|
B-flat Major
B-flat major is a major scale based on B, with pitches B, C, D, E, F, G, and A. Its key signature has two flats. Its relative minor is G minor and its parallel minor is B-flat minor. The B-flat major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B-flat harmonic major and melodic major scales are: Many transposing instruments are pitched in B-flat major, including the clarinet, trumpet, tenor saxophone, and soprano saxophone. As a result, B-flat major is one of the most popular keys for concert band compositions. Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of B-flat major are: * Tonic – B-flat major * Supertonic – C minor * Mediant – D minor * Subdominant – E-flat major * Dominant – F major * Submediant – G minor * Leading-tone – A diminished History Joseph Haydn's Symphony No. 98 is often credited as the first symphony written in that key, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Minor
G minor is a minor scale based on G, consisting of the pitches G, A, B, C, D, E, and F. Its key signature has two flats. Its relative major is B-flat major and its parallel major is G major. The G natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The G harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of G minor are: * Tonic – G minor * Supertonic – A diminished * Mediant – B-flat major * Subdominant – C minor * Dominant – D minor * Submediant – E-flat major * Subtonic – F major Mozart's use of G minor G minor has been considered the key through which Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart best expressed sadness and tragedy, and many of his minor key works are in G minor, such as Piano Quartet No. 1 and String Quintet No. 4. Though Mozart touched on various minor keys in his symphonies, G minor is the only minor key he used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
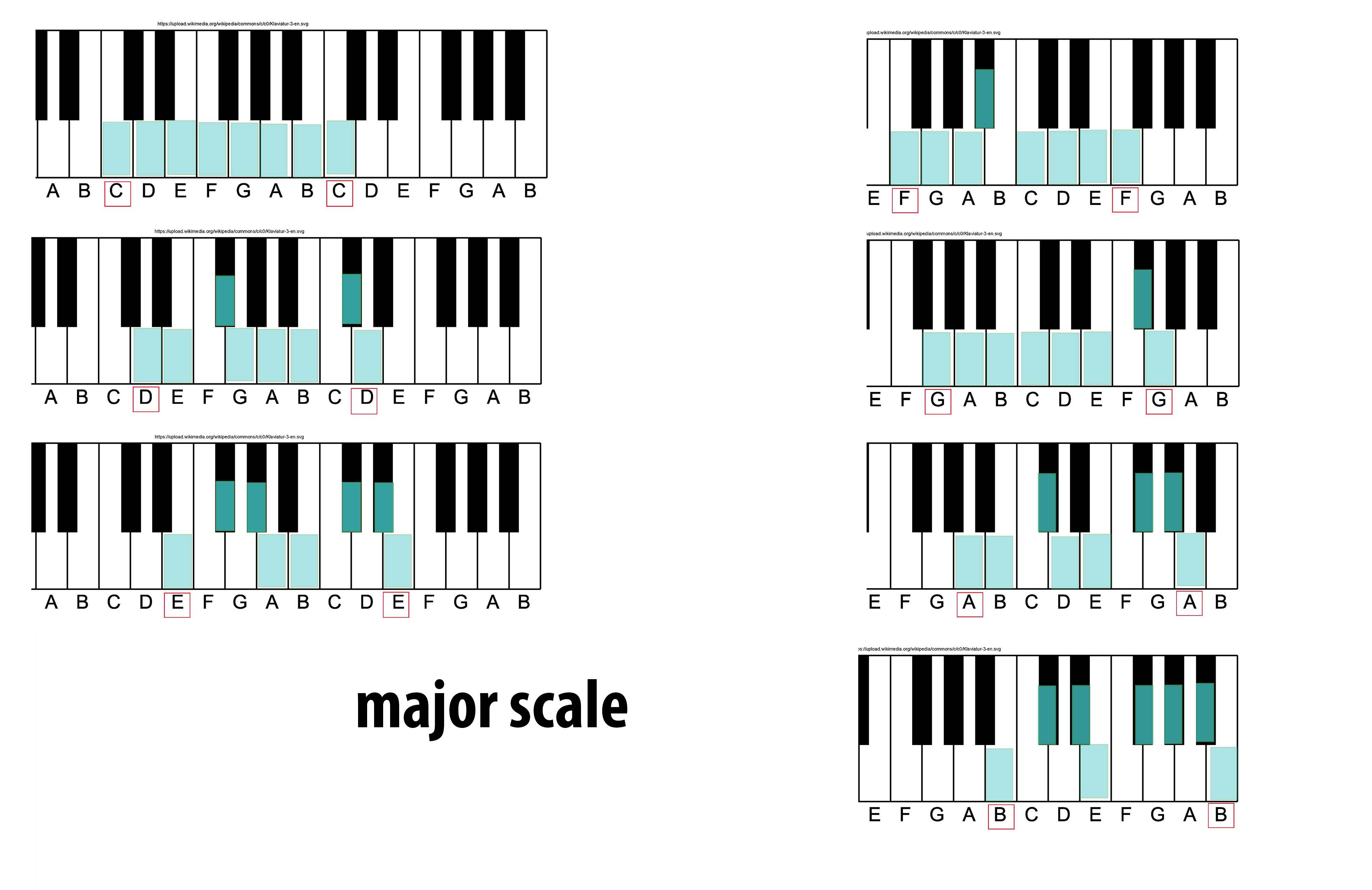
Melodic Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdominant. It also happens to be the note one step below the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the subdominant note is sung as ''fa''. The triad built on the subdominant note is called the subdominant chord. In Roman numeral analysis In music theory, Roman numeral analysis is a type of Harmony, harmonic analysis in which chord (music), chords are represented by Roman numerals, which encode the chord's Degree (music), degree and Function_(music), harmonic function within a given ..., the subdominant chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "IV" in a major key, indicating that the chord is a major triad. In a minor key, it is symbolized by "iv", indicating that the chord is a minor triad. These chords may also appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D Minor
D minor is a minor scale based on D, consisting of the pitches D, E, F, G, A, B, and C. Its key signature has one flat. Its relative major is F major and its parallel major is D major. The D natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The D harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of D minor are: * Tonic – D minor * Supertonic – E diminished * Mediant – F major * Subdominant – G minor * Dominant – A minor * Submediant – B-flat major * Subtonic – C major Music in D minor Of Domenico Scarlatti's 555 keyboard sonatas, 151 are in minor keys, and with 32 sonatas, D minor is the most often chosen minor key. '' The Art of Fugue'' by Johann Sebastian Bach is in D minor. Michael Haydn's only minor-key symphony, No. 29, is in D minor. According to Alfred Einstein, the history of tuning has led D mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediant
In music, the mediant (''Latin'': "being in the middle") is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as ''mi''. While the fifth scale degree is almost always a perfect fifth, the mediant can be a major or minor third. Schenkerian analysts consider the ''mediant'' (third scale degree) as an expansion or extension of the tonic since they are both common tones of the tonic chord. Thus, the third degree of a tonic triad is also the mediant iii note; furthermore, the 5th degree of the submediant chord vi is also the mediant iii note. On the other hand, in German theory derived from Hugo Riemann the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel, tP. In Roman numeral analysis, the mediant chord can take several forms. In major scales, the mediant chord is a minor triad and is symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Minor
C minor is a minor scale based on C, consisting of the pitches C, D, E, F, G, A, and B. Its key signature consists of three flats. Its relative major is E major and its parallel major is C major. The C natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The C harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of C minor are: * Tonic – C minor * Supertonic – D diminished * Mediant – E-flat major * Subdominant – F minor * Dominant – G minor * Submediant – A-flat major * Subtonic – B-flat major Notable compositions * Charles-Valentin Alkan ** Prelude Op. 31, No. 16 (Assez lentement) ** Symphony for Solo Piano, 1st movement: Allegro ** Trois grandes études, Op. 76, No. 3 "Mouvement semblable et perpetuel" * Johannes Sebastian Bach ** Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, BWV 582 ** Lute Suite in C minor, BWV 997 ** Cello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supertonic
In music, the supertonic is the second degree () of a diatonic scale, one whole step above the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the supertonic note is sung as ''re''. The triad built on the supertonic note is called the supertonic chord. In Roman numeral analysis, the supertonic chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "ii" in a major key, indicating that the chord is a minor chord (in C: D–F–A). In a minor key, it is indicated by "ii," indicating that the chord is a diminished chord (in C: D–F–A). Because it is a diminished chord, it usually appears in first inversion (iio6) so that no note dissonates with the bass note. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: in major, as ii7 (in C: D–F–A–C), while in minor as ii7 (in C: D–F–A–C) or rarely ii7. They are the second-most common form of nondominant seventh chords. The supertonic chord normally functions as a predominant chord, a chord that resolves to a chord wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonic (music)
In music, the tonic is the first scale degree () of the diatonic scale (the first note of a scale) and the tonal center or final resolution tone that is commonly used in the final cadence in tonal (musical key-based) classical music, popular music, and traditional music. In the movable do solfège system, the tonic note is sung as ''do''. More generally, the tonic is the note upon which all other notes of a piece are hierarchically referenced. Scales are named after their tonics: for instance, the tonic of the C major scale is the note C. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord in these styles of music. In Roman numeral analysis, the tonic chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "" if it is major and by "" if it is minor. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: in major, as M7, or in minor as 7 or rarely M7: The tonic is distinguished from the root, which is the reference note of a chord, rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Degree
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic—the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals and chords and whether an interval is major or minor. In the most general sense, the scale degree is the number given to each step of the scale, usually starting with 1 for tonic. Defining it like this implies that a tonic is specified. For instance, the 7-tone diatonic scale may become the major scale once the proper degree has been chosen as tonic (e.g. the C-major scale C–D–E–F–G–A–B, in which C is the tonic). If the scale has no tonic, the starting degree must be chosen arbitrarily. In set theory, for instance, the 12 degrees of the chromatic scale are usually numbered starting from C=0, the twelve pitch classes being numbered from 0 to 11. In a more specific sense, scale degrees are given names that indicate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concert Band
A concert band, also called a wind band, wind ensemble, wind symphony, wind orchestra, symphonic band, the symphonic winds, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind instrument, woodwind, brass instrument, brass, and percussion instrument, percussion families of instruments, and occasionally including the piano, double bass, and harp. On rare occasions, additional, non-traditional instruments may be added to such ensembles such as synthesizer, electric guitar, and bass guitar. Concert band music generally includes original wind instrument, wind compositions, concert marches, transcriptions of orchestral arrangements, light music, and pop music, popular music. Though the concert band does have similar Instrumentation (music), instrumentation to the marching band, a marching band's main purpose is to perform while marching. In contrast, a concert band usually performs as a concert, stationary ensemble, though European ensembles oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soprano Saxophone
The soprano saxophone is a small, high-pitched member of the saxophone family of woodwind instruments invented in the 1840s by Belgian instrument maker Adolphe Sax. Built in B♭ an octave above the tenor saxophone (or rarely, slightly smaller in C), the soprano is the third-smallest member of the saxophone family, which consists (from smallest to largest) of the soprillo, sopranino, soprano, alto, tenor, baritone, bass, contrabass, and subcontrabass. The soprillo and sopranino are rare instruments, making the soprano the smallest saxophone in common use. The instrument A transposing instrument pitched in the key of B, the modern soprano saxophone with a high F key has a range from concert A3 to E6 (written low B to high F) and is therefore pitched one octave above the tenor saxophone. There is also a soprano saxophone pitched in C, which is uncommon; most examples were produced in America in the 1920s. The soprano has all the keys of other saxophone models (with the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenor Saxophone
The tenor saxophone is a medium-sized member of the saxophone family, a group of instruments invented by Adolphe Sax in the 1840s. The tenor and the alto are the two most commonly used saxophones. The tenor is pitched in the key of B (while the alto is pitched in the key of E), and is a transposing instrument in the treble clef, sounding an octave and a major second lower than the written pitch. Modern tenor saxophones which have a high F key have a range from A2 to E5 (concert) and are therefore pitched one octave below the soprano saxophone. People who play the tenor saxophone are known as "tenor saxophonists", "tenor sax players", or "saxophonists". The tenor saxophone uses a larger mouthpiece, reed and ligature than the alto and soprano saxophones. Visually, it is easily distinguished by the curve in its neck, or its crook, near the mouthpiece. The alto saxophone lacks this and its neck goes straight to the mouthpiece. The tenor saxophone is most recognized for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |