|
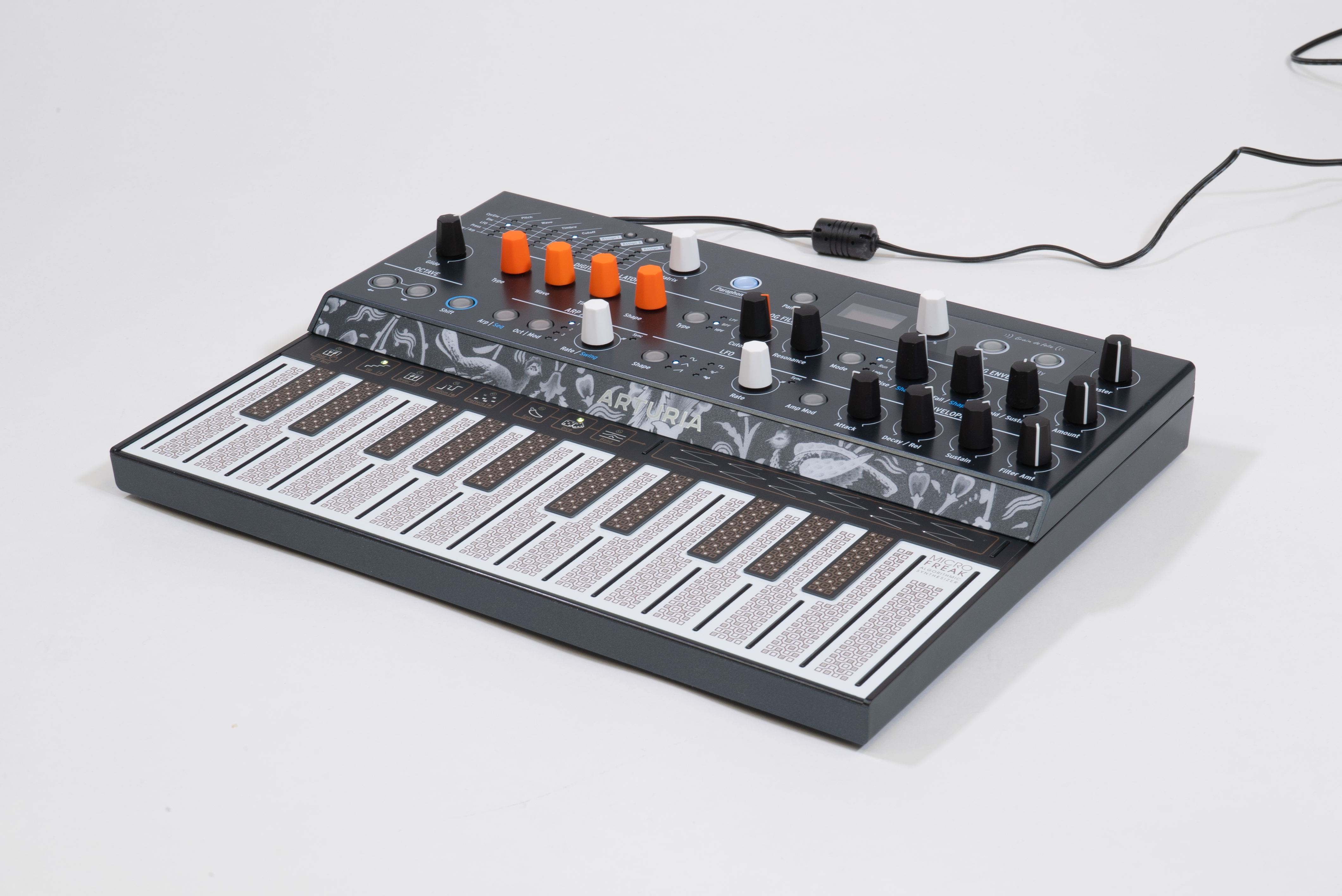
Arturia
Arturia is a French electronics company founded in 1999 and based in Grenoble, France. The company designs and manufactures audio interfaces and electronic musical instruments, including software synthesizers, drum machines, analog synthesizers, digital synthesizers, MIDI controllers, sequencers, and mobile apps. History Arturia was founded in 1999 in Grenoble by INPG engineers Frédéric Brun and Gilles Pommereuil to create affordable software synthesizers. The first product they developed was Storm, a virtual instrument workstation. The close emulation of classic analog synthesizers helped the company gain popularity in its market. In order to create sounds with minimal digital artifacts, Brun and Pommereuil developed new software algorithms to eliminate these issues. In 2003, using the algorithms they had developed, Arturia worked with Robert Moog to create the Modular V softsynth. The Modular V uses Arturia's True Analog Emulation (TAE) in an attempt to faithfull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arturia Matrixbrute Synthesizer
Arturia is a French electronics company founded in 1999 and based in Grenoble, France. The company designs and manufactures audio interfaces and electronic musical instruments, including software synthesizers, drum machines, analog synthesizers, digital synthesizers, MIDI controllers, sequencers, and mobile apps. History Arturia was founded in 1999 in Grenoble by INPG engineers Frédéric Brun and Gilles Pommereuil to create affordable software synthesizers. The first product they developed was Storm, a virtual instrument workstation. The close emulation of classic analog synthesizers helped the company gain popularity in its market. In order to create sounds with minimal digital artifacts, Brun and Pommereuil developed new software algorithms to eliminate these issues. In 2003, using the algorithms they had developed, Arturia worked with Robert Moog to create the Modular V softsynth. The Modular V uses Arturia's True Analog Emulation (TAE) in an attempt to faithfully repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
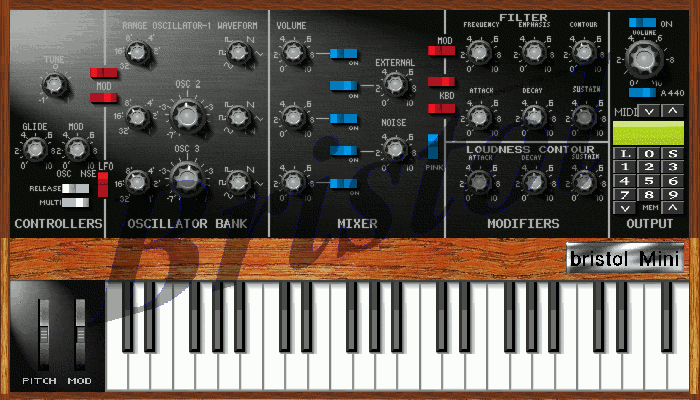
MiniBrute
The Arturia MiniBrute is a synthesizer manufactured by Arturia. Although the MiniBrute was the first piece of hardware created by Arturia—which had previously exclusively marketed software synthesizers—it generated strong sales. The MiniBrute takes some cues from vintage monophonic synthesizers, such as the Roland SH-101 and Minimoog. However, it also incorporates modern technology to increase its versatility, stability and depth of sound. The synthesizer uses a single, highly shapeable oscillator, which can be processed through a multimode Steiner-Parker filter and multiple LFOs. Background Before releasing the MiniBrute, Arturia was known for its affordable software synthesizers. These were generally faithful software emulations of classic analog synthesizers, such as the Moog 3C and Moog 55. The MiniBrute was the first piece of hardware manufactured by Arturia. Following the 2010 NAMM Show, Arturia CEO Frédéric Brun began to receive word that American customers wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Jupiter-8
The Jupiter-8, or JP-8, is an eight-voice polyphonic analog subtractive synthesizer introduced by Roland Corporation in early 1981. The Jupiter-8 was Roland's flagship synthesizer for the first half of the 1980s. Approximately 3300 units have been produced. Although it lacked the soon-to-be standard of MIDI control, later production series of the Jupiter-8 did include Roland's proprietary DCB interface. The instrument had many advanced features for its time, including the ability to split the keyboard into two zones, with separate patches active on each zone. Two years after the release of the Jupiter-8, Roland released the more affordable Jupiter-6 synthesizer with built-in MIDI control but an otherwise slightly reduced set of features. In 2011, three decades after the release of the original Jupiter series, Roland released the fully digital Jupiter-80 and Jupiter-50 synthesizers as successors to the 1980s originals. They were in turn succeeded by the Jupiter-X and Jupite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
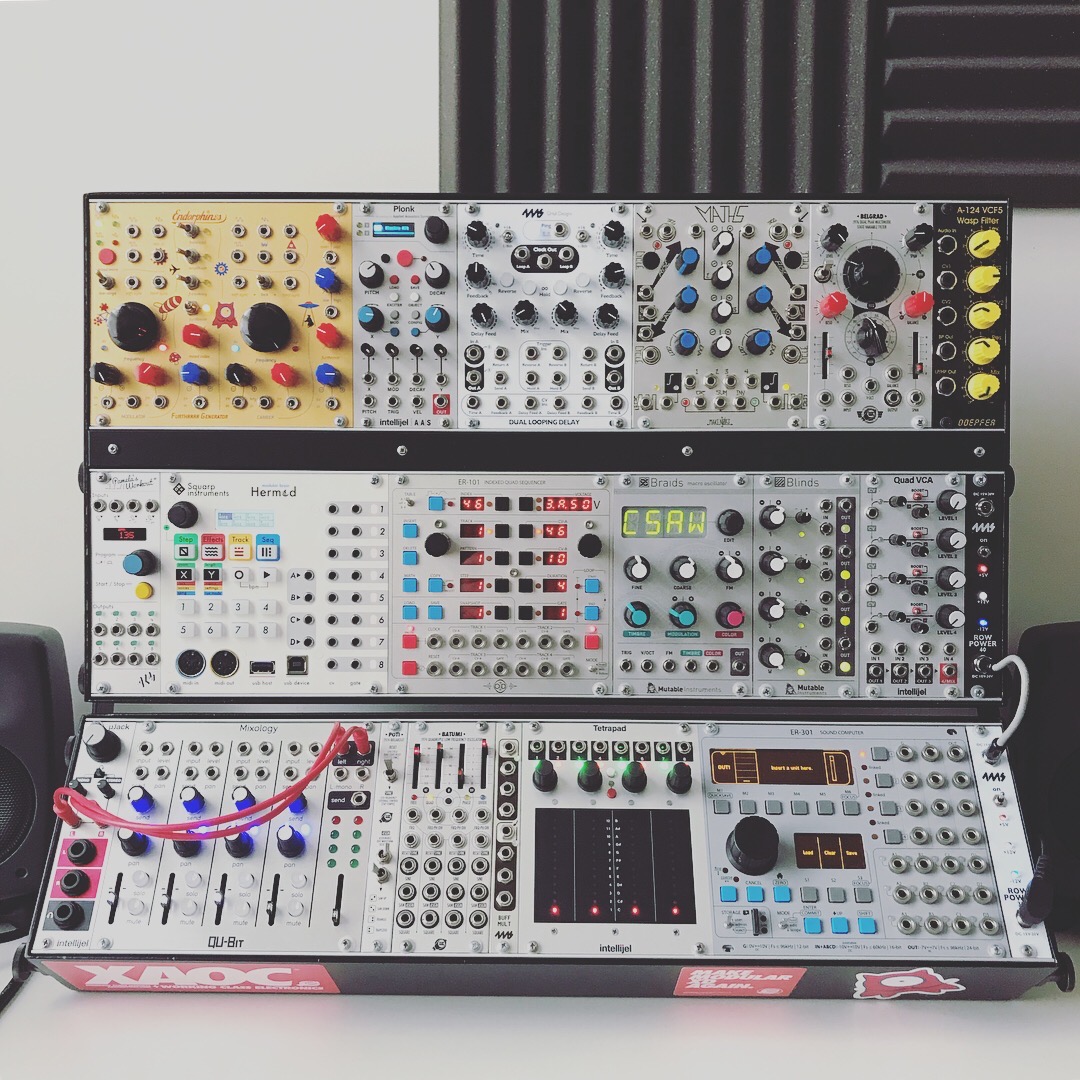
Eurorack
Eurorack is a modular synthesizer format originally specified in 1995 by Doepfer Musikelektronik. It has since grown in popularity, and as of 2022 has become a dominant hardware modular synthesizer format, with over 15,000 modules available from more than 1000 different manufacturers ranging from DIY kits and boutique, cottage-industry designers to well-known, established synth mass-manufacturers like Moog and Roland. Compact size, 3.5mm mono jacks and cables for patching all signals, and lack of a visual or sonic aesthetic defined by one manufacturer sets Eurorack apart from other modular synthesizer formats, and these factors have contributed to the popularity of Eurorack among both manufacturers and musicians. History Before Eurorack, in the late 1970s, several modular systems based on the industrial “Euro” card frames appeared: * Elektor Formant (3U or 6U x 7HP, 3.5 mm jacks, 31 pin bus, +/-15V) * BME PM10/Axiom (3U x 8HP, RCA/Phono jacks, 31 pin bus, +/-15V) * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI Keyboard
A MIDI keyboard or controller keyboard is typically a piano-style electronic musical keyboard, often with other buttons, wheels and sliders, used for sending MIDI signals or commands over a USB or MIDI 5-pin cable to other musical devices or computers. MIDI keyboards lacking an onboard sound module cannot produce sounds themselves, however some models of MIDI keyboards contain both a MIDI controller and sound module, allowing them to operate independently. When used as a MIDI controller, MIDI information on keys or buttons the performer has pressed is sent to a receiving device capable of creating sound through modeling synthesis, sample playback, or an analog hardware instrument. The receiving device could be: *a computer running a digital audio workstation (DAW) or a standalone VST/AU instrument (alternatively, the computer could be used to re-route the MIDI signal to other devices) *a sound module *a digital (digital piano/ stage piano) or analogue (synthesizer) hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Circuits Prophet-5
The Prophet-5 is an analog synthesizer manufactured by the American company Sequential. It was designed by Dave Smith and John Bowen in 1977, who used microprocessors, then a new technology, to create the first polyphonic synthesizer with fully programmable memory. This allowed users to store sounds and recall them instantly rather than having to reprogram them manually; whereas synthesizers had once created unpredictable sounds, the Prophet-5 moved synthesizers to producing "a standard package of familiar sounds". Between 1978 and 1984, about 6,000 units were produced across three revisions. In 1981, Sequential released a 10-voice, double-keyboard version, the Prophet-10. Sequential introduced new versions in 2020, and it has been emulated in software synthesizers and hardware. The Prophet-5 has been widely used in popular music and film soundtracks. Development The Prophet-5 was created in 1977 by Dave Smith and John Bowen at Sequential Circuits. At the time, Smith h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP 2600
The ARP 2600 is a semi-modular analog subtractive audio synthesizer produced by ARP Instruments, Inc. History Developed by a design team headed by ARP namesake Allen R. Pearlman and engineer Dennis Colin, the ARP 2600 was introduced in 1971 as the successor to ARP's first instrument, the ARP 2500, at a retail price of US$2600. Unlike other modular systems of the time, which required modules to be purchased individually and wired by the user, the 2600 was semi-modular with a fixed selection of basic synthesizer components internally pre-wired, with clear text labels and front panel screen printed graphics indicating the function of different sections of controls, and the signal flow between them. The 2600 was thus ideal for musicians new to synthesis, due to its ability to be operated either with or without patch cords. On its initial release it was heavily marketed to high schools and universities. Features and architecture The ARP 2600 features three VCOs, a 4-pole (24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
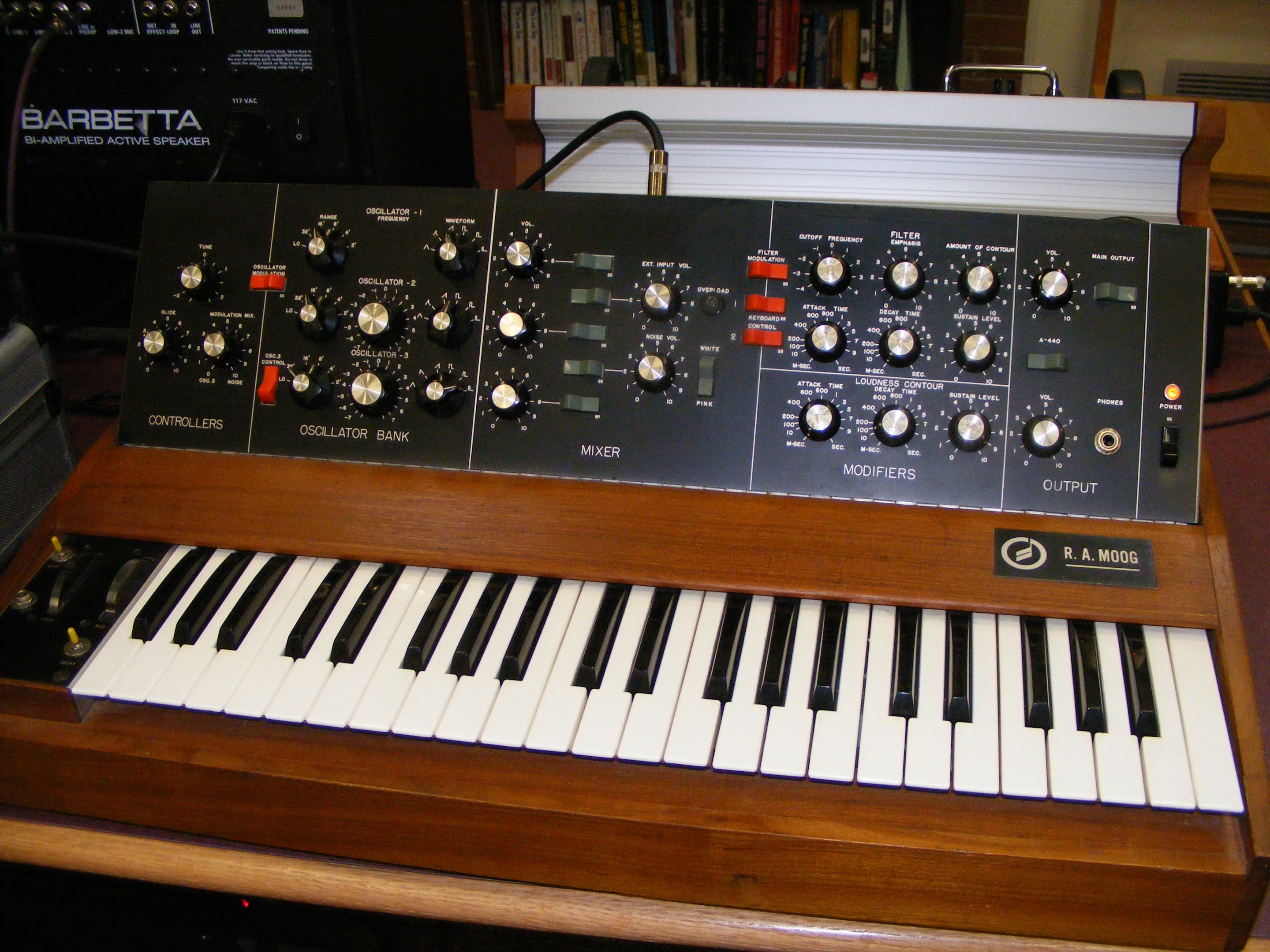
Synthesiser Clone
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI. Synthesizer-like instruments emerged in the United States in the mid-20th century with instruments such as the RCA Mark II, which was controlled with punch cards and used hundreds of vacuum tubes. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog and first sold in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesizer
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI. Synthesizer-like instruments emerged in the United States in the mid-20th century with instruments such as the RCA Mark II, which was controlled with punch cards and used hundreds of vacuum tubes. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog and first sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
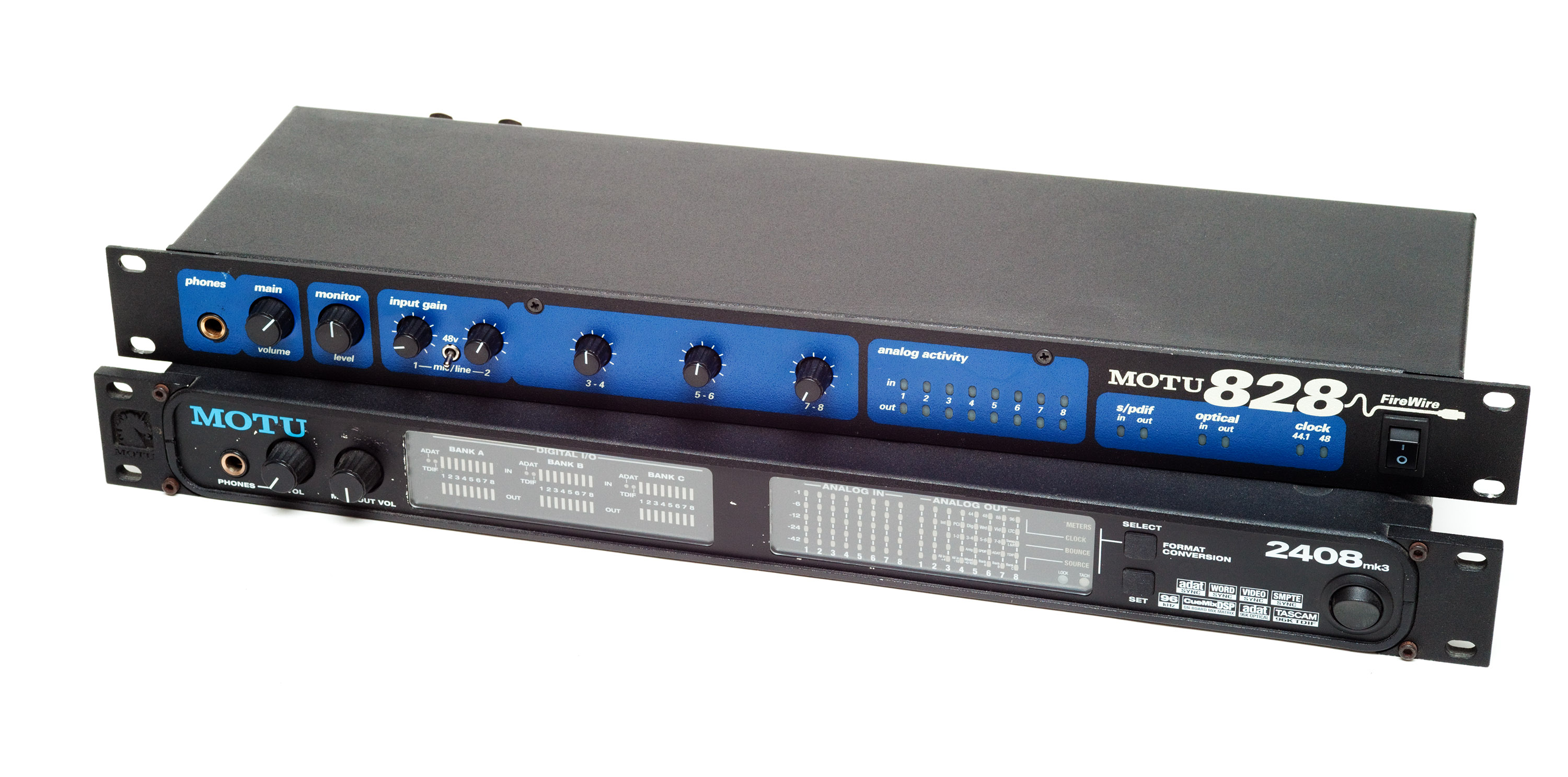
Audio Interface
An audio interface is a piece of computer hardware that allows the input and output of audio signals to and from a host computer or recording device. Audio interfaces are closely related to computer sound cards, but whereas sound cards are optimized for audio playback an audio interface is primarily intended to provide low-latency analog-to-digital and digital format conversion for professional audio applications. Audio Interfaces may include microphone preamps, as well as analog line inputs, DI inputs, and ADAT or S/PDIF digital inputs. Outputs are analog line, headphones and digital. They're typically available as external units, either as desktop devices or in a 19-inch rackmount format. Audio interfaces range from two channels in and out, to over 30. History Standalone audio interfaces grew from the proprietary hard disk recording market of the 1980s and 1990s, but advances in processor power and hard drive speed meant that, by the mid-1990s, standard home compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Synthesizer
A software synthesizer or softsynth is a computer program that generates digital audio, usually for music. Computer software that can create sounds or music is not new, but advances in processing speed now allow softsynths to accomplish the same tasks that previously required the dedicated hardware of a conventional synthesizer. Softsynths may be readily interfaced with other music software such as music sequencers typically in the context of a digital audio workstation. Softsynths are usually less expensive and can be more portable than dedicated hardware. Types Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype), FM synthesis (including the similar phase distortion synthesis), physical modelling synthesis, additive synthesis (including the related resynthesis), and sample-based synthesis. Many popular hardware synthesizers are no longer manufactured but have been emulated in software. The emulation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Synthesizer
A software synthesizer or softsynth is a computer program that generates digital audio, usually for music. Computer software that can create sounds or music is not new, but advances in processing speed now allow softsynths to accomplish the same tasks that previously required the dedicated hardware of a conventional synthesizer. Softsynths may be readily interfaced with other music software such as music sequencers typically in the context of a digital audio workstation. Softsynths are usually less expensive and can be more portable than dedicated hardware. Types Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype), FM synthesis (including the similar phase distortion synthesis), physical modelling synthesis, additive synthesis (including the related resynthesis), and sample-based synthesis. Many popular hardware synthesizers are no longer manufactured but have been emulated in software. The emulation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |