|
Akira Fujishima
is a Japanese chemist and president of Tokyo University of Science. He is known for significant contributions to the discovery and research of photocatalytic and superhydrophilic properties of titanium dioxide (TiO2), which is also known as the '' Honda-Fujishima effect''.(Originally published in Japanese 2 December 2003) Career and research In 1966 he earned his B. A. (Engineering) at the Faculty of Engineering, Yokohama National University, and in 1971 his Ph.D. (Engineering) at the Graduate School of Engineering, the University of Tokyo. In 1967, while working on his Ph.D. under the supervision of professor Kenichi Honda (本多 健一), he discovered the phenomenon of photocatalytic water decomposition (water photolysis) when he exposed a titanium dioxide electrode to strong light, later called the '' Honda-Fujishima effect''. The discovery of self-cleaning properties of titanium dioxide by the group under his supervision initiated a revolution in the ceramic, glass, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
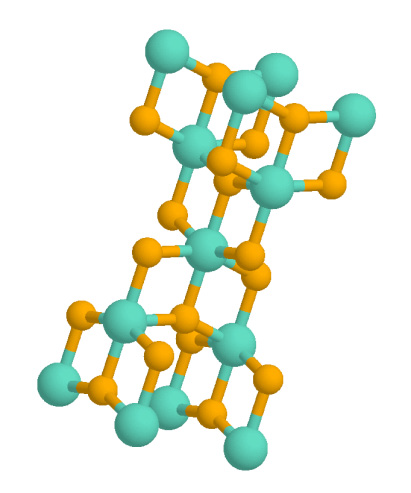
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medals Of Honor (Japan)
are medals awarded by the Government of Japan. They are awarded to individuals who have done meritorious deeds and also to those who have achieved excellence in their field of work. The Medals of Honor were established on December 7, 1881, and were first awarded the following year. Several expansions and amendments have been made since then. The medal design for all six types are the same, bearing the stylized characters on a gilt central disc surrounded by a silver ring of cherry blossoms on the obverse; only the colors of the ribbon differ. If for some reason an individual were to receive a second medal of the same ribbon colour, then a second medal is not issued but rather a new bar is added to their current medal. The Medals of Honor are awarded twice each year, on April 29 (the birthday of the Shōwa Emperor) and November 3 (the birthday of the Meiji Emperor). Types Red ribbon First awarded in 1882. Awarded to individuals who have risked their own lives to save the live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Electrochemical Society
The Electrochemical Society is a learned society ( professional association) based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of electrochemistry and solid-state science and related technology. The Society membership comprises more than 8,000 scientists and engineers in over 85 countries at all degree levels and in all fields of electrochemistry, solid state science and related technologies. Additional support is provided by institutional members including corporations and laboratories. ECS is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization. Scientists around the world rely on the Society as a leading source of scientific research through its peer-reviewed journals, international meetings, and the ECS Digital Library on IOPscience. The Society publishes numerous journals including the ''Journal of The Electrochemical Society'' (the oldest peer-reviewed journal in its field), ''Journal of Solid State Science and Technology'', ''ECS Meeting Abstracts'', ''ECS Transact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asahi Shimbun
is one of the four largest newspapers in Japan. Founded in 1879, it is also one of the oldest newspapers in Japan and Asia, and is considered a newspaper of record for Japan. Its circulation, which was 4.57 million for its morning edition and 1.33 million for its evening edition as of July 2021, was second behind that of the ''Yomiuri Shimbun''. By print circulation, it is the third largest newspaper in the world behind the ''Yomiuri'', though its digital size trails that of many global newspapers including '' The New York Times''. Its publisher, is a media conglomerate with its registered headquarters in Osaka. It is a privately held family business with ownership and control remaining with the founding Murayama and Ueno families. According to the Reuters Institute Digital Report 2018, public trust in the ''Asahi Shimbun'' is the lowest among Japan's major dailies, though confidence is declining in all the major newspapers. The ''Asahi Shimbun'' is one of the five l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Society Of Japan
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Science And Technology Agency
The Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST; Japanese: 科学技術振興機構) is a Japanese government agency which aims to build infrastructure that supports knowledge creation and dissemination in Japan. It is one of the , overseen by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI). It operates from headquarters in Kawaguchi, Saitama in the Greater Tokyo Area, and in Chiyoda in central Tokyo. The agency formed in 2003, as successor to the Japan Science and Technology Corporation. The corporation had formed in 1996 through the merging of the Japan Information Center of Science and Technology (JICST, est. 1957) and the Research Development Corporation of Japan (JRDC, est. 1961). Among other activities, the agency runs J-STAGE, an "electronic journal platform for science and technology information in Japan," and publishes the ''Journal of Information Processing and Management'' (). As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photochemistry Reviews
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet (wavelength from 100 to 400 nm), visible light (400–750 nm) or infrared radiation (750–2500 nm). In nature, photochemistry is of immense importance as it is the basis of photosynthesis, vision, and the formation of vitamin D with sunlight. Photochemical reactions proceed differently than temperature-driven reactions. Photochemical paths access high energy intermediates that cannot be generated thermally, thereby overcoming large activation barriers in a short period of time, and allowing reactions otherwise inaccessible by thermal processes. Photochemistry can also be destructive, as illustrated by the photodegradation of plastics. Concept Grotthuss–Draper law and Stark-Einstein law Photoexcitation is the first step in a photochemical process where the reactant is elevated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Society Of Japan
The (CSJ) is a learned society and professional association founded in 1878 in order to advance research in chemistry. The mission of the CSJ is to promote chemistry for science and industry in collaboration with other domestic and global societies.Chemical Society of Japan (CSJ) About CSJ/ref> History The organization was modeled after the British Chemical Society. This learned society in London was the precursor of the Royal Society of Chemistry. Like its British counterpart, the Japanese association sought to foster the communication of new ideas and facts throughout Japan and across international borders.Lagowski, J. J. (1991) "A British Sesquicentennial,"''Journal of Chemical Education,'' Vol 68, No. 1, p. 1; acknowledging the sesquicentennial of The Chemical Society in London, which eventually became The Royal Society of Chemistry. Membership was expanded in 1948 in a merger with the Society of Chemical Industry. In 2018 the first woman was announced as president ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanagawa University
, abbreviated to is a private university in Japan. The main campus is located in Rokkakubashi, Kanagawa-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa Prefecture. History The university was founded in 1928 by as . It was an evening school for the working youth. In 1929 the school was renamed , which had both day and evening schools (Day school: Department of Commerce / evening school: Departments of Commerce and Law). On 15 May 1930 the college moved to present-day Rokkakubashi Campus. In 1939 it added the technical departments (Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering and Industrial Administration). In 1949 the college was developed into Kanagawa University, under Japan's new educational system. The university at first had three faculties: the Faculties of Commerce and Engineering and the evening school's Faculty of Commerce. The latter history of the university is as follows: * 1950: the Faculty of Commerce was renamed Faculty of Law and Economics. * 1965: the Faculty of Foreign Languages (E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-cleaning Glass
Self-cleaning glass is a specific type of glass with a surface that keeps itself free of dirt and grime. The field of self-cleaning coatings on glass is divided into two categories: hydrophobic and hydrophilic. These two types of coating both clean themselves through the action of water, the former by rolling droplets and the latter by sheeting water that carries away dirt. Hydrophilic coatings based on titania (titanium dioxide), however, have an additional property: they can chemically break down absorbed dirt in sunlight. The requirements for a self-cleaning hydrophobic surface are a very high static water contact angle θ, the condition often quoted is θ>160°, and a very low roll-off angle, i.e. the minimum inclination angle necessary for a droplet to roll off the surface. Self-cleaning surfaces Several techniques are known for the patterning of hydrophobic surfaces through the use of moulded polymers and waxes, by physical processing methods such as ion etching and compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)


