|
Assyriology
Assyriology (from Greek , ''Assyriā''; and , '' -logia'') is the archaeological, anthropological, and linguistic study of Assyria and the rest of ancient Mesopotamia (a region that encompassed what is now modern Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, and northwestern and southwestern Iran) and of the related cultures that used cuneiform writing. The field covers Sumer, the early Sumero-Akkadian city-states, the Akkadian Empire, Ebla, the Akkadian and Imperial Aramaic speaking states of Assyria, Babylonia and the Sealand Dynasty, the migrant foreign dynasties of southern Mesopotamia, including the Gutians, Amorites, Kassites, Arameans, Suteans and Chaldeans. The large number of cuneiform clay tablets preserved by these Sumero-Akkadian and Assyro-Babylonian cultures provide an extremely large resource for the study of the period. The region's (and indeed the world's) first cities and city-states like Ur are archaeologically invaluable for studying the growth of urbaniza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the cuneiform lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishtar Gate In Pergamon Museum In Berlin
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, Divine law, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Sumer under the name "Inanna", and later by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian religion, Babylonians, and Assyrians under the name Ishtar, (occasionally represented by the logogram ). She was known as the "Queen of heaven (antiquity), Queen of Heaven" and was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, which was her main Cult (religious practice), cult center. She was associated with the planet Venus and her most prominent symbols included the Lion of Babylon, lion and the Star of Ishtar, eight-pointed star. Her husband was the god Dumuzid (later known as Tammuz) and her , or personal attendant, was the goddess Ninshubur (who later became conflated with the male deities Ilabrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutians
The Guti () or Quti, also known by the derived exonyms Gutians or Guteans, were a nomadic people of West Asia, around the Zagros Mountains (Modern Iran) during ancient times. Their homeland was known as Gutium (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ,''Gu-tu-umki'' or ,''Gu-ti-umki''). Conflict between people from Gutium and the Akkadian Empire has been linked to the collapse of the empire, towards the end of the 3rd millennium BC. The Guti subsequently overran southern Mesopotamia and formed the Gutian dynasty of Sumer. The Sumerian king list suggests that the Guti ruled over Sumer for several generations following the fall of the Akkadian Empire. By the 1st millennium BC, usage of the name Gutium, by the peoples of lowland Mesopotamia, had expanded to include all of western Medes, Media, between the Zagros and the Tigris. Various tribes and places to the east and northeast were often referred to as ''Gutians'' or ''Gutium''. For example, Assyrian royal annals use the term Gutians in rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the Assyrians from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 630) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC but there is no evidence yet discovered that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
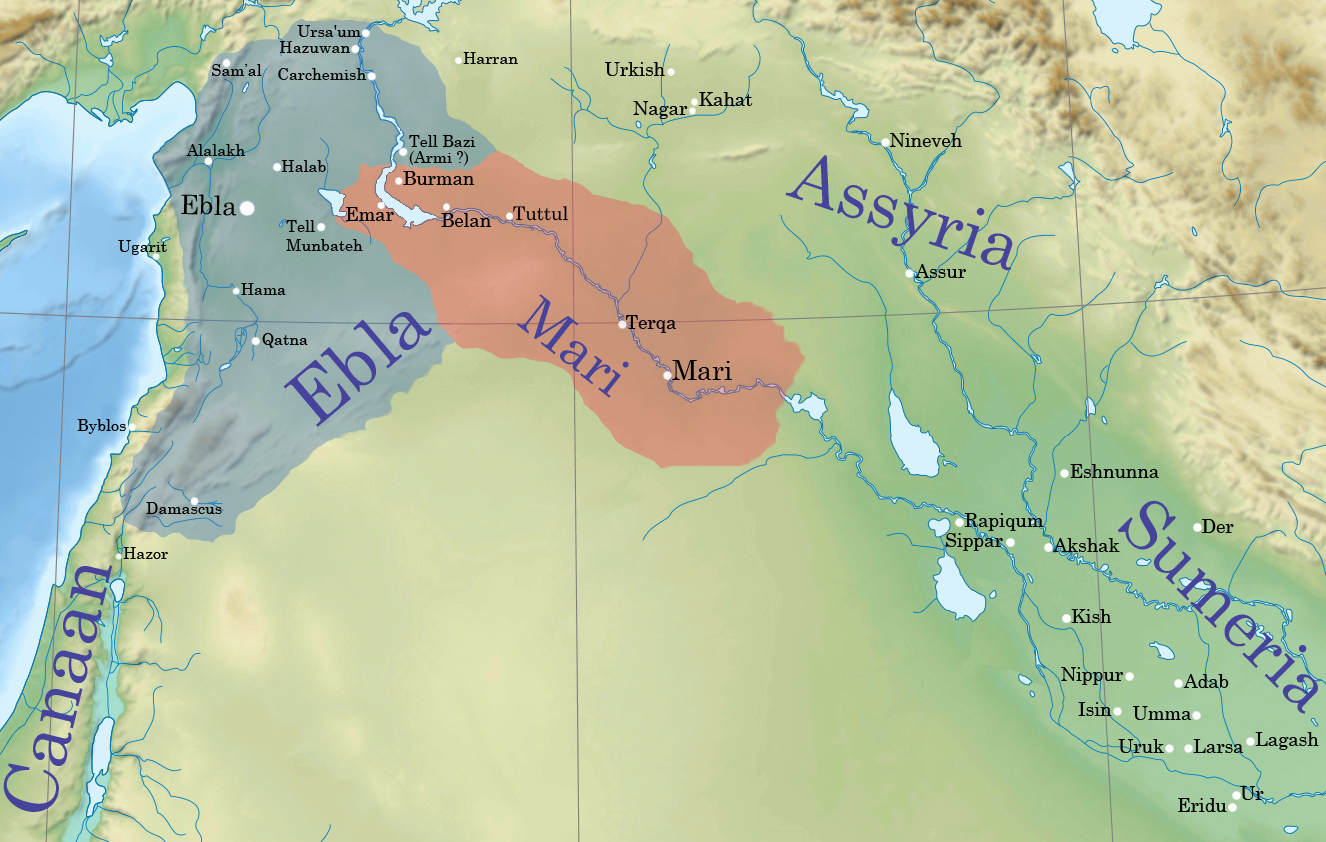
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sealand Dynasty
The First Sealand dynasty, (URU.KÙKIWhere ŠEŠ-ḪA of King List A and ŠEŠ-KÙ-KI of King List B are read as URU.KÙ.KI) or the 2nd Dynasty of Babylon (although it was independent of Amorite-ruled Babylon), very speculatively c. 1732–1460 BC ( short chronology), is an enigmatic series of kings attested to primarily in laconic references in the ''king lists A'' and ''B'', and as contemporaries recorded on the Assyrian ''Synchronistic king list A.117''. Initially it was named the "Dynasty of the Country of the Sea" with Sealand later becoming customary. The dynasty, which had broken free of the short lived, and by this time crumbling Old Babylonian Empire, was named for the province in the far south of Mesopotamia, a swampy region bereft of large settlements which gradually expanded southwards with the silting up of the mouths of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (the region known as ''mat Kaldi'' " Chaldaea" in the Iron Age). Sealand pottery has been found at Girsu, Uruk, and La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |