|
Arrhinia
Arrhinia (alternatively spelled "arhinia") is the congenital partial or complete absence of the nose at birth. It is an extremely rare condition, with few reported cases in the history of modern medicine. It is generally classified as a craniofacial abnormality. The cause of arrhinia is not known. One study of the literature found that all cases had presented a normal antenatal history. Conditions Arrhinia is associated with the following conditions and syndromes: * Arrhinia with choanal atresia and microphthalmia syndrome (Bosma arhinia microphthalmia syndrome) * Holoprosencephaly 1 * Holoprosencephaly 13, X-linked * Holoprosencephaly-radial heart renal anomalies syndrome History The term " arrhinia" is derived from the Greek roots "a-" (absence) and "rhinos" (nose); it is alternatively spelled "arhinia." The phenomenon of congenital arrhinia, which refers to the complete absence of the nose from birth, was initially documented in French literature during the 1800s. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhinia
Arrhinia (alternatively spelled "arhinia") is the congenital partial or complete absence of the nose at birth. It is an extremely rare condition, with few reported cases in the history of modern medicine. It is generally classified as a craniofacial abnormality. The cause of arrhinia is not known. One study of the literature found that all cases had presented a normal antenatal history. Conditions Arrhinia is associated with the following conditions and syndromes: * Arrhinia with choanal atresia and microphthalmia syndrome (Bosma arhinia microphthalmia syndrome) * Holoprosencephaly 1 * Holoprosencephaly 13, X-linked * Holoprosencephaly-radial heart renal anomalies syndrome History The term " arrhinia" is derived from the Greek roots "a-" (absence) and "rhinos" (nose); it is alternatively spelled "arhinia." The phenomenon of congenital arrhinia, which refers to the complete absence of the nose from birth, was initially documented in French literature during the 1800s. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craniofacial Abnormalities
Craniofacial abnormalities are congenital musculoskeletal disorders which primarily affect the cranium and facial bones. They are associated with the development of the pharyngeal arches. Approximately, 5% of the UK or USA population present with dentofacial deformities requiring Orthognathic surgery, jaw surgery, and Orthodontics, brace therapy, as a part of their definitive treatment. Notable conditions * Platybasia * Arrhinia - absence of the nose * Craniosynostosis - premature fusion of the cranial sutures * Cyclopia - one eye * Mobius syndrome Moebius, Möbius or Mobius may refer to: People * August Ferdinand Möbius (1790–1868), German mathematician and astronomer * Theodor Möbius (1821–1890), German philologist * Karl Möbius (1825–1908), German zoologist and ecologist * Paul ... - paralysis of the facial muscles References External links Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + '' rhino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
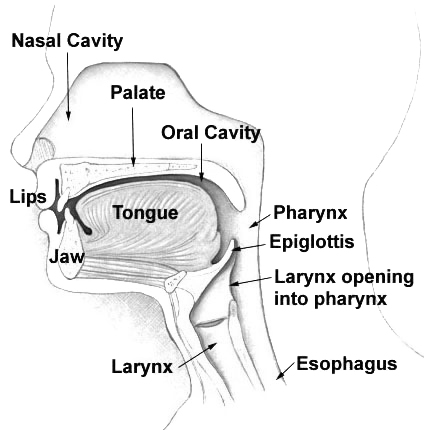
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Fort Osteotomy
A Le Fort osteotomy is the name for three types of osteotomies of the jaw and face. They are based on the analogous bone fractures described by the French surgeon and physician René Le Fort René Le Fort (30 March 1869 – 30 March 1951) was a French surgeon from Lille known for creating a classification for fractures of the face. Early life René Le Fort was born in 1869, in Lille. His father was a physician and his uncle a renow .... Type I The Le Fort I osteotomy advances the jaw in case of malocclusion and maxillomandibular deformities. Type II The Le Fort II osteotomy treats maxillary fractures. Type III The Le Fort III osteotomy treats midfacial abnormalities and deficiencies. Additional types "Le Fort IV" has been used to describe a monobloc frontofacial osteotomy in 2000s French literature, but the use is heavily disputed. In 2014, the same term was used by a Japanese group to describe a "monobloc minus Le Fort I" osteotomy. References {{Portal, Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the human nose, nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called Sinus ostium, ostia. Most of these ostia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics, also known as dental prosthetics or prosthetic dentistry, is the area of dentistry that focuses on dental prostheses. It is one of 12 dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association (ADA), Royal College of Surgeons of England, Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, Royal College of Surgeons of Ireland, Royal College of Surgeons of Glasgow, Royal College of Dentists of Canada, and Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons. The ADA defines it as "the dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance and health of patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth or oral and maxillofacial tissues using biocompatible substitutes." History Dental prostheory was pioneered by French surgeon Pierre Fauchard during the late 17th and early 18th century. Despite the limitations of the primitive surgical instruments, Fauchard discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth," refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening, and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |