|
Antarctic Specially Protected Area
An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarctic Treaty System russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption ..., which governs all the land and water south of 60 latitude and protects against human development. A permit is required for entry into any ASPA site. The ASPA sites are protected by the governments of Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom, Chile, France, Argentina, Poland, Russia, Norway, Japan, India, Italy, and Republic of Korea. There are currently 72 sites. List of ASPA sites See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dion Islands
The Dion Islands are a group of small islands and rocks lying in the northern part of Marguerite Bay, south-west of Cape Alexandra, Adelaide Island, off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. They were discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for the Marquis Jules-Albert de Dion, who donated three motor sledges and whose De Dion-Bouton works produced equipment for the expedition. Important Bird Area The islands have been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because they support a breeding colony of about 500 pairs of imperial shags. There is also a small colony of about 150 pairs of emperor penguins, the second-most northerly known of this species (the most northerly being Snow Hill Island) and one of only two on land. The site has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Harbor
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litchfield Island
Litchfield Island is a rocky island long and rising to , lying in Arthur Harbour, south of Norsel Point, off the south-west coast of Anvers Island in the Palmer Archipelago of Antarctica. History Litchfield Island was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1955. It was named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-names Committee (UK-APC) for Douglas B. Litchfield of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), general assistant and mountaineer at the Arthur Harbour station in 1955, who helped with the local survey and made numerous soundings through the sea ice in the vicinity of the island. Environment The island, together with its littoral zone, possesses an unusually high collection of marine and terrestrial life and is unique amongst the neighboring islands as a breeding place for six species of native birds. It provides an outstanding example of the natural ecological system of the Antarctic Peninsula area. In addition, Litchfield Island po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
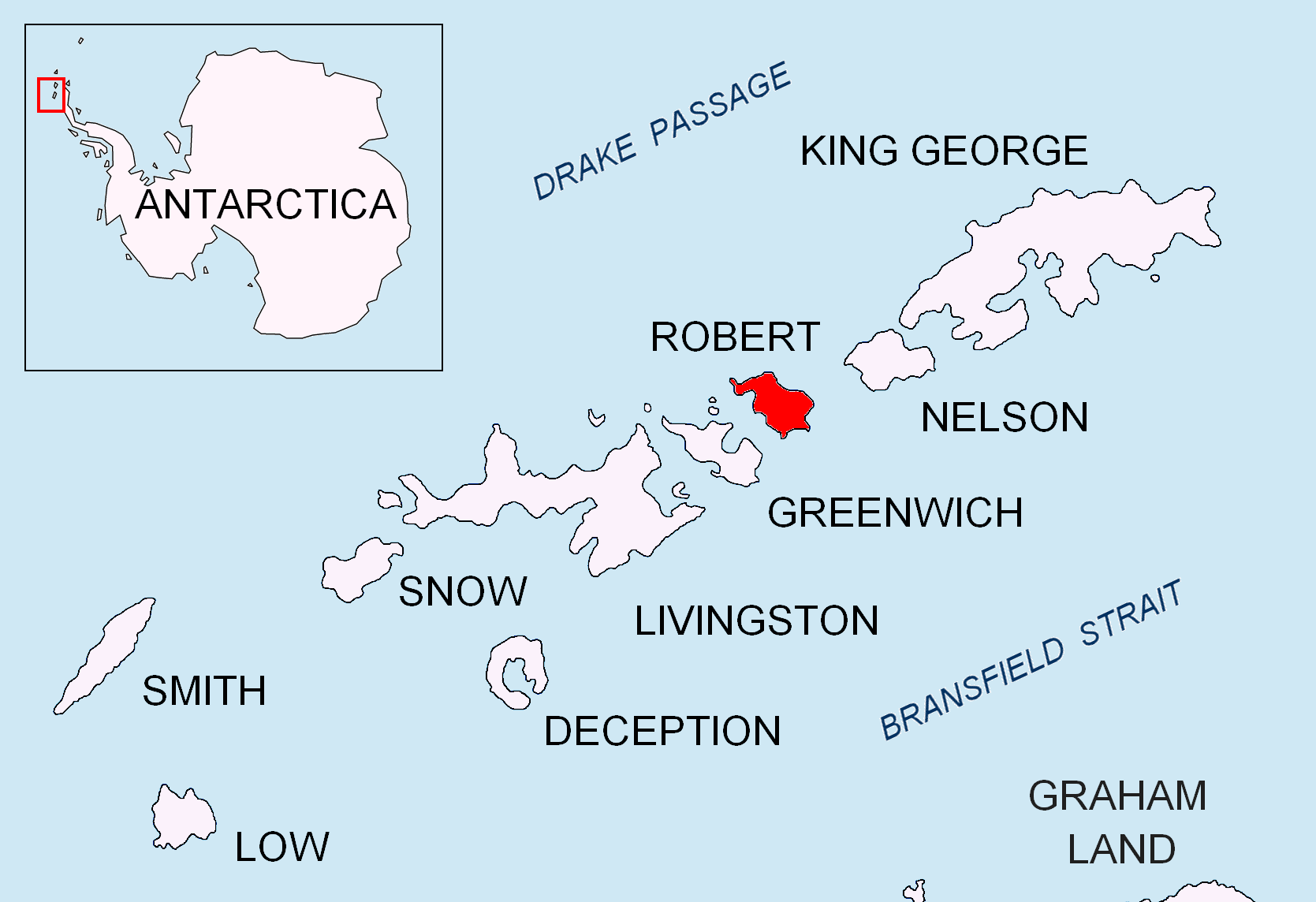
Robert Island
Robert Island or Mitchells Island or Polotsk Island or Roberts Island is an island long and wide, situated between Nelson Island and Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Robert Island is located at . Surface area . The name "Robert Island" dates back to around 1821 and is now established in international usage. Much of the Coppermine Peninsula in the west of the island is made up by a perched strandflat surface that was in past at sea level. Captain Richard Fildes may have named Robert Island for his brig . Fildes was sealing in the South Shetlands in 1821–1822 until ice destroyed his vessel in March 1822. Fildes Strait is named for him. See also * List of lighthouses in Antarctica * Clothier Harbor * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppermine Peninsula
Coppermine Peninsula is the rugged, rocky promontory forming the northwest extremity of Alfatar Peninsula and Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It lies between the English Strait to the west and Carlota Cove to the east. It is 1.7 km long, 500 m wide and rising to 105 m. Coppermine Peninsula is linked to Alfatar Peninsula to the southeast by a narrow isthmus bounded by Carlota Cove to the north and the 1 km wide and 460 m indenting ''Coppermine Cove'' () to the south. The feature is named in association with the adjacent Coppermine Cove, a descriptive name given by sealers in about 1821 from the copper-coloured staining of the lavas and tuffs in the area. Antarctic Specially Protected Area The Coppermine Peninsula has a regime of special environmental protection under the Antarctic Treaty System. All land west of a north-south line across the isthmus between Carlota Cove and Coppermine Cove, has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powell Island
Powell Island is a narrow island long and wide, lying between Coronation and Laurie Islands in the central part of the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. Its southern end lies 7 km east of the south-western extremity of Coronation Island, between Lewthwaite Strait and Washington Strait. History The island was discovered in the course of the joint cruise by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer in December 1821. It was correctly charted, though unnamed, on Powell's map published in 1822; it was subsequently named for Powell on an Admiralty chart of 1839. Birds An area including part of southern Powell Island (south of John Peaks on Coronation Island), along with neighbouring Christoffersen, Fredriksen, Michelsen and Grey Islands, with some other (unnamed) islands lying offshore, has been identified as a 2688 ha Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International as it supports several significant seabird Seabirds (also known as marine birds) ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynch Island
Lynch Island is an island lying in the eastern part of Marshall Bay, close off the south coast of Coronation Island in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. History The island was roughly charted in 1912–13 by Petter Sørlle, a Norwegian whaling captain, and surveyed in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel. The island was resurveyed in 1948–49 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Thomas Lynch, an American sealer who visited the South Orkney Islands in the schooner ''Express'' in 1880. Antarctic Specially Protected Area The island has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 110) for its biological values, especially its relatively luxuriant plant communities. The continent's only two flowering plants, Antarctic hair grass and Antarctic pearlwort, are abundant. The soils associated with the grass swards contain a rich invertebrate Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Orkney Islands
The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula''Antarctica: Secrets of the Southern Continent'' p. 122 David McGonigal, 2009 and south-west of South Georgia Island. They have a total area of about . The islands are claimed both by Britain (as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962, previously as a Falkland Islands Dependency), and by Argentina as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moe Island
Moe Island is an island long in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica, separated from the south-west end of Signy Island by Fyr Channel. It was charted by Captain Petter Sørlle in 1912–13, and named after M. Thoralf Moe of Sandefjord, Norway, a contemporary whaling captain who worked in this area. The northernmost point of the island is Spaull Point, named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Vaughan W. Spaull, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) biologist on Signy Island, 1969. Antarctic Specially Protected Area The island has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA 109) mainly for its biological values, especially the banks of '' Chorisodontium''–'' Polytrichum'' moss turf and ''Andreaea''–'' Usnea '' fellfield. The cryptogamic flora is diverse, though in places the moss turf is subject to damage by Antarctic fur seals. The mites '' Stereotydeus villosus'' and ''Gamasellus racovitzai'', as well as the springtail ''Cry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthelot Islands
The Berthelot Islands are a group of rocky islands, the largest long, lying south-west of Deliverance Point, off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. They were discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and named by him for Marcellin Berthelot, a prominent French chemist. One of the group, Green Island, is protected as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.108 because of its relatively luxuriant vegetation and large Antarctic shag colony In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state' .... See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * Urchin Rock References Islands of Graham Land Graham Coast {{GrahamCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |