|
Asymptomatic Carrier
An asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has become infected with a pathogen, but shows no signs or symptoms. Although unaffected by the pathogen, carriers can transmit it to others or develop symptoms in later stages of the disease. Asymptomatic carriers play a critical role in the transmission of common infectious diseases such as typhoid, HIV, '' C. difficile'', influenzas, cholera, tuberculosis and COVID-19, although the last is often associated with "robust T-cell immunity" in more than a quarter of patients studied. While the mechanism of disease-carrying is still unknown, researchers have made progress towards understanding how certain pathogens can remain dormant in a human for a period of time. A better understanding of asymptomatic disease carriers is crucial to the fields of medicine and public health as they work towards mitigating the spread of common infectious diseases. Types of asymptomatic carriers Asymptomatic carriers can be categorized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriuria
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. ''Escherichia coli'' is the most common bacterium found. People without symptoms should generally not be tested for the condition. Differential diagnosis include contamination. If symptoms are present treatment is generally with antibiotics. Bacteriuria without symptoms generally does not require treatment. Exceptions may include pregnant women, those who have had a recent kidney transplant, young children with significant vesicoureteral reflux, and those undergoing surgery of the urinary tract. Bacteriuria without symptoms is present in about 3% of otherwise healthy middle aged women. In nursing homes rates are as high as 50% among women and 40% in men. In those with a long term indwelling urinary catheter rates are 100%. Up to 10% of women have a urinary trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to that which the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal-oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral-oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
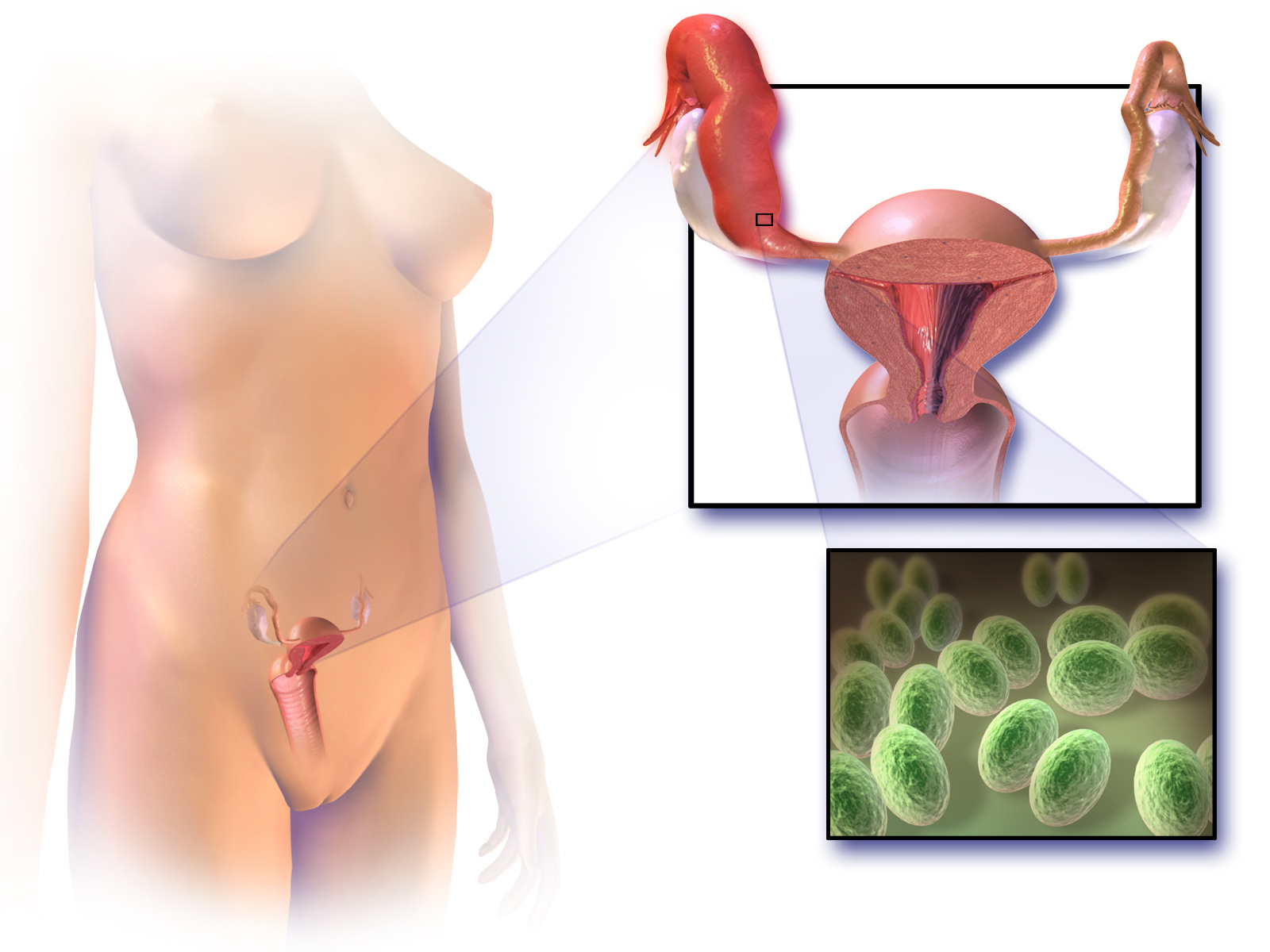
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer. The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or '' Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often, multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID. Risk factors are generally similar to thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridioides Difficile (bacteria)
''Clostridioides difficile'' (synonym (taxonomy), syn. ''Clostridium difficile'') is a bacterium that is well known for causing serious diarrheal infections, and may also cause colon cancer. Also known as ''C. difficile'', or ''C. diff'' (), is Gram-positive species of Bacterial spore, spore-forming bacteria. ''Clostridioides'' spp. are Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, Motility, motile bacteria, ubiquitous in nature and especially prevalent in soil. Its vegetative cells are rod-shaped, Pleomorphism (microbiology), pleomorphic, and occur in pairs or short chains. Under the microscope, they appear as long, irregular (often drumstick- or spindle-shaped) cells with a bulge at their terminal ends (forms subterminal spores). Under Gram staining, ''C. difficile'' cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen. ''C. difficile'' is catalase- and superoxide dismutase-negative, and produces up to three types of toxins: Clostr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epstein–Barr Virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus. It is best known as the cause of infectious mononucleosis ("mono" or "glandular fever"). It is also associated with various non-malignant, premalignant, and malignant Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases such as Burkitt lymphoma, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, and Hodgkin's lymphoma; non-lymphoid malignancies such as gastric cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma; and conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus such as hairy leukoplakia and central nervous system lymphomas. The virus is also associated with the childhood disorders of Alice in Wonderland syndrome and acute cerebellar ataxia and, by some evidence, higher risks of developing certain autoimmune diseases, especially dermatomyositis, systemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV Infection
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to child dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also reports on related subjects such as technology, communications, science, politics, and law. It is based in Jersey City, New Jersey. Competitors in the national business magazine category include '' Fortune'' and '' Bloomberg Businessweek''. ''Forbes'' has an international edition in Asia as well as editions produced under license in 27 countries and regions worldwide. The magazine is well known for its lists and rankings, including of the richest Americans (the Forbes 400), of the America's Wealthiest Celebrities, of the world's top companies (the Forbes Global 2000), Forbes list of the World's Most Powerful People, and The World's Billionaires. The motto of ''Forbes'' magazine is "Change the World". Its chair and editor-in-chief is Stev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Mallon
Mary Mallon (September 23, 1869 – November 11, 1938), commonly known as Typhoid Mary, was an Irish-born American cook believed to have infected between 51 and 122 people with typhoid fever. The infections caused three confirmed deaths, with unconfirmed estimates of up to 50. She was the first person in the United States identified as an asymptomatic carrier of the pathogenic bacteria ''Salmonella typhi''. She persisted in working as a cook and thereby exposed others to the disease. Because of that, she was twice forcibly quarantined by authorities, eventually for the final two decades of her life. Mallon died after a total of nearly 30 years in isolation. Her popular nickname has since gained currency as a term for persons who spread disease or other misfortune, not always aware that they are doing so. Biography Early life Mary Mallon was born in 1869 in Cookstown, County Tyrone, Ireland. Presumably, she was born with typhoid fever because her mother was infected duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |