atoms, the bulkier derivatives DM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphine
Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air. Properties, preparation, reactions Diphosphane adopts the gauche conformation (like hydrazine, less symmetrical than shown in the image) with a P−P distance of 2.219 angstroms. It is nonbasic, unstable at room temperature, and spontaneously flammable in air. It is only poorly soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents. Its 1H NMR spectrum consists of 32 lines resulting from an A2XX'A'2 splitting system. Diphosphane is produced by the hydrolysis of calcium monophosphide, which can be described as the Ca2+ derivative of . According to an optimized procedure, hydrolysis of 400 g of CaP at −30 °C gives about 20 g of product, slightly contaminated with phosphine Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
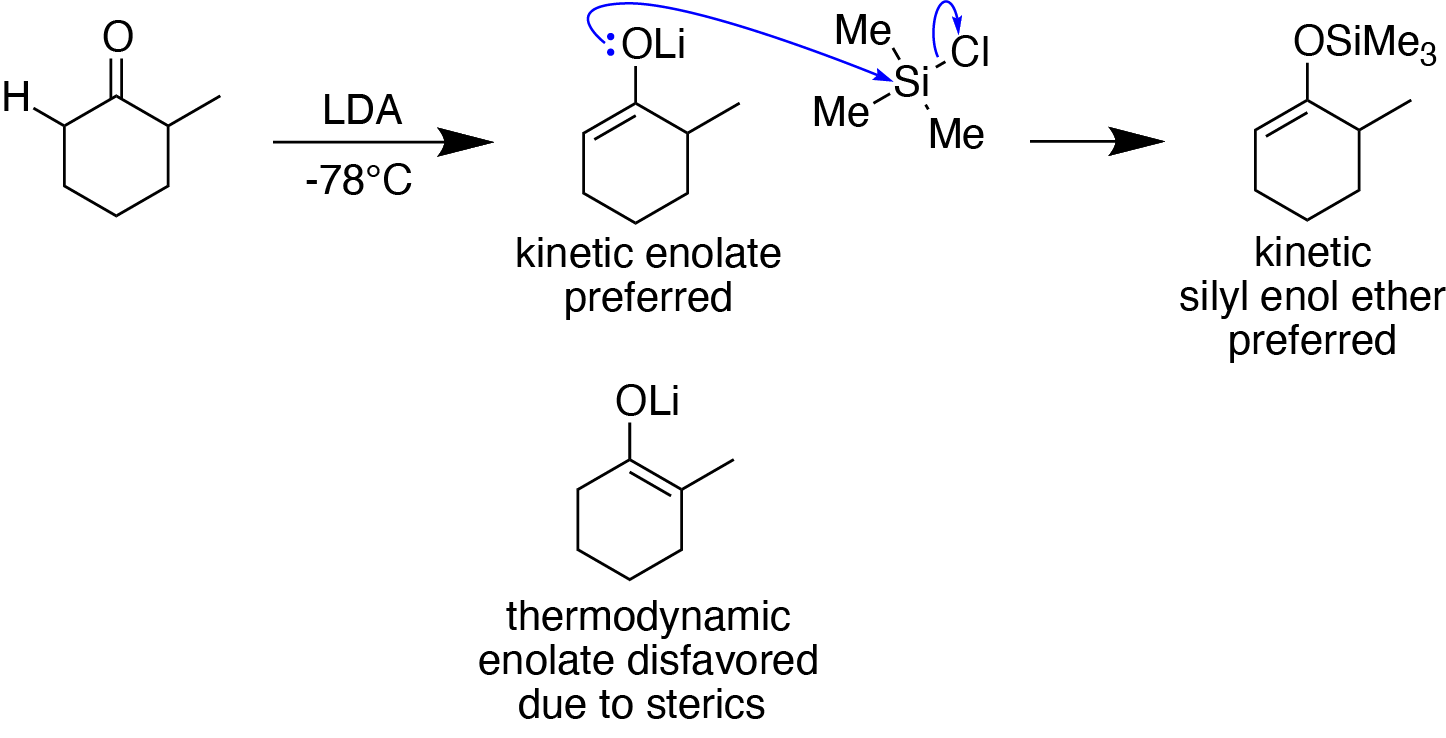
Silyl Enol Ether
In organosilicon chemistry, silyl enol ethers are a class of organic compounds that share the common functional group , composed of an enolate () bonded to a silane () through its oxygen end and an ethene group () as its carbon end. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis. Synthesis Silyl enol ethers are generally prepared by reacting an enolizable carbonyl compound with a silyl electrophile and a base, or just reacting an enolate with a silyl electrophile.Clayden, J., Greeves, N., & Warren, S. (2012). Silyl enol ethers. In ''Organic chemistry'' (Second ed., pp. 466-467). Oxford University Press. Since silyl electrophiles are hard and silicon-oxygen bonds are very strong, the oxygen (of the carbonyl compound or enolate) acts as the nucleophile to form a Si-O single bond. The most commonly used silyl electrophile is trimethylsilyl chloride. To increase the rate of reaction, trimethylsilyl triflate may also be used in the place of trimethylsilyl chloride as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoselectivity
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non- stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation of a pre-existing one. The selectivity arises from differences in steric and electronic effects in the mechanistic pathways leading to the different products. Stereoselectivity can vary in degree but it can never be total since the activation energy difference between the two pathways is finite: both products are at least possible and merely differ in amount. However, in favorable cases, the minor stereoisomer may not be detectable by the analytic methods used. An enantioselective reaction is one in which one enantiomer is formed in preference to the other, in a reaction that creates an optically active product from an achiral starting material, using either a chiral catalyst, an enzyme or a chiral reagent. The degree of selectivity is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(I) Fluoride
Silver(I) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula AgF. It is one of the three main fluorides of silver, the others being silver subfluoride and silver(II) fluoride. AgF has relatively few niche applications; it has been employed as a fluorination and desilylation reagent in organic synthesis and in aqueous solution as a topical caries treatment in dentistry. The hydrates of AgF present as colorless, while pure anhydrous samples are yellow. Preparation High-purity silver(I) fluoride can be produced by the heating of silver carbonate to under a hydrogen fluoride environment, in a platinum tube: : Laboratory routes to the compound typically avoid the use of gaseous hydrogen fluoride. One method is the thermal decomposition of silver tetrafluoroborate: : In an alternative route, silver(I) oxide is dissolved in concentrated aqueous hydrofluoric acid, and the silver fluoride is precipitated out of the resulting solution by acetone. : Properties Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nippon Kagaku Kaishi
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |