|
Aiadaba
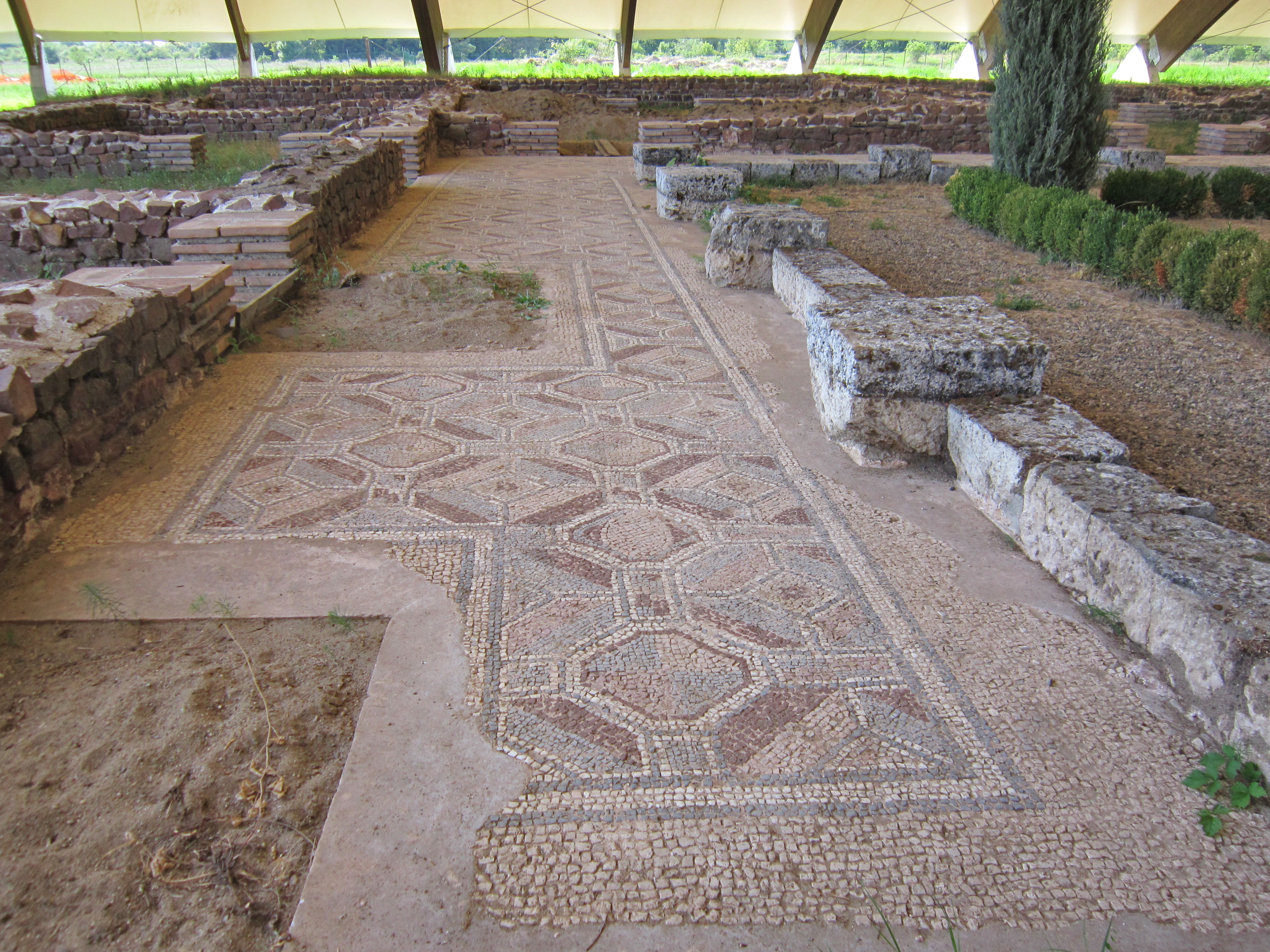
Aiadava (''Aiadaba'' or ''Aeadaba'', gr, Αἰάδαβα) was a Dacian town in the Remesiana region, present day Bela Palanka, Serbia. After the Romans conquered Moesia in the 75 BC, the new castrum (imperial domain with estates) and municipium was known initially as ''Ulpianorum'' and then ''Remesiana'' (Moesi) and laid on the Via Militaris road, between Naissus and Serdica. Emperor Justinian (r. 527–565) had following strongholds in the district of Remesiana: The patron saint of Romania, Nicetas of Remesiana, was a 4th-century bishop at Remesiana, of possible Dacian descent. Excavations include well-preserved castrum dating to 4th century, a hoard of 260 coins minted during the rule of Constantine I, Theodosius I, Tiberius Claudius Nero.Ancient diseases: the elements of palaeopathology-Srboljub Živanović 1982 File:BelaPalankaIskopine.jpg, Basilica Apse under excavation in Remesiana. Basilica is found under modern residential building. File:Bela Palanka Sept Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Towns
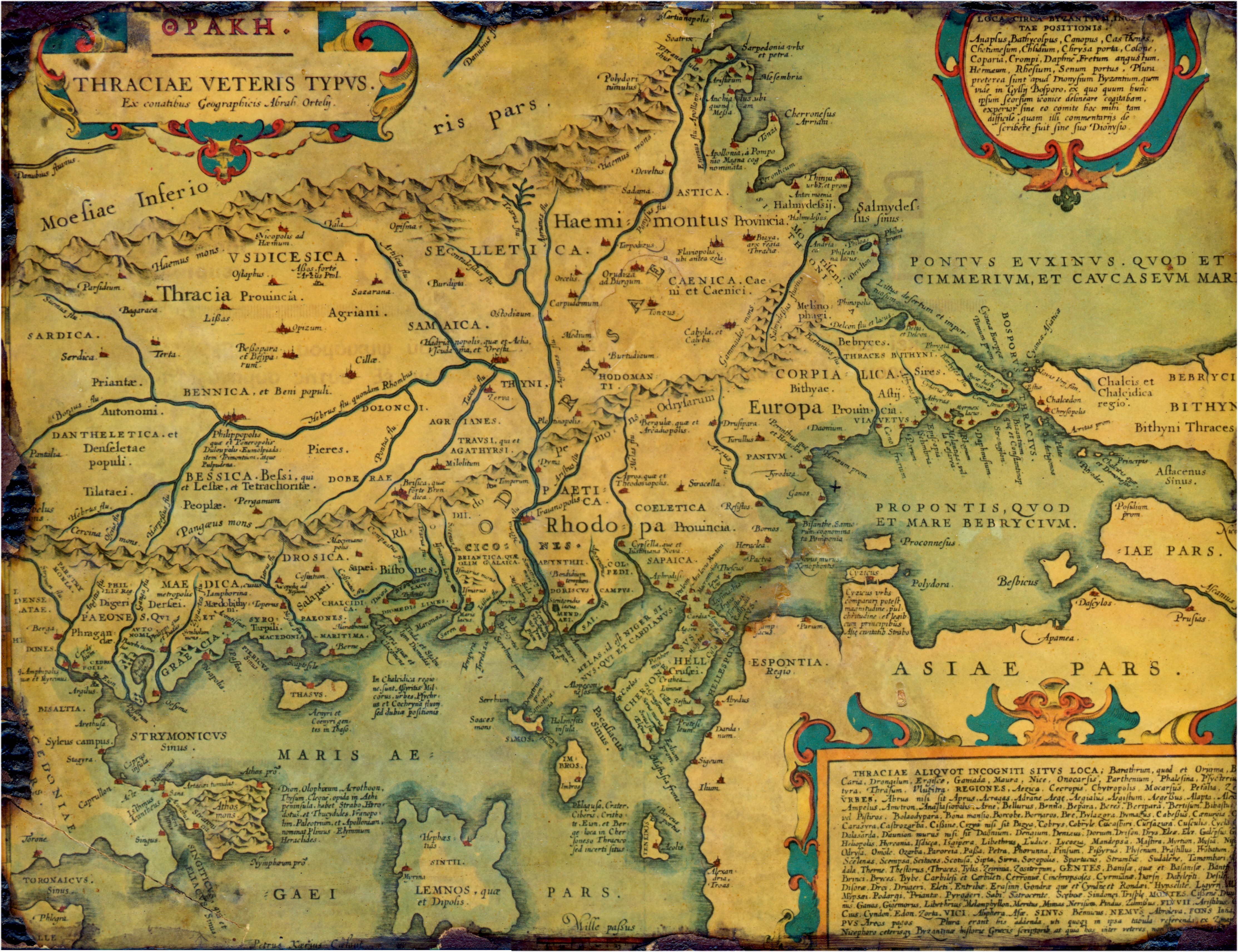
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under King Burebista. As a result of the two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the Ancient Greeks, in Herodotu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bela Palanka
Bela Palanka (Serbian Cyrillic: Бела Паланка, ) is a town and municipality located in the Pirot District of southeastern Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the population of the town is 8,143, and the population of the municipality is 12,126. In ancient times, the town was known as Remesiana in Dacia Mediterranea. The name ''Bela Palanka'' means 'white town'. History Ancient Bela Palanka The town was originally settled by the Dacians and was known under the ancient name of Aiadava or Aeadaba. Thracians inhabited the area until their assimilation into contemporary ethnic groups in the area. After the Romans conquered Moesia in 75 BC, the new castrum (imperial domain with estates) and municipium was known initially as ''Ulpianorum'' and then ''Remesiana'' (Moesi) and stood along the Via Militaris between Naissus and Serdica. Emperor Justinian had following strongholds in the district of Remesiana: The patron saint of Romania, Nicetas of Remesiana, was a 4th-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicetas Of Remesiana
Nicetas (c. 335–414) was Bishop of Remesiana (present-day Bela Palanka, Serbia), which was then in the Roman province of Dacia Mediterranea. Biography Nicetas promoted Latin sacred music for use during the Eucharistic worship and reputedly composed a number of liturgical hymns, among which some twentieth-century scholars number the major Latin Christian hymn of praise, ''Te Deum'', traditionally attributed to Ambrose and Augustine. He is presumed to be the missionary to the barbarian Thracian tribe of the Bessi. Because of his missionary activity, his contemporary and friend, Paulinus of Nola, lauded him poetically for instructing in the Gospel barbarians changed by him from wolves to sheep and brought into the fold of peace, and for teaching to sing of Christ with Roman heart bandits, who previously had no such ability. However, it is doubtful whether these barbarians really were barbarians, or whether their mention is only a poetical topos. Indeed, Paulinus, who wrote a qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Cities In Serbia
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites Of Great Importance (Serbia)
Immovable Cultural Heritage of Great Importance ( sr, Непокретна културна добра од великог значаја / ''Nepokretna kulturna dobra od velikog značaja'') are those objects of Immovable Cultural Heritage of Serbia, cultural heritage that enjoy the second-highest level of state protection in the Republic of Serbia, behind the Immovable Cultural Heritage of Exceptional Importance (Serbia), Immovable Cultural Heritage of Exceptional Importance. Immovable Cultural Heritage is classified as being of Great Importance upon decision by the National Assembly of Serbia. They are inscribed in the ''Central Register of Immovable cultural property'' maintained by the Institute for the Protection of Cultural Monuments of Serbia. Objects of Immovable cultural heritage have to fulfill one or more of those criteria defined in the ''Law on Cultural Heritage'' of 1994 in order to be categorized as being "of great importance": # importance for a certain area or time-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors. After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus in Cilicia. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Gaul. Following the consolidation of his rule over the western provinces, Severus waged another brief, more successful war in the east agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father was the politician Tiberius Claudius Nero and his mother was Livia Drusilla, who would eventually divorce his father, and marry the future-emperor Augustus in 38 BC. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus' two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus' successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat, and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for the empire's northern frontier. Early in his career, Tiberius was happily married to Vipsania, daughter of Augustus' friend, distinguished general and intended heir, Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa. They had a son, Drus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two civil wars, and recognized the Catholic orthodoxy of Nicene Christians as the Roman Empire's state religion. Theodosius was the last emperor to rule the entire Roman Empire before its administration was permanently split between two separate courts (one western, the other eastern). Born in Hispania, Theodosius was the son of a high-ranking general, Theodosius the Elder, under whose guidance he rose through the ranks of the Roman Army. Theodosius held independent command in Moesia in 374, where he had some success against the invading Sarmatians. Not long afterwards, he was forced into retirement, and his father was executed under obscure circumstances. Theodosius soon regained his position following a series of intrigues and executio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Constantius Chlorus, Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrians, Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helena, was a Greeks, Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Sasanian Empire, Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Roman Britain, Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |