|
Anrep Effect
The Anrep effect is an autoregulation method in which myocardial contractility increases with afterload. It was experimentally determined that increasing afterload caused a proportional linear increase in ventricular inotropy. This effect is found in denervated heart preparations, such as the Starling Preparation, and represents an intrinsic autoregulation mechanism. Physiology Sustained myocardial stretch activates tension-dependent Na+/H+ exchangers, bringing Na+ ions into the sarcolemma. This increase in Na+ in the sarcolemma, reduces the Na+ gradient exploited by sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX), and stops them from working effectively. Ca2+ ions accumulate inside the sarcolemma as a result, and are taken up by sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) pumps. Calcium induced calcium release (CICR) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is thus increased upon the next activation of the cardiac myocyte. This leads to an increase in the force of contraction of the cardiac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
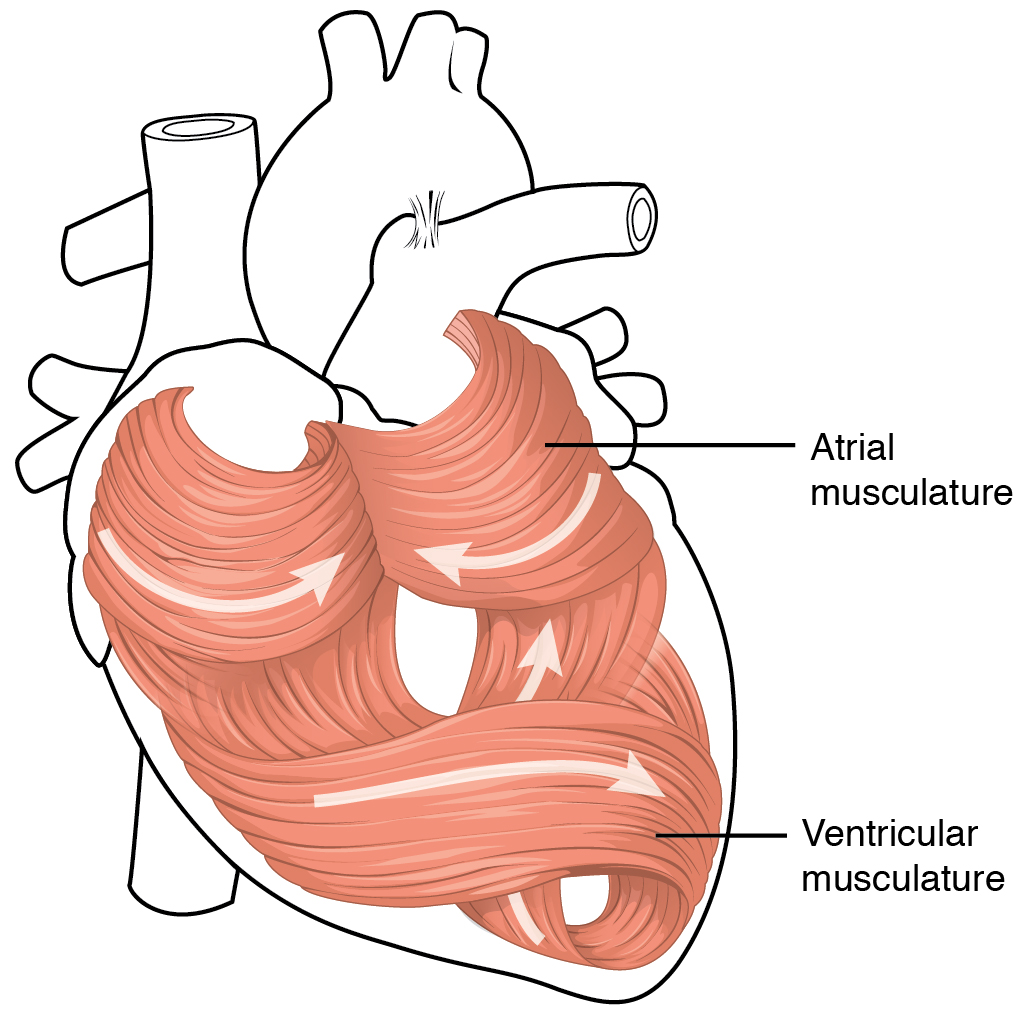
Myocardial
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Myocyte
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912
Events January * January 1 – The Republic of China is established. * January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens. * January 6 ** German geophysicist Alfred Wegener first presents his theory of continental drift. ** New Mexico become the 47th U.S. State. * January 8 – The African National Congress is founded as the South African Native National Congress, at the Waaihoek Wesleyan Church in Bloemfontein, to promote improved rights for black South Africans, with John Langalibalele Dube as its first president. * January 14 – Raymond Poincaré forms a coalition government in France, beginning his first term of office as Prime Minister on 21 January. * January 17 – British polar explorer Captain Robert Falcon Scott and a team of four become the second expeditionary group to reach the South Pole. * January 18 (Old Style January 5) – Prague Conference: Vladimir Lenin and the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru , image = , caption = , population = , popplace = 118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate) , region1 = , pop1 = approx. 7,500,000 (including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 7,170,000 (2018) ''including Crimea'' , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 3,512,925 (2020) , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 3,072,756 (2009)(including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 1,800,000 (2010)(Russian ancestry and Russian Germans and Jews) , ref5 = 35,000 (2018)(born in Russia) , region6 = , pop6 = 938,500 (2011)(including Russian Jews) , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 809,530 (2019) , ref7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Pressure
Central aortic blood pressure (CAP or CASP) is the blood pressure at the root of aorta. Studies have shown the importance of central aortic pressure and its implications in assessing the efficacy of antihypertensive treatment with respect to cardiovascular risk factors. The traditional method of measuring blood pressure in the arms has been shown to underestimate the efficacy of medications such as amlodipine and overestimate the efficacy of those like atenolol. A clinical trial demonstrated that different medications for lowering blood pressure have different effects on the central aortic pressure and blood flow characteristics, despite producing similar branchial blood pressure readings. The study also indicated that the CAP is a better independent predictor of cardiovascular and kidney The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-systolic Volume
End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventri .... ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle. The main factors that affect the end-systolic volume are afterload and the contractility of the heart. __TOC__ Uses End systolic volume can be used clinically as a measurement of the adequacy of cardiac emptying, related to systolic function. On an electrocardiogram, or ECG, the end-systolic volume will be seen at the end of the T wave. Clinically, ESV can be measured using two-dimensional echocardiography, MRI ( magnetic resonance tomography) or cardiac CT ( computed tomography) or SPECT (single ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Ischemic Attack
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a minor stroke whose noticeable symptoms usually end in less than an hour. TIA causes the same symptoms associated with strokes, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, sudden dimming or loss of vision, difficulty speaking or understanding language, slurred speech, or confusion. All forms of stroke, including TIA, result from a disruption in blood flow to the central nervous system. A TIA is caused by a temporary disruption in blood flow to the brain, or cerebral blood flow (CBF). The primary difference between a major stroke and the TIA's minor stroke is how much tissue death ( infarction) can be detected afterwards through medical imaging. While a TIA must by definition be associated with symptoms, strokes can also be symptomatic or silent. In silent stroke, also known as ''silent cerebral infarct'' (SCI), there is permanent infarction detectable on imaging, but there are no immediatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time (blood flow) per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb "perfuser" meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions. Tests verifying that adequate perfusion exists are a part of a patient's assessment process that are performed by medical or emergency personnel. The most common methods include eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula: :CO = HR \times SV Values for cardiac output are usually denoted as L/min. For a healthy individual weighing 70 kg, the cardiac output at rest averages about 5 L/min; assuming a heart rate of 70 beats/min, the stroke volume would be approximately 70 mL. Because cardiac output is related to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is an important component of how eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The term ''stroke volume'' can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Stroke volume is an important determinant of cardiac output, which is the product of stroke volume and heart rate, and is also used to calculate ejection fraction, which is stroke volume divided by end-diastolic volume. Because stroke volume decreases in certain conditions and disease states, stroke volume itself correlates with cardiac function. Calcula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |